The British Virgin Islands, officially simply the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands and north-west of Anguilla. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles and part of the West Indies.

The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles to the east of Puerto Rico and west of the British Virgin Islands.

The Virgin Islands are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rico Trench and St. Croix being a displaced part of the same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.

Her Majesty's Government of the Virgin Islands is the democratically elected government of the British Overseas Territory of the British Virgin Islands. It is regulated by the Constitution of the British Virgin Islands.

The Governor of the Virgin Islands is the representative of the British monarch in the United Kingdom's overseas territory of the British Virgin Islands. The governor is appointed by the monarch on the advice of the British government. The role of the governor is to act as the de facto head of state, and he or she is responsible for appointing the chief minister and the executive council.

Saint Croix is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States.
The Garífuna are a mixed African and indigenous people originally from the Caribbean island of St. Vincent who speak the Garifuna dialect of the Arawakan language.

Tortola is the largest and most populated of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. It has a surface area of 55.7 square kilometres with a total population of 23,908, with 9,400 residents in Road Town. Mount Sage is its highest point at 530 metres above sea level.

Commonwealth Caribbean is a term used to refer to the English-speaking nations and territories of the Caribbean, which once constituted the Caribbean portion of the British Empire and are now part of the Commonwealth of Nations. The term includes many independent island nations, British Overseas Territories and nations on the mainland. The emphasis on the English language has led other terms to also describe the grouping, such as the Anglo Caribbean, Anglophone Caribbean or English-speaking Caribbean. The term is now used in preference over the older term "British West Indies" which was used to describe the British colonies in the West Indies (therefore not including Belize and Guyana) during decolonisation and following independence from the United Kingdom. The term Anglo Caribbean or the British Commonwealth Caribbean, traditionally becomes the preferred sub-regional term as a replacement to British West Indies.
Virgin Islands Creole, or Virgin Islands Creole English, is an English-based creole consisting of several varieties spoken in the Virgin Islands and the nearby SSS islands of Saba, Saint Martin and Sint Eustatius, where it is known as Saban English, Saint Martin English, and Statian English, respectively.

The University of the Virgin Islands is a public, historically black university in the United States Virgin Islands.
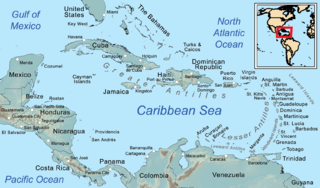
The West Indies is a region of the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean that includes the island countries and surrounding waters of three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically situated a part of the Leeward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The island is located near Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Its area is 750 km2 (290 sq mi), and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at 1,447 m (4,747 ft) in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the British Virgin Islands:

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the territory of the United States Virgin Islands.
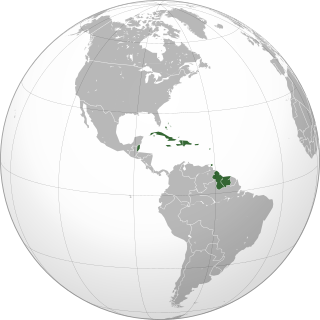
The Caribbean is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.

Women in the Caribbean are women who were born in, who live in, or are from the region of the Caribbean in the Americas. Historically, Caribbean women have been significant contributors to the economy and the "domestic sphere" of the Caribbean region since the time of slavery, during the time of "free labor forces" in the late 19th and 20th centuries, as well as during the time of "contemporary politics" and economics. Their position and status may vary "among Caribbean societies", cultural groups, and geographical locations, that have different language backgrounds which include English-, Spanish-, and French-speaking communities in the West Indies.

Women in the United States Virgin Islands are women who were born in, who live in, and are from the Virgin Islands of the United States, a group of islands in the Caribbean that are an insular area of the United States, and is composed of the islands of St. Croix, St. John, and St. Thomas. According to Countries and Their Culture, the women of the U.S. Virgin Islands are participating increasingly in the fields of economics, business, and politics.

The foreign relations of the British Virgin Islands are largely conducted on behalf of the British Virgin Islands Government by the United Kingdom through the Foreign and Commonwealth Office as a result of the Territory's status as a British Overseas Territory. However the Constitution of the British Virgin Islands provides that this power is delegated to Premier and Ministers of Government in relation to certain specific areas:
- the Caribbean Community, the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States, the Association of Caribbean States, the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, or any other Caribbean regional organisation or institution;
- other Caribbean regional affairs relating specifically to issues that are of interest to or affect the British Virgin Islands;
- the relationship between the British Virgin Islands and the United States Virgin Islands in matters of mutual interest;
- tourism and tourism-related matters;
- taxation and the regulation of finance and financial services; and
- European Union matters directly affecting the interests of the Territory.