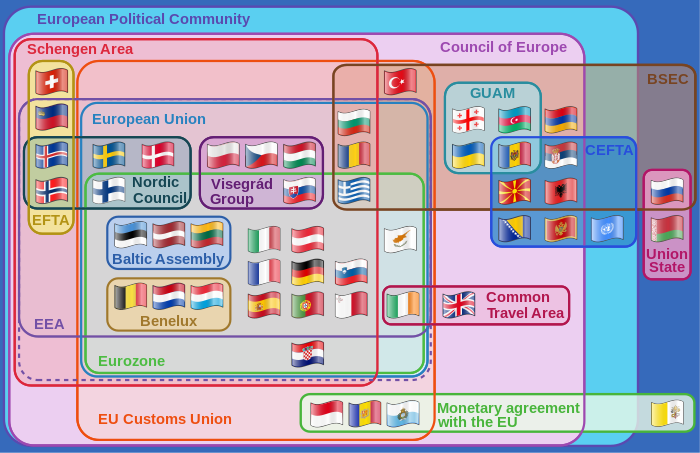
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU), and all four member states participate in the European single market and are part of the Schengen Area. They are not, however, party to the European Union Customs Union.
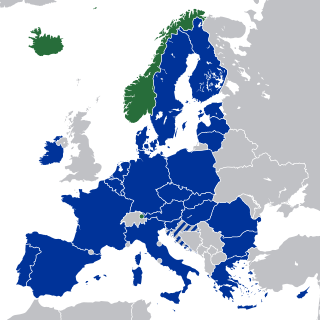
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). The EEA links the EU member states and three of the four EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. New members of EFTA would not automatically become party to the EEA Agreement, as each EFTA State decides on its own whether it applies to be party to the EEA Agreement or not. According to Article 128 of the EEA Agreement, "any European State becoming a member of the Community shall, and the Swiss Confederation or any European State becoming a member of EFTA may, apply to become a party to this Agreement. It shall address its application to the EEA Council." EFTA does not envisage political integration. It does not issue legislation, nor does it establish a customs union. Schengen is not a part of the EEA Agreement. However, all of the four EFTA States participate in Schengen and Dublin through bilateral agreements. They all apply the provisions of the relevant Acquis.
The European Union has a number of relationships with foreign states. According to the European Union's official site, and a statement by Commissioner Günter Verheugen, the aim is to have a ring of countries, sharing EU's democratic ideals and joining them in further integration without necessarily becoming full member states.
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union and its policies.
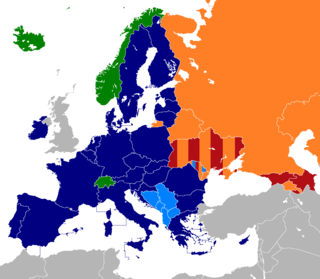
At present, there are six multi-lateral free trade areas in Europe, and one former free trade area in recent history. Note that there are also a number of bilateral free trade agreements between states and between trade blocks; and that some states participate in more than one free trade area.

A customs union is the principal area of robust formal agreement between the Principality of Andorra and the European Union (EU). Andorra borders two EU member states: France and Spain.

The visa policy of the Schengen Area is a component within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union. It applies to the Schengen Area and to other EU member states except Ireland. The visa policy allows nationals of certain countries to enter the Schengen Area via air, land or sea without a visa for up to 90 days within any 180-day period. Nationals of certain other countries are required to have a visa to enter and, in some cases, transit through the Schengen area.
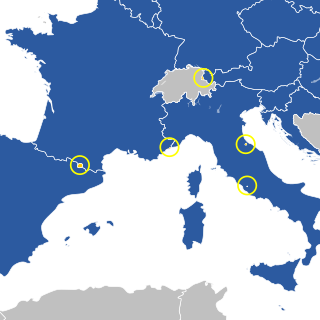
Currently, all of the European microstates have some form of relations with the European Union (EU).

The Citizens' Rights Directive 2004/38/EC sets out the conditions for the exercise of the right of free movement for citizens of the European Economic Area (EEA), which includes the member states of the European Union (EU) and the three European Free Trade Association (EFTA) members Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein. Switzerland, which is a member of EFTA but not of the EEA, is not bound by the Directive but rather has a separate multilateral sectoral agreement on free movement with the EU and its member states.

Liechtenstein passports are issued to nationals of Liechtenstein for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Liechtenstein citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Liechtenstein consular officials abroad.

The European Union Customs Union (EUCU), formally known as the Community Customs Union, is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia. Some detached territories of EU states do not participate in the customs union, usually as a result of their geographic separation. In addition to the EUCU, the EU is in customs unions with Andorra, San Marino and Turkey, through separate bilateral agreements.

The Schengen Area is an area encompassing 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.
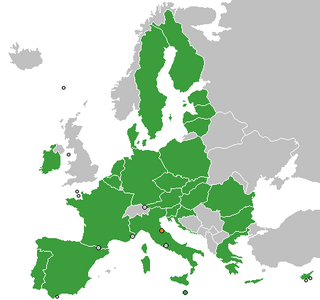
Relations between the Republic of San Marino and the European Union (EU) began in February 1983. San Marino is completely surrounded by one EU member state, Italy.

Relations between the Principality of Monaco and the European Union (EU) are primarily conducted through France. Through that relationship Monaco directly participates in certain EU policies. Monaco is an integral part of the EU customs territory and VAT area, and therefore applies most measures on excise duties and VAT. Monaco borders one EU member state: France. However this relationship does not extend to external trade. Preferential trade agreements between the EU and third countries apply only to goods originating from the customs territory – Monaco may not claim EU origin in this respect.

National identity cards are identity documents issued to citizens of most European Union and European Economic Area (EEA) member states, with the exception of Denmark and Ireland. As a new common identity card model replaced the various formats in use from 2 August 2021, recently issued ID cards are harmonized across the EEA, while older ID cards are currently being phased out according to Regulation (EU) 2019/1157.

The United Kingdom (UK) was a member of the European Economic Area (EEA) from 1 January 1994 to 31 December 2020, following the coming into force of the 1992 EEA Agreement. Membership of the EEA is a consequence of membership of the European Union (EU). The UK ceased to be a Contracting Party to the EEA Agreement after its withdrawal from the EU on 31 January 2020, as it was a member of the EEA by virtue of its EU membership, but retained EEA rights during the Brexit transition period, based on Article 126 of the withdrawal agreement between the EU and the UK. During the transition period, which ended on 31 December 2020, the UK and EU negotiated their future relationship.

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.
In British politics, the "Norway-plus model" was a proposal for a post-Brexit settlement, which the British government did not pursue. Proposed in November 2018 as an alternative to the Chequers plan, it would have consisted of membership of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and of membership of the European Economic Area (EEA) as an EFTA member state, combined with a separate customs union with the EU to create a trade relationship similar to that between the EU and its member states today, with the exception of the political representation in the EU's bodies. Michel Barnier, the EU's Chief Negotiator, has always said that a model that combined EEA/EFTA and a customs union was one that he would be happy to consider.

Passports in Europe are issued by each state individually, e.g. the Netherlands or United Kingdom. In general, passports issued in Europe either grant the holder the right of freedom of movement within the European Economic Area, to those that don't. The majority of European states are members of the European Union, and therefore issue EU passports.