
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals.

Etonitazene, also known as EA-4941 or CS-4640, is a benzimidazole opioid, first reported in 1957, that has been shown to have approximately 1,000 to 1,500 times the potency of morphine in animals.
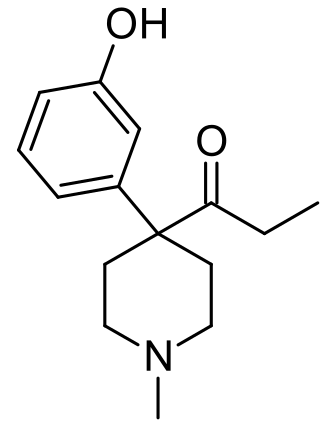
Ketobemidone, sold under the brand name Ketogan among others, is a powerful synthetic opioid painkiller. Its effectiveness against pain is in the same range as morphine, and it also has some NMDA-antagonist properties imparted, in part, by its metabolite norketobemidone. This may make it useful for some types of pain that do not respond well to other opioids. It is marketed in Denmark, Iceland, Norway. Until 2024 it was available in, but is now withdrawn in Sweden. It is used for severe pain.

Benzylmorphine (Peronine) is a semi-synthetic opioid narcotic introduced to the international market in 1896 and that of the United States very shortly thereafter. It is much like codeine, containing a benzyl group attached to the morphine molecule just as the methyl group creates codeine and the ethyl group creates ethylmorphine or dionine. It is about 90% as strong as codeine by weight.

MCOPPB is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, with a pKi of 10.07 and much weaker activity at other opioid receptors. It has only moderate affinity for the mu opioid receptor, weak affinity for the kappa opioid receptor and negligible binding at the delta opioid receptor. In animal studies, MCOPPB produces potent anxiolytic effects, with no inhibition of memory or motor function, and only slight sedative side effects which do not appear until much higher doses than the effective anxiolytic dose range.

Metonitazene is an analgesic compound related to etonitazene, which was first reported in 1957, and has been shown to have approximately 1000 times the potency of morphine by central routes of administration, but if used orally it has been shown to have approximately 10 times the potency of morphine.

Isotonitazene is a benzimidazole-derived opioid analgesic drug related to etonitazene, which has been sold as a designer drug. It has only around half the potency of etonitazene in animal studies, but it is likely even less potent in humans as was seen with etonitazene. Isotonitazene was fully characterized in November 2019 in a paper where the authors performed a full analytical structure elucidation in addition to determination of the potency at the μ-opioid receptor using a biological functional assay in vitro. While isotonitazene was not compared directly to morphine in this assay, it was found to be around 2.5 times more potent than hydromorphone and slightly more potent than fentanyl.

Etodesnitazene is a benzimidazole-derived opioid analgesic drug, which was originally developed in the late 1950s alongside etonitazene and a range of related derivatives. It is many times less potent than etonitazene itself, but still 70 times more potent than morphine in animal studies. Corresponding analogues where the N,N-diethyl group is replaced by piperidine or pyrrolidine rings also retain significant activity. Etodesnitazene has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in both Poland and Finland in March 2020.
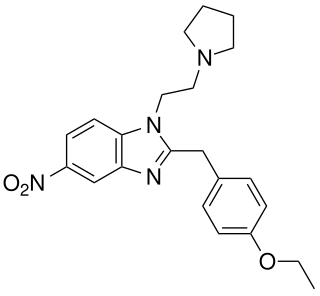
Etonitazepyne is a benzimidazole derivative with potent opioid effects which has been sold over the internet as a designer drug and linked to numerous cases of overdose.

Etonitazepipne is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects around 100 times more potent than morphine, which has been sold over the internet as a designer drug.
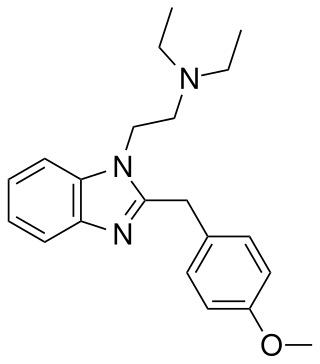
Metodesnitazene is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, though unlike related compounds such as metonitazene and etodesnitazene which are quite potent, metodesnitazene is only around the same potency as morphine in animal studies. It is illegal in both the US and UK.

Etomethazene (5-methyldesnitroetonitazene, 5-methyl etodesnitazene, Eto) is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects which has been sold as a designer drug over the internet since 2022, first being definitively identified in Sweden in January 2023. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the nitro (NO2) group has been replaced by a methyl (CH3) group. While formal studies into its pharmacology have yet to be carried out, it showed far less potency than etonitazene itself. Etomethazene has an analgesic potency around 20 times that of morphine with a relatively short duration of about 120 min.

Protonitazepyne is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, which has been sold as a designer drug over the internet, first being mentioned in mid 2022 and definitively identified in drug seizures in Canada in early 2023 and Ireland in late 2023. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the ethoxy group has been extended to propoxy, and the N,N-diethyl substitution has been cyclised into a pyrrolidine ring. While formal studies into its pharmacology have yet to be carried out, it is believed to be slightly less potent than the ethoxy analogue etonitazepyne but still a potent opioid.
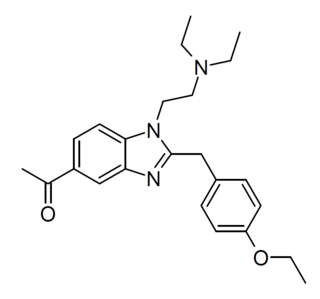
Etonitazene 5-acetyl analogue (Etoacetazene, 5-acetyldesnitroetonitazene) is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, first developed in the 1950s as part of the research that led to better-known compounds such as etonitazene. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the 5-nitro (NO2) group has been replaced by an acetyl (COCH3) group. It is described as having "reduced but still significant" potency compared to etonitazene itself. This compound was also tested as part of a series of cannabinoid receptor 2 agonists, and was found to be active though with fairly low potency of 960 nM at CB2, and negligible activity at CB1.

Etonitazene 5-cyano analogue (Etocyanazene, 5-cyanodesnitroetonitazene) is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, first developed in the 1950s as part of the research that led to better-known compounds such as etonitazene. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the 5-nitro (NO2) group has been replaced by a nitrile (C≡N) group. It is described as having "reduced but still significant" potency compared to etonitazene itself. It was made illegal in Germany in July 2021.
Etoetonitazene is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, first developed in the 1950s as part of the research that led to better-known compounds such as etonitazene. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the ethoxy sidechain has been extended to ethoxyethoxy. It is less potent than other benzimidazole class opioids, but is still a potent mu opioid receptor agonist with around 50x the potency of morphine, and has been sold as a designer drug since around 2022.

Flunitazene (Fluonitazene) is a benzimidazole derivative with opioid effects, first developed in the 1950s as part of the research that led to better-known compounds such as etonitazene. It is one of the least potent derivatives from this class to have appeared as a designer drug, with only around the same potency as morphine, but nevertheless has been sold since around 2020, and has been linked to numerous drug overdose cases.

Isotonitazepyne is a benzimidazole derivative with potent opioid effects, which has been sold as a designer drug over the internet. It has since been identified by the drug checking service CanTEST, in Canberra Australia, and tentatively in New Zealand. It's in vitro potency is approximately 1000 times that of morphine. It is specifically listed as an illegal drug in the US state of Virginia.

Ethyleneoxynitazene (Tetrahydrofuranitazene) is a benzimidazole derivative which has been sold as a designer drug over the internet and presumably has opioid effects. It is an analogue of etonitazene where the 4-ethoxy group attached to the benzyl ring has been cyclised round to the 3-position to form a 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran ring system. It was first reported in Estonia in February 2023, subsequently in the UK in late 2023 and in China July 1st.



















