
Human habitation of Cyprus dates back to the Paleolithic era. Cyprus's geographic position has caused the island to be influenced by differing Eastern Mediterranean civilisations over the millennia.

The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was first proposed by the 19th century Egyptologists Emmanuel de Rougé and Gaston Maspero, on the basis of primary sources such as the reliefs on the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III at Medinet Habu. Subsequent research developed the hypothesis further, attempting to link these sources to other Late Bronze Age evidence of migration, piracy, and destruction. While initial versions of the hypothesis regarded the Sea Peoples as a primary cause of the Late Bronze Age collapse, more recent versions generally regard them as a symptom of events which were already in motion before their purported attacks.
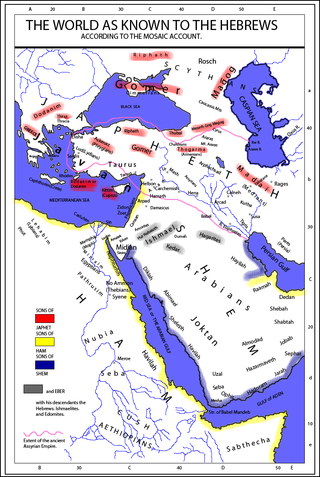
Caphtor is a locality mentioned in the Bible, in which its people are called Caphtorites or Caphtorim and are named as a division of the ancient Egyptians. Caphtor is also mentioned in ancient inscriptions from Egypt, Mari, and Ugarit.

The Cypriot or Cypriote syllabary is a syllabic script used in Iron Age Cyprus, from about the 11th to the 4th centuries BCE, when it was replaced by the Greek alphabet. It has been suggested that the script remained in use as late as the 1st century BC. A pioneer of that change was King Evagoras of Salamis. It is thought to be descended from the Cypro-Minoan syllabary, itself a variant or derivative of Linear A. Most texts using the script are in the Arcadocypriot dialect of Greek, but also one bilingual inscription was found in Amathus.

Alashiya, also spelled Alasiya, also known as the Kingdom of Alashiya, was a state which existed in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, and was situated somewhere in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was a major source of goods, especially copper, for ancient Egypt and other states in the Ancient Near East. It is referred to in a number of the surviving texts and is now thought to be the ancient name of Cyprus, or an area of Cyprus. This was confirmed by the scientific analysis performed in Tel Aviv University of the clay tablets which were sent from Alashiya to other rulers.

The ancient history of Cyprus shows a precocious sophistication in the Neolithic era visible in settlements such as at Choirokoitia dating from the 9th millennium BC, and at Kalavassos from about 7500 BC.

A kettle hat, also known as a war hat, was a type of combat helmet made of iron or steel in the shape of a brimmed hat. There were many design variations, with the common element being a wide brim that afforded extra protection to the wearer. It gained its common English language name from its resemblance to a metal cooking pot. The kettle hat was common all over Medieval Europe, and was called Eisenhut in German and chapel de fer in French.

Assuwa was a region of Bronze Age Anatolia located west of the Kızılırmak River. It was mentioned in Aegean, Anatolian and Egyptian inscriptions but is best known from Hittite records describing a league of 22 towns or states that rebelled against Hittite authority. It disappears from history during the thirteenth century BC.
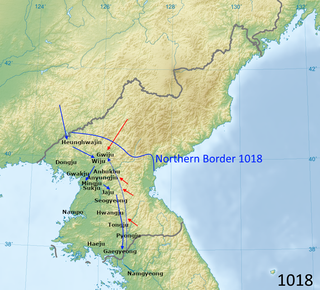
The Third Goryeo–Khitan War was an 11th-century conflict between the Goryeo dynasty of Korea and the Khitan-led Liao dynasty of China near what is now the border between China and North Korea. The Goryeo–Khitan Wars began in 993 with the first campaign and continued with the second campaign.

Khirokitia is an archaeological site on the island of Cyprus dating from the Neolithic age. It has been listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO since 1998. The site is known as one of the most important and best preserved prehistoric sites of the eastern Mediterranean. Much of its importance lies in the evidence of an organised functional society in the form of a collective settlement, with surrounding fortifications for communal protection. The Neolithic aceramic period is represented by this settlement and around 20 other similar settlements spread throughout the island.

The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aegean, eastern Libya, and the Balkans. The collapse was sudden, violent, and culturally disruptive for many Bronze Age civilizations, creating a sharp material decline for the region's previously existing powers.
This is a timeline of Cypriot history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Cyprus. To read about the background to these events, see History of Cyprus. See also the list of presidents of Cyprus.

Oxhide ingots are heavy (20–30 kg) metal slabs, usually of copper but sometimes of tin, produced and widely distributed during the Mediterranean Late Bronze Age (LBA). Their shape resembles the hide of an ox with a protruding handle in each of the ingot’s four corners. Early thought was that each ingot was equivalent to the value of one ox. However, the similarity in shape is simply a coincidence. The ingots' producers probably designed these protrusions to make the ingots easily transportable overland on the backs of pack animals. Complete or partial oxhide ingots have been discovered in Sardinia, Crete, Peloponnese, Cyprus, Cannatello in Sicily, Boğazköy in Turkey, Qantir in Egypt, and Sozopol in Bulgaria. Archaeologists have recovered many oxhide ingots from two shipwrecks off the coast of Turkey.
The Çekerek River is a tributary of the Yeşil River in Turkey. It flows for about 270 km (170 mi) in a "southwest-northeast arc". Its source is near Tokat. The confluence with the Yeşil is just to the southeast of the village of Kayabaşı.

The Achaeans were one of the four major tribes into which Herodotus divided the Greeks, along with the Aeolians, Ionians and Dorians. They inhabited the region of Achaea in the northern Peloponnese, and played an active role in the colonization of Italy, founding the city of Kroton. Unlike the other major tribes, the Achaeans did not have a separate dialect in the Classical period, instead using a form of Doric.
The Pompeian–Parthian invasion of 40 BC occurred after the Pompeians, backed by the Parthian Empire, had been defeated during the Liberators' civil war by Mark Antony and Octavian.
The Hittite Navy was the main naval force of the Hittites from ca. 16th–12th century BC. The navy took part in three land and sea military campaigns of the Hittite Kingdom against the Kingdom of Alashiya between 1275 and 1205 BC. It was also one of the main adversaries of the Egyptian Navy.
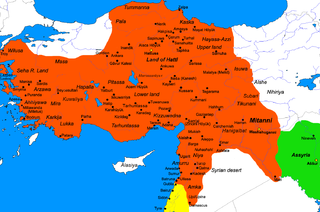
The Hittite Plague or Hand of Nergal was an epidemic, possibly of tularemia, which occurred in the mid-to-late 14th century BC.
The Battle of Dachangyuan took place between the Mongol Empire and the Jin Dynasty in 1229 during the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty.












