Major road and railway bridges
This table presents the structures with spans greater than 100 meters (non-exhaustive list).
This is a list of bridges and viaducts in Angola, including those for pedestrians and vehicular traffic.
This table presents the structures with spans greater than 100 meters (non-exhaustive list).
Transport in Angola comprises:

Luanda is the capital and largest city in Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Angola's administrative centre, its chief seaport, and also the capital of the Luanda Province. Luanda and its metropolitan area is the most populous Portuguese-speaking capital city in the world and the most populous Lusophone city outside Brazil, with over 8.3 million inhabitants in 2020.

Benguela is a province of Angola, situated in the west of the country. It lies on the Atlantic Ocean, and borders the provinces of Cuanza Sul, Namibe, Huila, and Huambo. The province has an area of 39,826 square kilometres (15,377 sq mi) and its capital is Benguela. According to the 2014 census, there were 2,231,385 inhabitants in the province. The current governor of Benguela is Isaac dos Anjos.

The Kwanza River, also known as the Coanza, the Quanza, and the Cuanza, is one of the longest rivers in Angola. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean just south of the national capital Luanda.

The Benguela Railway is a Cape gauge railway line that runs through Angola from west to east, being the largest and most important railway line in the country. It also connects to Tenke in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and to the Cape to Cairo Railway.

Girabola, or Campeonato Nacional de Futebol em Séniores Masculinos, is the top division of Angolan football. It is organized by the Angolan Football Federation.
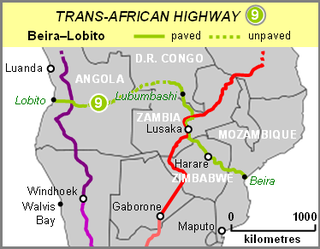
The Beira–Lobito Highway or TAH 9 is Trans-African Highway 9 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 3,523 km (2,189 mi) crossing Angola, the most southerly part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and central Mozambique.
The colonial history of Angola is usually considered to run from the appearance of the Portuguese under Diogo Cão in 1482 (Congo) or 1484 until the independence of Angola in November 1975. Settlement did not begin until Novais's establishment of São Paulo de Loanda (Luanda) in 1575, however, and the Portuguese government only formally incorporated Angola as a colony in 1655 or on May 12, 1886.
Teixeira Duarte, S.A. is the company that leads a large conglomerate with more than 11,000 workers, present in 22 countries, in 6 activity sectors, achieving in 2019 a turnover of 877 million Euros.

Railway stations in Angola include:

Angola is located on the western Atlantic Coast of Southern Africa between Namibia and the Republic of the Congo. It also is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia to the east. The country consists of a sparsely watered and somewhat sterile coastal plain extending inland for a distance varying from 50 to 160 km. Slightly inland and parallel to the coast is a belt of hills and mountains and behind those a large plateau. The total land size is 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 518,433 km2 (200,168 sq mi).
The Portuguese colony of Angola was founded in 1575 with the arrival of Paulo Dias de Novais with a hundred families of colonists and four hundred soldiers. Luanda was granted the status of city in 1605. The fortified Portuguese towns of Luanda and Benguela.
Grupo Opaia SA is a holding company operating under Angolan law based in Luanda, Angola, running projects in civil construction services, solar energy technology, drinking water systems, hotel service and tourism, agriculture, finance and more. It was founded by the Angolan Agostinho Kapaia, from Huambo, in 2002. From the year 2012 it began to be present on a national scale while it is planned to cover every province with its services. Most of the projects are yet in an early stage, but the companies Greenpower and NBASIT and the projects Meña of Opaia Water and Casa Feliz of Opaia Construction already got a lot of attention. For reasons of purchase, investment and international knowledge among others, there are offices abroad in Lisbon in Portugal, São Paulo in Brazil, Guangzhou in China, Miami in the US and the main office is in the own capital Luanda.

The Catumbela is a river in central Angola. The river mouth is at the Catumbela Estuary on the Atlantic Ocean at Catumbela, between Lobito and Benguela, and 240 kilometres (150 mi) from where it rises in the hills of Cassoco. The Catumbela supplies water to the city of Lobito. The mouth of the Catumbela was noted as a green vegetated region surrounded by barren land along the coast and a couple miles inland where it cuts a gorge through bare mountains. Alternate spellings are Catumbella and Cata-Bella.

Catumbela Bridge is a bridge over the Catumbela River, located in the municipality of Catumbela, Angola. The bridge, which was inaugurated on 10 September 2009, by the President of the Republic of Angola, José Eduardo dos Santos, connects the cities of Benguela and Lobito, in addition to other provinces of the country.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Benguela, Angola.

The port of Lobito is an Angolan port located in the city of Lobito, in the province of Benguela. It is connected to the commercial area of the city and the neighborhood of Canata. It is located in Lobito Bay, which is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Lobito Peninsula.
The Lobito–Dar es Salaam Railway is a planned narrow gauge railway line that connects the Angolan port city of Lobito to the Tanzanian port city of Dar es Salaam, through the Zambian city of Kapiri Mposhi. It is an African transcontinental railroad connecting the Atlantic and Indian oceans and it is financed by China.
The 1984 Taça de Angola was the 3rd edition of the Taça de Angola, the second most important and the top knock-out football club competition following the Girabola.