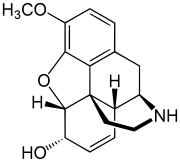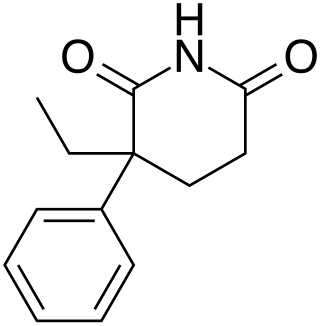
Glutethimide is a hypnotic sedative that was introduced by Ciba in 1954 as a safe alternative to barbiturates to treat insomnia. Before long, however, it had become clear that glutethimide was just as likely to cause addiction and caused similar withdrawal symptoms. Doriden was the brand-name version. Current production levels in the United States point to its use only in small-scale research. Manufacturing of the drug was discontinued in the US in 1993 and discontinued in several eastern European countries in 2006.

Ethylmorphine is an opioid analgesic and antitussive.
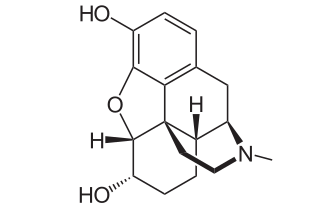
Dihydromorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid structurally related to and derived from morphine. The 7,8-double bond in morphine is reduced to a single bond to get dihydromorphine. Dihydromorphine is a moderately strong analgesic and is used clinically in the treatment of pain and also is an active metabolite of the analgesic opioid drug dihydrocodeine. Dihydromorphine occurs in trace quantities in assays of opium on occasion, as does dihydrocodeine, dihydrothebaine, tetrahydrothebaine, etc. The process for manufacturing dihydromorphine from morphine for pharmaceutical use was developed in Germany in the late 19th century, with the synthesis being published in 1900 and the drug introduced clinically as Paramorfan shortly thereafter. A high-yield synthesis from tetrahydrothebaine was later developed.
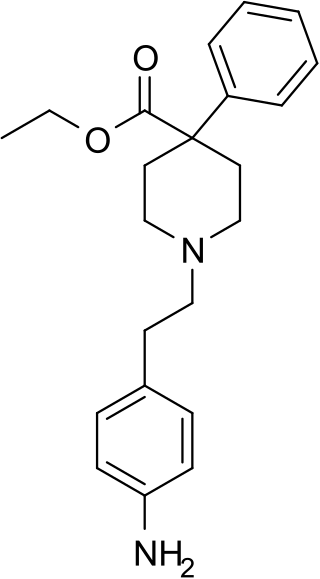
Anileridine is a synthetic analgesic drug and is a member of the piperidine class of analgesic agents developed by Merck & Co. in the 1950s. It differs from pethidine (meperidine) in that the N-methyl group of meperidine is replaced by an N-aminophenethyl group, which increases its analgesic activity.

Methorphan comes in two isomeric forms, each with differing pharmacology and effects:

Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine.

Nicocodeine is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were synthesized in 1904, and introduced in 1957 by Lannacher Heilmittel of Austria. Nicocodeine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce nicomorphine, also known as 6-nicotinoylmorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to morphine. Side effects are similar to those of other opiates and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression. Related opioid analogues such as nicomorphine and nicodicodeine were first synthesized. The definitive synthesis, which involves treating anhydrous codeine base with nicotinic anhydride at 130 °C, was published by Pongratz and Zirm in Monatshefte für Chemie in 1957, simultaneously with the two analogues in an article about amides and esters of various organic acids.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Ethylmethylthiambutene (N-ethyl-N-methyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine; Emethibutin) is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, around 1.3x the potency of morphine. It is under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential.
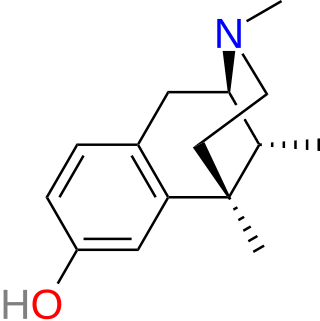
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.
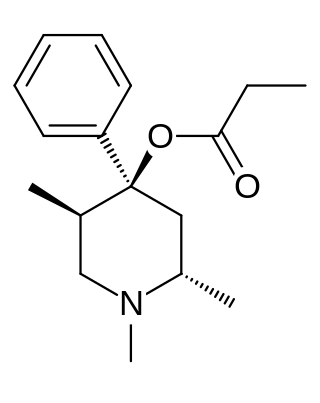
Trimeperidine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.
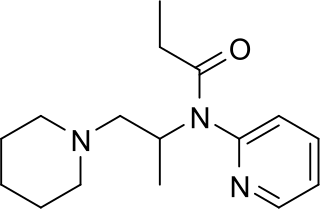
Propiram is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist and weak μ antagonist analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs related to other drugs such as phenampromide and diampromide. It was invented in 1963 in the United Kingdom by Bayer but was not widely marketed, although it saw some limited clinical use, especially in dentistry. Propiram reached Phase III clinical trials in the United States and Canada.

Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid Co. Although never given a general release, it was research found that 60 mg of phenampromide is equivalent to about 50 mg of codeine. Tests on its two enantiomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S)-isomer. Introduction of a phenyl group to the 4-position of the piperidine-ring produces a drug 60-fold more potent than morphine. The most potent reported derivative is 4-hydroxy-4-phenyl phenapromide which displays analgesic activity some x150 greater than morphine.

Dimenoxadol (INN), or dimenoxadole (BAN), is an opioid analgesic which is a benzilic acid derivative, closely related to benactyzine. Further, the structure is similar to methadone and related compounds like dextropropoxyphene.

Drotebanol (Oxymethebanol) is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It was invented by Sankyo Company in Japan during the 1970s. It is synthesised from thebaine.

Normorphine is an opiate analogue, the N-demethylated derivative of morphine, that was first described in the 1950s when a large group of N-substituted morphine analogues were characterized for activity. The compound has relatively little opioid activity in its own right, but is a useful intermediate which can be used to produce both opioid antagonists such as nalorphine, and also potent opioid agonists such as N-phenethylnormorphine. with its formation from morphine catalyzed by the liver enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2C8.

Racemorphan, or morphanol, is the racemic mixture of the two stereoisomers of 17-methylmorphinan-3-ol, each with differing pharmacology and effects:

Isomethadone (INN, BAN; trade name Liden; also known as isoamidone) is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive related to methadone that was used formerly as a pharmaceutical drug but is now no longer marketed. Isomethadone was used as both an analgesic and antitussive. It binds to and activates both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with the (S)-isomer being the more potent of the two enantiomers. Isomethadone is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States, with an ACSCN of 9226 and a 2014 aggregate manufacturing quota of 5 g. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (HBr, free base conversion ratio 0.793), hydrochloride (HCl, 0.894), and HCl monohydrate (0.850). Isomethadone is also regulated internationally as a Schedule I controlled substance under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961.

Morphine-N-oxide (genomorphine) is an active opioid metabolite of morphine. Morphine itself, in trials with rats, is 11–22 times more potent than morphine-N-oxide subcutaneously and 39–89 times more potent intraperitoneally. However, pretreatment with amiphenazole or tacrine increases the potency of morphine-N-oxide in relation to morphine. A possible explanation is that morphine-N-oxide is rapidly inactivated in the liver and impairment of inactivation processes or enzymes increases functionality.

Noracymethadol (INN) is a synthetic opioid analgesic related to methadone that was never marketed. In a clinical trial of postpartum patients it was reported to produce analgesia comparable to that of morphine but with less nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. Other side effects included salivation, ataxia, and respiratory depression that was reversible by naloxone. Similarly to many of its analogues, noracymethadol is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States with an ACSCN of 9633 and 2013 annual manufacturing quota of 12 grammes. and is also controlled internationally under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961. The salts known are the gluconate and hydrochloride (0.903).