
In amniotes, the clitoris is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.
Orgasm or sexual climax is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region. Orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system and experienced by both males and females; the body's response includes muscular spasms, a general euphoric sensation, and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm is typically a relaxing experience after the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin, as well as endorphins.

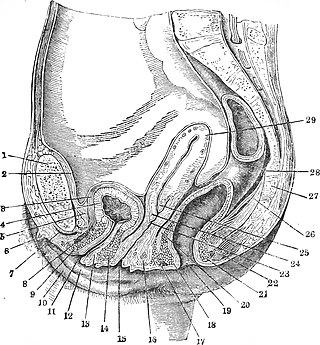
In mammals and other animals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix. The vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for copulation and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle.

The G-spot, also called the Gräfenberg spot, is characterized as an erogenous area of the vagina that, when stimulated, may lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and potential female ejaculation. It is typically reported to be located 5–8 cm (2–3 in) up the front (anterior) vaginal wall between the vaginal opening and the urethra and is a sensitive area that may be part of the female prostate.

The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.

The missionary position or man-on-top position is a sex position in which, generally, a woman lies on her back and spreads her legs and a man lies on top of her while they face each other and engage in vaginal intercourse. The position may also be used for other sexual activity, such as anal sex. It is commonly associated with heterosexual sexual activity, but is also used by same-sex couples. It may involve sexual penetration or non-penetrative sex, and its penile-vaginal aspect is an example of ventro-ventral (front-to-front) reproductive activity. Variations of the position allow varying degrees of clitoral stimulation, depth of penetration, participation on the part of the woman, and the likelihood and speed of orgasm.

Vaginismus is a condition in which involuntary muscle spasm interferes with vaginal intercourse or other penetration of the vagina. This often results in pain with attempts at sex. Often it begins when vaginal intercourse is first attempted. Vaginismus may be considered an older term for pelvic floor dysfunction.

An erogenous zone is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response such as relaxation, sexual fantasies, sexual arousal, and orgasm.

Kegel exercise, also known as pelvic floor exercise, involves repeatedly contracting and relaxing the muscles that form part of the pelvic floor, now sometimes colloquially referred to as the "Kegel muscles". The exercise can be performed many times a day, for several minutes at a time but takes one to three months to begin to have an effect.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.
The human sexual response cycle is a four-stage model of physiological responses to sexual stimulation, which, in order of their occurrence, are the excitement, plateau, orgasmic, and resolution phases. This physiological response model was first formulated by William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson, in their 1966 book Human Sexual Response. Since that time, other models regarding human sexual response have been formulated by several scholars who have criticized certain inaccuracies in the human sexual response cycle model.
The urethral sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue, found in the lower genital area of females, that sits against both the pubic bone and vaginal wall, and surrounds the urethra.

Ben Wa balls, also known as orgasm balls, rin-no-tama, Venus balls, or mien-ling, are marble-sized balls, usually hollow and containing a small weight, that may be inserted into a female’s vagina, and held in place by the pubococcygeus muscles. They may be used as a sex toy by creating sexual stimulation or pleasure by rolling around in the vagina stimulating movement and/or vibration. They create a subtle stimulation that do not bring the user to immediate orgasm but rather to tease.

Fingering is sexual stimulation of the vulva or vagina by using the fingers. Vaginal fingering is legally and medically called digital penetration or digital penetration of the vagina. The term "digital" takes its significance from the English word 'digit', which refers to a finger, thumb, or toe. Fingering may also include the use of fingers to stimulate the anus.

A forced orgasm is consensual BDSM or kinky sexual play whereby a person consents to be forced to orgasm in a way that is beyond their control.

A G-spot vibrator is a sex toy with female and male varieties. The female version of the device is built to massage the G-spot, described as a bean-shaped area of the vagina. Some women report that it is an erogenous zone which, when stimulated, can lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and female ejaculation. The male version of the G-spot vibrator is used for massaging the prostate for both sexual and health-related reasons.

Non-penetrative sex or outercourse is sexual activity that usually does not include sexual penetration, but some forms, particularly when termed outercourse, include penetrative aspects, that may result from forms of fingering or oral sex. It generally excludes the penetrative aspects of vaginal, anal, or oral sex, but includes various forms of sexual and non-sexual activity, such as frottage, manual sex, mutual masturbation, kissing, or hugging.

Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle.
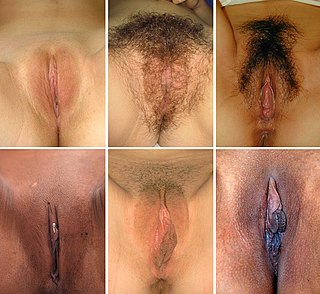
In mammals, the vulva comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands. The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.

Penile–vaginal intercourse, or vaginal intercourse, is a form of penetrative sexual intercourse in human sexuality, in which an erect penis is inserted into a vagina. Synonyms are: vaginal sex, cohabitation, coitus, intimacy, or (poetic) lovemaking. It corresponds to mating or copulation in non-human animals.



















