
Nordazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.

Phenprobamate is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, with additional sedative and anticonvulsant effects. Its mechanism of action is probably similar to meprobamate. Phenprobamate has been used in humans as an anxiolytic, and is still sometimes used in general anesthesia and for treating muscle cramps and spasticity. Phenprobamate is still used and available OTC in some European countries, but it has generally been replaced by newer drugs. It has been sold labeled as a nootropic. Phenprobamate is metabolized by oxidative degradation of the carbamate group and ortho-hydroxylation of the benzene ring, and is eliminated in urine by the kidneys.

Medazepam is a drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is known by the following brand names: Azepamid, Nobrium, Tranquirax, Rudotel, Raporan, Ansilan and Mezapam. Medazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine drug. The half-life of medazepam is 36–200 hours.
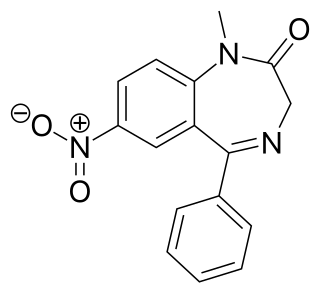
Nimetazepam is an intermediate-acting hypnotic drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was first synthesized by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in 1964. It possesses powerful hypnotic, anxiolytic, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Nimetazepam is also a particularly potent anticonvulsant. It is marketed in 5 mg tablets known as Erimin, which is the brand name manufactured and marketed by the large Japanese corporation Sumitomo. Japan is the sole manufacturer of nimetazepam in the world. Outside of Japan, Erimin is available in much of East and Southeast Asia and was widely prescribed for the short-term treatment of severe insomnia in patients who have difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep. Sumitomo has ceased manufacturing Erimin since November 2015. It is still available as a generic drug or as Lavol.

Cloxazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative that has anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant properties. It is not widely used; as of August 2018 it was marketed in Belgium, Luxembourg, Portugal, Brazil, and Japan. In 2019, it has been retired from the Belgian market.

Vinylbital, also known as butylvinal, is a sedative hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It was developed by Aktiebolaget Pharmacia in the 1950s.

Cyclobarbital, also known as cyclobarbitol or cyclobarbitone, is a barbiturate derivative. It was available in Russia as a fixed-dose combination with diazepam for the treatment of insomnia but was discontinued in 2019.

Ethinamate is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependence.

Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine.

Triclofos is a sedative drug used rarely for treating insomnia.

Aprobarbital, sold under the brand names Oramon, Somnifaine, and Allonal, is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s by Ernst Preiswerk. It has sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily for the treatment of insomnia. Aprobarbital was never as widely used as more common barbiturate derivatives such as phenobarbital and is now rarely prescribed. It has been largely replaced by newer drugs with a better safety margin.

Acetyldihydrocodeine is an opiate derivative discovered in Germany in 1914 and was used as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used, but has activity similar to other opiates. Acetyldihydrocodeine is a very close relative derivative of thebacon, where only the 6-7 bond is unsaturated. Acetyldihydrocodeine can be described as the 6-acetyl derivative of dihydrocodeine and is metabolised in the liver by demethylation and deacetylation to produce dihydromorphine.
Thiamylal (Surital) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1950s. It has sedative, anticonvulsant, and hypnotic effects, and is used as a strong but short acting sedative. Thiamylal is still in current use, primarily for induction in surgical anaesthesia or as an anticonvulsant to counteract side effects from other anaesthetics. It is the thiobarbiturate analogue of secobarbital.

Oxazolam is a drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is a prodrug for desmethyldiazepam.

Dioxaphetyl butyrate is an opioid analgesic which is a diphenylacetic acid derivative, related to other open-chain opioid drugs such as dextropropoxyphene, levacetylmethadol (LAAM), lefetamine and dimenoxadol.

Myrophine (Myristylbenzylmorphine) is an opiate analogue that was developed in 1952. It is a derivative of morphine.

Levophenacylmorphan is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It has potent analgesic effects and is around 10x more potent than morphine. Adverse effects associated with its use are those of the opioids as a whole, including pruritus, nausea, respiratory depression, euphoria and development of tolerance and dependence to its effects.

Drotebanol (Oxymethebanol) is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It was invented by Sankyo Company in Japan during the 1970s. It is synthesised from thebaine.
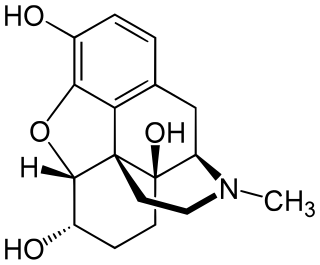
Hydromorphinol, is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

Periciazine (INN), also known as pericyazine (BAN) or propericiazine, is a drug that belongs to the phenothiazine class of typical antipsychotics.



















