
Adinazolam is a tranquilizer of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and antidepressant properties. Adinazolam was developed by Jackson B. Hester, who was seeking to enhance the antidepressant properties of alprazolam, which he also developed. Adinazolam was never FDA approved and never made available to the public market; however, it has been sold as a designer drug.

Diethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1950s which was mainly used as an anesthetic in veterinary medicine and continues, along with the other two thiambutenes dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene to be used for this purpose, particularly in Japan. It is now under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential, although little more information is available. It is listed under Schedule I of the US Controlled Substances Act as a Narcotic and has an ACSCN of 9616 with zero annual manufacturing quota as of 2013.

Dexibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is the active dextrorotatory enantiomer of ibuprofen. Most ibuprofen formulations contain a racemic mixture of both isomers.

Tifluadom is a benzodiazepine derivative with an unusual activity profile. Unlike most benzodiazepines, tifluadom has no activity at the GABAA receptor, but instead is a selective agonist for the κ-opioid receptor. It has potent analgesic and diuretic effects in animals, and also has sedative effects and stimulates appetite.
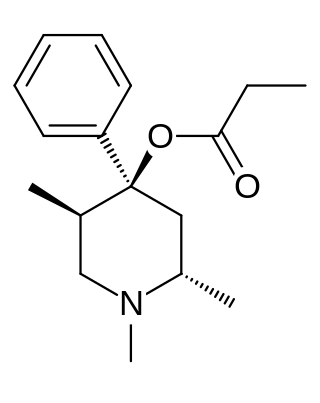
Trimeperidine (Promedol) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.

Azidomorphine is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 7,8 double bond has been saturated and the 6-hydroxy group has been replaced by an azide group.
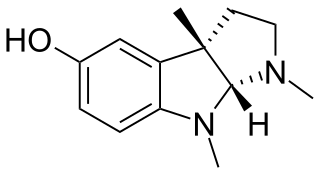
Eseroline is a drug which acts as an opioid agonist. It is a metabolite of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor physostigmine but unlike physostigmine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibition produced by eseroline is weak and easily reversible, and it produces fairly potent analgesic effects mediated through the μ-opioid receptor. This mixture of activities gives eseroline an unusual pharmacological profile, although its uses are limited by side effects such as respiratory depression and neurotoxicity.
An equianalgesic chart is a conversion chart that lists equivalent doses of analgesics. Equianalgesic charts are used for calculation of an equivalent dose between different analgesics. Tables of this general type are also available for NSAIDs, benzodiazepines, depressants, stimulants, anticholinergics and others.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher neurotoxicity, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

Amfonelic acid is a research chemical and dopaminergic stimulant with antibiotic properties. Although limited clinical trials have been conducted, it's primarily used in scientific research.

Ricasetron (BRL-46470) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor. It has antiemetic effects as with other 5-HT3 antagonists, and also has anxiolytic effects significantly stronger than other related drugs, and with less side effects than benzodiazepine anxiolytics. However, it has never been developed for medical use.

Candocuronium iodide is a aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocking drug. Its use within anesthesia for endotracheal intubation and for providing skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation was briefly evaluated in clinical studies in India, though further development was discontinued due to attendant cardiovascular effects, primarily tachycardia that was about the same as the clinically established pancuronium bromide. Candocuronium demonstrated a short duration in the body, but a rapid onset of action. It had little to no ganglion blocking activity, with a greater potency than pancuronium.

MT-45 (IC-6) is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl) piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. Racemic MT-45 has around 80% the potency of morphine, with almost all opioid activity residing in the (S) enantiomer. It has been used as a lead compound from which a large family of potent opioid drugs have been developed, including full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists at the three main opioid receptor subtypes. Fluorinated derivatives of MT-45 such as 2F-MT-45 are significantly more potent as μ-opioid receptor agonists, and one of its main metabolites 1,2-diphenylethylpiperazine also blocks NMDA receptors.

AD-1211 is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-prenyl-piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. The (S)-enantiomers in this series are more active as opioid agonists, but the less active (R)-enantiomer of this compound, AD-1211, is a mixed agonist–antagonist at opioid receptors with a similar pharmacological profile to pentazocine, and has atypical opioid effects with little development of tolerance or dependence seen after extended administration in animal studies.

Noracymethadol (INN) is a synthetic opioid analgesic related to methadone that was never marketed. In a clinical trial of postpartum patients it was reported to produce analgesia comparable to that of morphine but with less nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. Other side effects included salivation, ataxia, and respiratory depression that was reversible by naloxone. Similarly to many of its analogues, noracymethadol is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States with an ACSCN of 9633 and 2013 annual manufacturing quota of 12 grammes. and is also controlled internationally under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961. The salts known are the gluconate and hydrochloride (0.903).
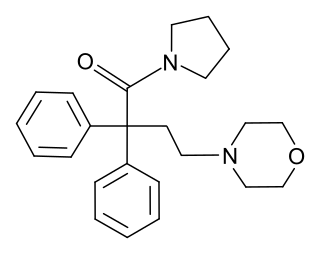
Desmethylmoramide (INN) is an opioid analgesic related to dextromoramide that was synthesized and characterized in the late 1950s but was never marketed.

Tiodazosin is an α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
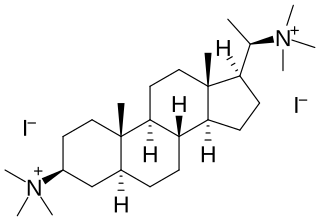
Malouetine is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent and antinicotinic alkaloid isolated from Malouetia spp.

Isotonitazene is a benzimidazole derived opioid analgesic drug related to etonitazene, which has been sold as a designer drug. It has only around half the potency of etonitazene in animal studies, but it is likely even less potent in humans as was seen with etonitazene. Isotonitazene was fully characterized in November 2019 in a paper where the authors performed a full analytical structure elucidation in addition to determination of the potency at the μ-opioid receptor using a biological functional assay in vitro. While isotonitazene was not compared directly to morphine in this assay, it was found to be around 2.5 times more potent than hydromorphone and slightly more potent than fentanyl.

3'-Hydroxy-THC (3'-OH-Δ9-THC) is a minor active metabolite of THC, the main psychoactive component of cannabis. It is one of a number of metabolites of THC hydroxylated on the pentyl side chain, but while the other side-chain hydroxyl isomers are much weaker or inactive, the S enantiomer of 3'-OH-THC is several times more potent than THC itself, and while it is produced in smaller amounts than other active metabolites such as 11-Hydroxy-THC and 8,11-Dihydroxy-THC, it is thought to contribute to the overall pharmacological profile of cannabis.




















