
The politics of Bulgaria take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The Movement for Rights and Freedoms was a centrist political party in Bulgaria with a support base among ethnic minority communities.

Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 25 June 2005, for the 240 members of the National Assembly. According to exit polls, the Socialists had a lead with around 31%, but without a majority, necessitating the creation of a coalition. The National Movement for Simeon II, in power before the election, was in second place, with around 21%. Following the election, Socialist Party leader Sergei Stanishev became prime minister.

European Parliament elections were held in Bulgaria on 20 May 2007. It was the country's first European election, having joined the Union on 1 January of that year. The country still had 18 MEPs, no change from before the election. Until Bulgaria could hold these elections, the country was represented by MEPs appointed by the National Assembly.

The eighty-ninth cabinet of Bulgaria, also known as the Three-party coalition cabinet and the Stanishev Government, ruled from August 17, 2005, to July 27, 2009. The cabinet was formed with the coalition of the three leading at that time: BSP, NDSV and DPS, in order of their parliamentary representation. Their parliamentary representation also determined the number of cabinet appointments.

Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 12 May 2013, two months ahead of schedule. Protests had forced the resignation of the GERB government in February, leading to the election being moved up.

Mihail Raykov Mikov is a Bulgarian politician who was Chairman of the Bulgarian Socialist Party (BSP) from 2014 to 2016. He is a parliamentarian with six consecutive terms as a deputy in the National Assembly. His career in the legislature culminated in his election as Chairman of the 42nd National Assembly on May 21, 2013. Mikov was Minister of Interior from 24 April 2008 to 29 July 2009 in Sergei Stanishev's government. Currently he is the leader of the Parliamentary Group of BSP Left Bulgaria in the 43rd National Assembly, the coalition led by the socialist party. Mihail Mikov was elected as Chairman of the BSP on 27 July 2014, succeeding Sergei Stanishev. He won a run-off against outgoing Economy and Energy Minister Dragomir Stoynev with a final tally of 377-333.
The Oresharski Government was the ninety-second cabinet of Bulgaria which took office on 29 May 2013. The government, led by Prime Minister Plamen Oresharski, is one of technocrats created following the 2013 election. The cabinet was dissolved on 6 August 2014 to make way for a caretaker government that would lead Bulgaria through early elections in October of the same year.
Delyan Slavchev Peevski is a Bulgarian politician, oligarch, sanctioned by Magnitsky Act by UK and US for corruption, bribery and embezzlement also a former media mogul who has served as a Member of the National Assembly of Bulgaria since 2009. A member of the DPS party, he was elected for a short time in 2013 as the Director of the State Agency for National Security, which triggered long lasting national protests. Peevski was also unanimously elected in 2024 as the co-leader of the DPS party alongside Dzhevdet Chakarov.

A referendum on introducing electronic voting was held in Bulgaria on 25 October 2015 alongside local elections. Although the referendum resulted was approved by a wide margin, turnout was far below the required threshold to make its result binding.

The Reformist Bloc was a centre-right electoral alliance in Bulgaria.

Nikolay Tihomirov Barekov (Bulgarian: Николай Тихомиров Бареков; born 16 October 1972) is a Bulgarian journalist, politician, and businessman. Since January 2014 he has been the leader of the political party Bulgaria Without Censorship.

Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 5 October 2014 to elect the 43rd National Assembly. GERB remained the largest party, winning 84 of the 240 seats with around a third of the vote. A total of eight parties won seats, the first time since the beginning of democratic elections in 1990 that more than seven parties entered parliament. Boyko Borisov then became prime minister as head of a coalition with the Reformist Bloc and with outside support from the Patriotic Front and the Alternative for Bulgarian Revival.

Reload Bulgaria is a populist political party in Bulgaria.

Angel Chavdarov Dzhambazki is a Bulgarian nationalist politician who served as Member of the European Parliament from 2014 to 2024. He is also a co-chairman of VMRO, having joined the nationalist party's youth organization in 1997 and gradually progressed through its ranks.

Sotir Stefanov Tsatsarov is a Bulgarian jurist who served as the chief prosecutor of Bulgaria from December 2012 until December 2019. Tsatsarov allegedly owes his appointment to Delyan Peevski, a media mogul and member of Bulgaria's Parliament, and Prime Minister Boyko Borisov. His time in office has been overshadowed by controversial investigations of political opposition leaders, famous businessmen, and independent media. Prominent Bulgarian jurists, including the heads of Bulgaria's main appellate courts, have asked for his resignation.
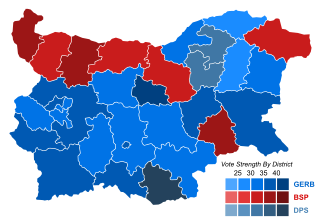
Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 26 March 2017. They had originally been scheduled for 2018 at the end of the four-year term of the National Assembly. However, following the resignation of Prime Minister Boyko Borisov and the failure of Bulgarian parties to form a government, early elections were called. Borisov resigned following the defeat of Tsetska Tsacheva, the candidate of his GERB party, in the November 2016 presidential elections. The official election campaign began on 24 February.

General elections were held in Bulgaria on 14 November 2021 to elect both the President and the National Assembly. They were the country's third parliamentary elections in 2021, with no party able to form a government after the elections in April and July. A second round of the presidential elections were held on 21 November 2021 as no candidate was able to receive a majority of the vote in the first round.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 9 June 2024, to elect members of the National Assembly. The election coincided with the European Parliament election on the same day.

Early parliamentary elections are expected to be held in Bulgaria in 27 October 2024, after all three attempts to form a government following the latest June 2024 elections failed. They will be the country's sixth snap elections since 2021.






















