
Closteroviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four genera and 59 species in this family, seven of which are unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.

Tymoviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 42 species in this family, assigned to three genera, with two species unassigned to a genus.

Lipothrixviridae is a family of viruses in the order Ligamenvirales. Thermophilic archaea in the phylum Thermoproteota serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera. The genus
Pecluvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Cereal crops and graminaceous weeds serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: (SBWMV): green and yellow mosaic. The name of the genus is derived from Peanut clump virus: Peanut clump virus, giving rise to Pecluvirus.
Tobravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: SBWMV: green and yellow mosaic.
Fuselloviridae is a family of viruses. Sulfolobus species, specifically shibatae, solfataricus, and islandicus, serve as natural hosts. There are two genera and nine species in the family. The Fuselloviridae are ubiquitous in high-temperature (≥70 °C), acidic hot springs around the world.

Trichovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically angiosperms such as pome fruits, citrus, and pear, serve as natural hosts for this plant pathogen. There are seven species in this genus.

Globuloviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Crenarchaea of the genera Pyrobaculum and Thermoproteus serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this family, assigned to a single genus, Alphaglobulovirus.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Ampullaviridae is a family of viruses that infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. Only one genus in this family has been described, Bottigliavirus, which contains three species. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.
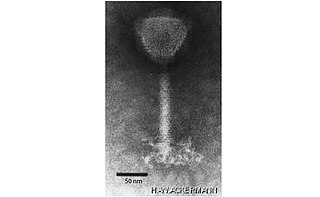
Okubovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Herelleviridae, in the subfamily Spounavirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus.
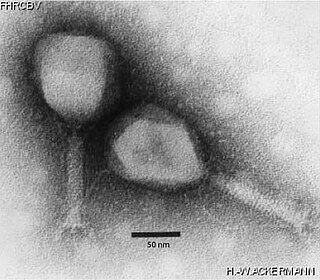
Tevenvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are 135 species in this subfamily, most included in 12 genera.
Myohalovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus.
Allexivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Shallot, onion, and garlic serve as natural hosts. There are 13 species in this genus, seven of which are assigned to a subgenus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Betalipothrixvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Lipothrixviridae. Archaea serve as natural hosts. The genus contains six species.
Capillovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, pome fruits, citrus, and pear serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: abnormal graft union, possibly black necrotic leaf spot disease.
Epsilonpapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Cattle serve as natural hosts and it is one of the bovine papillomaviruses. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: fibropapillomas and true epithelial papillomas of the skin.
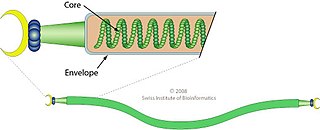
Gammalipothrixvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Lipothrixviridae. Archaea acidianus serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Acidianus filamentous virus 1.
Turriviridae is a family of viruses; it contains only one genus, Alphaturrivirus. The archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus serve as natural hosts. There are two species in the genus Alphaturrivirus.
Tepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants as well as some other root and tuber crops in the andes serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus.










