
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their distinct material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. The Lapita people are believed to have originated from the northern Philippines, either directly, via the Mariana Islands, or both. They were notable for their distinctive geometric designs on dentate-stamped pottery, which closely resemble the pottery recovered from the Nagsabaran archaeological site in northern Luzon. The Lapita intermarried with the Papuan populations to various degrees, and are the direct ancestors of the Austronesian peoples of Polynesia, eastern Micronesia, and Island Melanesia.

The Sa Huỳnh culture was a culture in what is now central and southern Vietnam that flourished between 1000 BC and 200 AD. Archaeological sites from the culture have been discovered from the Mekong Delta to Quảng Bình province in central Vietnam. The Sa Huynh people were most likely the predecessors of the Cham people, an Austronesian-speaking people and the founders of the kingdom of Champa.

The Tabon Caves is a cave system located in Lipuun Point, Panitian, Quezon, Palawan in the Philippines. Dubbed as the country's "cradle of civilization", it is a site of archaeological importance due to the number of jar burials and prehistoric human remains found starting from the 1960s, most notably the Tabon Man. The system is a part of the Lipuun Point Reservation, which has been protected by the Philippine government as a museum reservation to protect the caves and its immediate vicinity from deforestation and to preserve the cultural artifacts present there.
Most information about Taiwan before the arrival of the Dutch East India Company in 1624 comes from archaeological finds throughout the island. The earliest evidence of human habitation dates back 20,000 to 30,000 years, when lower sea levels exposed the Taiwan Strait as a land bridge. Around 5,000 years ago, farmers from the southeast Chinese coast settled on the island. These people are believed to have been speakers of Austronesian languages, which dispersed from Taiwan across the islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. The current Taiwanese aborigines are believed to be their descendants.

The Manunggul Jar is a secondary burial jar excavated from a Neolithic burial site in the Manunggul cave of the Tabon Caves at Lipuun Point in Palawan, Philippines. It dates from 890–710 B.C. and the two prominent figures at the top handle of its cover represent the journey of the soul to the afterlife.

Wilhelm G. Solheim II (1924—2014) was an American anthropologist recognized as the most senior practitioner of archaeology in Southeast Asia, and as a pioneer in the study of Philippine and Southeast Asian prehistoric archaeology. He is perhaps best known, however, for hypothesizing the existence of the Nusantao Maritime Trading and Communication Network (NMTCN), one of two dominant hypotheses regarding the peopling of the Asia-Pacific region during the Neolithic age.
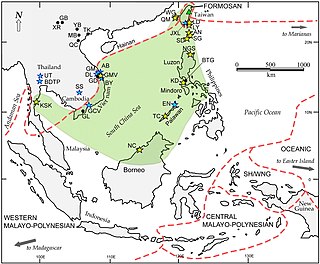
In a hypothesis developed by Wilhelm Solheim, the Nusantao Maritime Trading and Communication Network (NMTCN) is a trade and communication network that first appeared in the Asia-Pacific region during its Neolithic age, or beginning roughly around 5000 BC. Nusantao is an artificial term coined by Solheim, derived from the Austronesian root words nusa "island" and tao "man, people". Solheim's theory is an alternative hypothesis to the spread of the Austronesian language family in Southeast Asia. It contrasts the more widely accepted Out-of-Taiwan hypothesis (OOT) by Peter Bellwood.
Alfredo E. Evangelista was a Filipino archeologist and former director of the Anthropology division of the National Museum of the Philippines.

The prehistory of the Philippines covers the events prior to the written history of what is now the Philippines. The current demarcation between this period and the early history of the Philippines is April 21, 900, which is the equivalent on the Proleptic Gregorian calendar for the date indicated on the Laguna Copperplate Inscription—the earliest known surviving written record to come from the Philippines. This period saw the immense change that took hold of the archipelago from Stone Age cultures in 50000 BC to the emergence of developed thalassocratic civilizations in the fourth century, continuing on with the gradual widening of trade until 900 and the first surviving written records.

The Buni culture is a prehistoric clay pottery culture that flourished in coastal northern West Java, Jakarta and Banten around 400 BC to 100 AD and probably survived until 500 AD. The culture was named after its first discovered archaeological site, Buni village in Babelan, Bekasi, east of Jakarta.
Dewil Valley, located in the northernmost part of Palawan, an island province of the Philippines that is located in the Mimaropa region, is an archaeological site composed of thousands of artifacts and features. According to the University of the Philippines Archaeological Studies Program, or UP-ASP, the closest settlement can be found in New Ibajay, which is covered by the town capital of El Nido, which is located around 9 km (5.6 mi) south-east of Dewil Valley. Physically it measures around 7 km (4.3 mi) long, and 4 km (2.5 mi) wide. It is in this place which the Ille Cave, one of the main archaeological sites, can be found. It is actually a network of 3 cave mouths located at its base. It has been discovered that this site in particular has been used and occupied by humans over multiple time periods.

Sarangani is a province located in the Mindanao region of the Philippines and has a total land area of 4,441.79 square kilometers.. Historically, Sarangani already had an established community even before the Westerners came. The early Sarangani society was greatly affected by the Indian and Muslim cultures, and the first inhabitants were the indigenous natives called
Minori Cave is part of the Callao limestone formation, located in Barangay Quibal, Municipality of Peñablanca, Cagayan Province in Northern Luzon. The said cave has two openings. One, designated as Mouth B, is located at 17° 43' 17" N latitude and 121° 49' 42" E longitude. The other opening, Mouth A is located 17° 43' 21" N latitude and 121° 49' 44" E longitude. The cave has an average elevation of about 200 m (656.2 ft) above sea level, and length and width of 147 m (482.3 ft) and 7 to 11 m, respectively. The cave is divided into four chambers with mouth A as chamber A and mouth B as chamber D. Chambers B and C are in between the two mouths.
Philippine jade culture, or jade artifacts, made from white and green nephrite and dating as far back as 2000–1500 BC, have been discovered at a number of archaeological excavations in the Philippines since the 1930s. The artifacts have been both tools like chisels and ornaments such as lingling-o earrings, bracelets, and beads.

The archaeology of the Philippines is the study of past societies in the territory of the modern Republic of the Philippines, an island country in Southeast Asia, through material culture.

Lingling-o or ling-ling-o, are a type of penannular or double-headed pendant or amulet that have been associated with various late Neolithic to late Iron Age Austronesian cultures. Most lingling-o were made in jade workshops in the Philippines, and to a lesser extent in the Sa Huỳnh culture of Vietnam, although the raw jade was mostly sourced from Taiwan.

Philippine ceramics refers to ceramic art and pottery designed or produced as a form of Philippine art.
Philippine ceramics are mostly earthenware, pottery that has not been fired to the point of vitrification. Other types of pottery like tradeware and stoneware have been fired at high enough temperatures to vitrify. Earthenware ceramics in the Philippines are mainly differentiated from tradeware and stoneware by the materials used during the process and the temperature at which they are fired. Additionally, earthenware and stoneware pottery can generally be referred to as ceramics that are made with local materials, while tradeware ceramics can generally be referred to as ceramics that are made with non-local materials.
Symbolism is an abstract meaning given to an object or representative of one. Symbols can define certain aspects of cultures making them initially exclusive to particular groups. When it comes to symbolism in archaeology, artifacts found may display iconography with these abstract symbols or tell us more about the people who made them through their construction. Symbolism is not limited to only inanimate objects but can be found in the actions or being of living things as well. The Philippines, comprising more than 7,000 islands, is an archipelago where symbols of the past and present contribute to its unique culture. These symbols are influenced by and noticeable in burial practices, rituals, social status, architecture, agriculture, and The Philippines' place in the Austronesian world.

Gò Cầm is a village and an archaeological site, located in Duy Trung Commune, Duy Xuyên district, Quảng Nam province, Vietnam. The site is located nearby to another significant site, that of Trà Kiệu. Both are considered important sites for understanding the history of the Hindu Champa Kingdom.




















