Pseudoviridae is a family of viruses, which includes the following genera:
Caulimoviridae is a family of viruses infecting plants. There are currently 85 species in this family, divided among 10 genera. Viruses belonging to the family Caulimoviridae are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses i.e. viruses that contain a reverse transcription stage in their replication cycle. This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle.
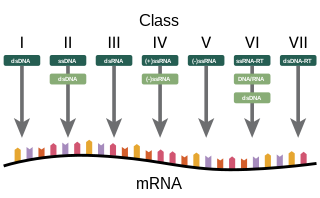
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.
Cypovirus, short for cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus, is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Spinareovirinae. Cypoviruses have only been isolated from insects. Diseases associated with this genus include: larvae chronic disease. There are currently 16 species in this genus including the type species Cypovirus 1.

Iltovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. Birds, galliform birds, psittacine birds, chickens, turkeys, and quail serve as natural hosts. There are currently only two species in this genus including the type species Gallid alphaherpesvirus 1. Diseases associated with this genus include: acute respiratory diseases: gaHV-1: infectious laryngotracheitis; psHV-1: Pacheco's disease.
Proboscivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Elephants serve as natural hosts. The type species is Elephantid betaherpesvirus 1. EEHV1 is apathogenic for African elephants but causes fatal haemorrhagic disease in Asian elephants. The name "Proboscivirus" comes from the Greek word προβοσκίς or "proboscis" meaning "the elephant trunk," for which the virus accordingly uses as its means of contraction and transmission to enter the elephant's body.
Babuvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Nanoviridae. Musa species serve as natural hosts. There are currently three species in this genus including the type species Banana bunchy top virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: stunting, severe necrosis and early plant death. BBTV induces banana bunchy top disease (BBTD).
Badnavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 59 species in this genus including the type species Commelina yellow mottle virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: CSSV: leaf chlorosis, root necrosis, red vein banding in young leaves, small mottled pods, and stem/root swelling followed by die-back. Infection decreases yield by 25% within one year, 50% within two years and usually kills trees within 3–4 years.

Caulimovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 13 species in this genus including the type species Cauliflower mosaic virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.
Cavemovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently only two species in this genus including the type species Cassava vein mosaic virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.
Epsilonpapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Cattle serve as natural hosts and it is one of the bovine papillomaviruses. There are currently two species in this genus, including the type species Epsilonpapillomavirus 1. Diseases associated with this genus include: fibropapillomas and true epithelial papillomas of the skin.
Iotapapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Rodents serve as natural hosts. There are currently two species in this genus, including the type species Iotapapillomavirus 1. Diseases associated with this genus include: cutaneous lesions and benign skin tumours, such as papillomas and keratoacanthomas.
Kappapapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Rabbits serve as natural hosts. There are currently only two species in this genus including the type species Kappapapillomavirus 2. Diseases associated with this genus include: cutaneous and mucosal lesions.
Nupapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Humans serve as natural hosts. There is currently only one species in this genus: the type species Nupapillomavirus 1. Diseases associated with this genus include: facial warts. It has also been detected in some skin carcinomas and premalignant keratoses.
Percavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are currently six species in this genus including the type species Equid gammaherpesvirus 2. Diseases associated with this genus include: conjunctivitis, immunosuppression in foals, pneumonia, respiratory disease.
Siadenovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Adenoviridae. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. There are currently six species in this genus including the type species Frog siadenovirus A.
Soymovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Soybean chlorotic mottle virus.
Tungrovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Monocots and family Poaceae serve as natural hosts. There is currently only one species in this genus: the type species Rice tungro bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: stunting, yellow to orange leaf discoloration with fewer tillers. Tungro means 'degenerated growth' in a Filipino dialect and the virus was first observed in the Philippines 1975.
Xipapillomavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Papillomaviridae. Bovine serve as natural hosts. There are currently five species in this genus including the type species Xipapillomavirus 1. Diseases associated with this genus include: true papillomas on the cutaneous or mucosal surfaces of cattle.
Solendovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently only two species in this genus, including the type species Tobacco vein clearing virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: TVCV: vein-clearing symptoms in N. edwardsonii.



