
Natufian culture is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Neolithic prehistoric Levant in Western Asia, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the first Neolithic settlements of the region, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence of possible beer-brewing, dating to approximately 13,000 BC, was found in Raqefet Cave on Mount Carmel, although the beer-related residues may simply be a result of a spontaneous fermentation.

The Guanche were the indigenous inhabitants of the Spanish Canary Islands, located in the Atlantic Ocean some 100 kilometres (60 mi) to the west of modern Morocco and the North African coast. The islanders spoke the Guanche language, which is believed to have been related to the Berber languages of mainland North Africa; the language became extinct in the 17th century, soon after the islands were colonized.

The Capsian culture was a late Mesolithic and Neolithic culture centered in the Maghreb that lasted from about 8,000 to 2,700 BC. It was named after the town of Gafsa in Tunisia, which was known as Capsa in Roman times.

Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to c. 10,800 – c. 8,500 years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon during her archaeological excavations at Jericho in the West Bank, territory of Palestine.
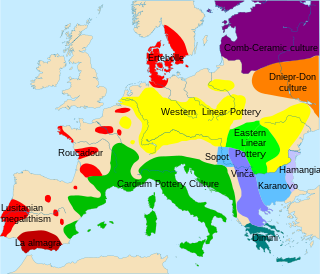
Cardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the Corculum cardissa, a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery are in turn used to define the Neolithic culture which produced and spread them, commonly called the "Cardial culture".

Haplogroup X is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is found in North America, Europe, Western Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.
Haplogroup K, formerly Haplogroup UK, is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is defined by the HVR1 mutations 16224C and 16311C. It is now known that K is a subclade of U8.
Canary Islanders, or Canarians, are the people of the Canary Islands, an autonomous community of Spain near the coast of Northwest Africa. The distinctive variety of the Spanish language spoken in the region is known as habla canaria or the (dialecto) canario. The Canarians, and their descendants, played a major role during the conquest, colonization, and eventual independence movements of various countries in Latin America. Their ethnic and cultural presence is most palpable in the countries of Uruguay, Venezuela, Cuba and the Dominican Republic as well as the US territory of Puerto Rico.

The genetic history of the Middle East is the subject of research within the fields of human population genomics, archaeogenetics and Middle Eastern studies. Researchers use Y-DNA, mtDNA, and other autosomal DNA tests to identify the genetic history of ancient and modern populations of Egypt, Persia, Mesopotamia, Anatolia, Arabia, the Levant, and other areas.
The Kiffian culture is a prehistoric industry, or domain, that existed between approximately 8,000 BC and 6,000 BC in the Sahara Desert, during the African humid period referred to as the Neolithic Subpluvial. Human remains from this culture were found in 2000 AD at a site known as Gobero, located in Niger in the Ténéré Desert. The site is known as the largest and earliest burial place of Stone Age people in the Sahara desert.
Haplogroup H is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade is believed to have originated in Southwest Asia, near present day Syria, around 20,000 to 25,000 years ago. Mitochondrial haplogroup H is today predominantly found in Europe, and is believed to have evolved before the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). It first expanded in the northern Near East and Southern Caucasus, and later migrations from Iberia suggest that the clade reached Europe before the Last Glacial Maximum. The haplogroup has also spread to parts of Africa, Siberia and Inner Asia. Today, around 40% of all maternal lineages in Europe belong to haplogroup H.
African admixture in Europe refers to the presence of human genotypes attributable to periods of human population dispersals out of Africa in the genetic history of Europe.
Genetic studies of Jews are part of the population genetics discipline and are used to analyze the ancestry of Jewish populations, complementing research in other fields such as history, linguistics, archaeology, and paleontology. These studies investigate the origins of various Jewish ethnic divisions. In particular, they examine whether there is a common genetic heritage among them. The medical genetics of Jews are studied for population-specific diseases.
The genetic history of North Africa encompasses the genetic history of the people of North Africa. The most important source of gene flow to North Africa from the Neolithic Era onwards was from Western Asia, while the Sahara desert to the south and the Mediterranean Sea to the north were also important barriers to gene flow from sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Europe in prehistory. However, North Africa is connected to Western Asia via the Isthmus of Suez and the Sinai peninsula, while at the Straits of Gibraltar, North Africa and Europe are separated by only 15 km (9 mi), similarly Malta, Sicily, Canary Islands, Lampedusa and Crete are close to the coasts of North Africa, with the indigenous Guanche people of the Canary Islands being Berber.
E-Z827, also known as E1b1b1b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the parent lineage to the E-Z830 and E-V257 subclades, and defines their common phylogeny. The former is predominantly found in the Middle East; the latter is most frequently observed in North Africa, with its E-M81 subclade observed among the ancient Guanche natives of the Canary Islands. E-Z827 is also found at lower frequencies in Europe, and in isolated parts of Southeast Africa.

Moroccan genetics encompasses the genetic history of the people of Morocco, and the genetic influence of this ancestry on world populations. It has been heavily influenced by geography.

Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as younger ones, from the Upper Palaeolithic between 15,100 and 14,000 calendar years ago. There is archaeological evidence for Iberomaurusian occupation at the site between 23,200 and 12,600 calendar years ago, as well as evidence for Aterian occupation as old as 85,000 years.
Ifri Oudadane is an archaeological site in the northeastern Rif region of Morocco. It is located on the southwestern coast of the Cape Three Forks on the Mediterranean Sea, and is one of the most important sites in the northwestern Maghreb region of Africa. Discovered during road construction, the site consists of a fairly large rock shelter above the modern coastline, the site has been excavated since 2006 by a team of Moroccan and German archaeologists. Although much is known about the transition of humans from hunter gatherer groups to food production in Europe and the Middle East, much of North Africa has not been researched. Ifri Oudadane is one of the first of such sites in North Africa. Dated to between 11000 and 5700 years BP, the site contains evidence that documents the shift of local inhabitants from hunter-gatherer groups to food producers. Such elements of change found at Ifri Oudadane include evidence of animal husbandry, domestication of legumes, and decoration of pottery. The site is known to contain the earliest dated crop in Northern Africa, a lentil.
Ifri n'Amr Ou Moussa is an archaeological site discovered in 2005, located in the rural commune of Aït Siberne, Khémisset Province, in Western Morocco. This site has revealed burials associated with both Moroccan Early Neolithic and Bell Beaker culture.

The Cave of El Toro is a cave complex located in the El Torcal de Antequera natural reserve near Málaga, Andalusia, Spain. It lies at about 1,190 meters above sea level. The cave has yielded evidence of human occupation as early as the Early Neolithic.











