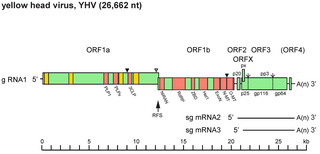
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Closteroviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four genera and 59 species in this family, seven of which are unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.

Potyviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to a genus.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plant serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.

Lipothrixviridae is a family of viruses in the order Ligamenvirales. Thermophilic archaea in the phylum Crenarchaeota serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera.

Ourmiavirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses. Cucurbits, cherry, and cassava serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: OuMV: yellowing and chlorotic spot symptoms.
Tobravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: SBWMV: green and yellow mosaic.
Fuselloviridae is a family of viruses. Sulfolobus species, specifically shibatae, solfataricus, and islandicus, serve as natural hosts. There are two genera and nine species in the family. The Fuselloviridae are ubiquitous in high-temperature (≥70 °C), acidic hot springs around the world.
Guttaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in this family, containing one species each. The name is derived from the Latin gutta, meaning 'droplet'.

Globuloviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Crenarchaea of the genera Pyrobaculum and Thermoproteus serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this family, assigned to a single genus, Alphaglobulovirus.
Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Bicaudaviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Members of the genus Acidianus serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus (Bicaudavirus) and one species in this family: Acidianus two-tailed virus. However, Sulfolobus tengchongensis spindle-shaped viruses 1 and 2 are regarded to belong to this family also.
Twortvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Herelleviridae, in the subfamily Twortvirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Staphylococcus virus Twort.
Alphafusellovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Fuselloviridae. Species in the genus Sulfolobus serve as natural hosts. There are seven species in this genus.
Betalipothrixvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Lipothrixviridae. Archaea serve as natural hosts. The genus contains six species.
Ephemerovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Rhabdoviridae, order Mononegavirales. Cattle and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with viruses in this genus include: sudden fever.

Iridovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Iridoviridae. Insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently only two species in this genus. Invertebrate iridescent virus 6 (IIV-6) was recognised as the type species until such a designation was abolished. IIV-6 is hosted by mosquitos and usually causes covert (inapparent) infection that reduces fitness. The remaining species Invertebrate iridescent virus 31 (IIV-31) is hosted by isopods and causes patent (apparent) infection characterised by blue to bluish-purple iridescence and a shortened lifespan.
Oleavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Bromoviridae. Olive trees serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Olive latent virus 2.
Turriviridae is a family of viruses; it contains only one genus, Alphaturrivirus. The archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus serve as natural hosts. There are two species in the genus Alphaturrivirus.
Cryspovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Partitiviridae. Protists serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Cryptosporidium parvum virus 1.









