| Limnognathia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Schematic drawing of Limnognathia maerski | |
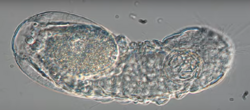 | |
| Microscopic view of L. maerski | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Subkingdom: | Eumetazoa |
| Clade: | ParaHoxozoa |
| Clade: | Bilateria |
| Clade: | Nephrozoa |
| Clade: | Protostomia |
| Clade: | Spiralia |
| Clade: | Gnathifera |
| Phylum: | Micrognathozoa Funch & Kristensen, 1995 |
| Order: | Limnognathida Funch & Kristensen, 1995 |
| Family: | Limnognathiidae Funch & Kristensen, 1995 |
| Genus: | Limnognathia Funch & Kristensen, 1995 |
| Species | |
| |
Limnognathia is a genus of microscopic acoelomate freshwater animal that was discovered in Disko Island, Greenland, in 1994. [1] Since then, it has also been found on the Crozet Islands of Antarctica as well as in the British Isles and the Spanish Pyrenees, [2] suggesting a worldwide distribution. [3] [4] There are two known species of Limnognathia: L. maerski, described in 2000, and L. desmeti, described in 2025.
Contents
- Description
- Feeding
- Anatomy
- Reproduction
- Taxonomy and phylogeny
- Taxonomic status
- Species
- Phylogeny
- References
- External links
Limnognathia is the only genus in the phylum Micrognathozoa ("small-jawed animal"). [5] [6]