
On the Consolation of Philosophy, often titled as The Consolation of Philosophy or simply the Consolation, is a philosophical work by the Roman philosopher Boethius. Written in 523 while he was imprisoned and awaiting execution by the Ostrogothic King Theodoric, it is often described as the last great Western work of the Classical Period. Boethius' Consolation heavily influenced the philosophy of late antiquity, as well as Medieval and early Renaissance Christianity.

Geoffrey Chaucer was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for The Canterbury Tales. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He was the first writer to be buried in what has since come to be called Poets' Corner, in Westminster Abbey. Chaucer also gained fame as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific A Treatise on the Astrolabe for his 10-year-old son, Lewis. He maintained a career in the civil service as a bureaucrat, courtier, diplomat, and member of parliament.

Tyche was the presiding tutelary deity who governed the fortune and prosperity of a city, its destiny. In Classical Greek mythology, she is usually the daughter of the Titans Tethys and Oceanus, or sometimes Zeus, and at this time served to bring positive messages to people, relating to external events outside their control.

Guinevere, also often written in Modern English as Guenevere or Guenever, was, according to Arthurian legend, an early-medieval queen of Great Britain and the wife of King Arthur. First mentioned in literature in the early 12th century, nearly 700 years after the purported times of Arthur, Guinevere has since been portrayed as everything from a fatally flawed, villainous, and opportunistic traitor to a noble and virtuous lady. The variably told motif of abduction of Guinevere, or of her being rescued from some other peril, features recurrently and prominently in many versions of the legend.

The Lady of the Lake is a title used by multiple characters in the Matter of Britain, the body of medieval literature and mythology associated with the legend of King Arthur. As either actually fairy or fairy-like yet human enchantresses, they play important roles in various stories, notably by providing Arthur with the sword Excalibur, eliminating the wizard Merlin, raising the knight Lancelot after the death of his father, and helping to take the dying Arthur to Avalon after his final battle. Different Ladies of the Lake appear concurrently as separate characters in some versions of the legend since at least the Post-Vulgate Cycle and consequently the seminal Le Morte d'Arthur, with the latter describing them as members of a hierarchical group, while some texts also give this title to either Morgan or her sister.

Morgan le Fay, alternatively known as Morgan[n]a, Morgain[a/e], Morgant[e], Morg[a]ne, Morgayn[e], Morgein[e], and Morgue[in] among other names and spellings, is a powerful and ambiguous enchantress from the legend of King Arthur, in which most often she and he are siblings. Early appearances of Morgan in Arthurian literature do not elaborate her character beyond her role as a goddess, a fay, a witch, or a sorceress, generally benevolent and connected to Arthur as his magical saviour and protector. Her prominence increased as the legend of Arthur developed over time, as did her moral ambivalence, and in some texts there is an evolutionary transformation of her to an antagonist, particularly as portrayed in cyclical prose such as the Lancelot-Grail and the Post-Vulgate Cycle. A significant aspect in many of Morgan's medieval and later iterations is the unpredictable duality of her nature, with potential for both good and evil.

"The Knight's Tale" is the first tale from Geoffrey Chaucer's The Canterbury Tales.

"The Merchant's Tale" is one of Geoffrey Chaucer's Canterbury Tales. In it Chaucer subtly mocks antifeminist literature like that of Theophrastus ("Theofraste"). The tale also shows the influence of Boccaccio, Deschamps' Le Miroir de Mariage, Roman de la Rose by Guillaume de Lorris, Andreas Capellanus, Statius, and Cato. The tale is found in Persia in the Bahar Danush, in which the husband climbs a date tree instead of a pear tree. It could have arrived in Europe through the One Thousand and One Nights, or perhaps the version in book VI of the Masnavi by Rumi. Though several of the tales are sexually explicit by modern standards, this one is especially so. Larry Benson remarks:
The central episode of the Merchant's Tale is like a fabliau, though of a very unusual sort: It is cast in the high style, and some of the scenes are among Chaucer's most elaborate displays of rhetorical art.

Le Morte d'Arthur is a 15th-century Middle English prose reworking by Sir Thomas Malory of tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table, along with their respective folklore. In order to tell a "complete" story of Arthur from his conception to his death, Malory compiled, rearranged, interpreted and modified material from various French and English sources. Today, this is one of the best-known works of Arthurian literature. Many authors since the 19th-century revival of the legend have used Malory as their principal source.
Destiny, sometimes also called fate, is a predetermined course of events. It may be conceived as a predetermined future, whether in general or of an individual.

Fortuna is the goddess of fortune and the personification of luck in Roman religion who, largely thanks to the Late Antique author Boethius, remained popular through the Middle Ages until at least the Renaissance. The blindfolded depiction of her is still an important figure in many aspects of today's Italian culture, where the dichotomy fortuna / sfortuna plays a prominent role in everyday social life, also represented by the very common refrain "La [dea] fortuna è cieca".

Troilus and Criseyde is an epic poem by Geoffrey Chaucer which re-tells in Middle English the tragic story of the lovers Troilus and Criseyde set against a backdrop of war during the siege of Troy. It was written in rime royale and probably completed during the mid-1380s. Many Chaucer scholars regard it as the poet's finest work. As a finished long poem, it is more self-contained than the better known but ultimately unfinished The Canterbury Tales. This poem is often considered the source of the phrase: "all good things must come to an end" (3.615).

Troilus is a legendary character associated with the story of the Trojan War. The first surviving reference to him is in Homer's Iliad, composed in the late 8th century BC.
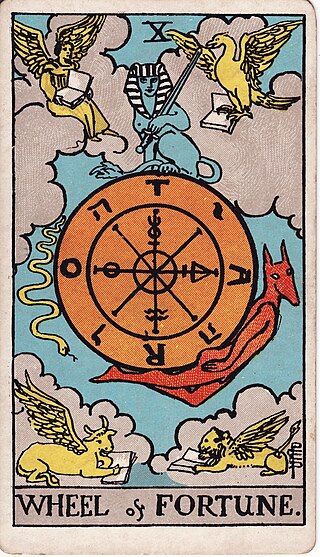
Wheel of Fortune is one of 78 cards in a tarot deck and is the tenth trump or Major Arcana card in most tarot decks. It is used in game playing as well as in divination.
Elizabeth Helen Cooper,, known as Helen Cooper, is a British literary scholar. From 2004 to 2014, she was Professor of Medieval and Renaissance English at the University of Cambridge, and a fellow of Magdalene College, Cambridge.

The Kingis Quair is a fifteenth-century Early Scots poem attributed to James I of Scotland. It is semi-autobiographical in nature, describing the King's capture by the English in 1406 on his way to France and his subsequent imprisonment by Henry IV of England and his successors, Henry V and Henry VI.

"O Fortuna" is a medieval Latin Goliardic poem which is part of the collection known as the Carmina Burana, written in the early 13th century. It is a complaint about Fortuna, the inexorable fate that rules both gods and mortals in Roman mythology.
In the time of William Shakespeare, there were commonly reckoned to be five wits and five senses. The five wits were sometimes taken to be synonymous with the five senses, but were otherwise also known and regarded as the five inward wits, distinguishing them from the five senses, which were the five outward wits.
A gubernaculum in classical references describes a ship's rudder or steering oar. The English word government is related to the word. The Old English word governail and the Scots word gouernaill are both derived from it.

"O Fortuna" is a movement in Carl Orff's 1935–36 cantata Carmina Burana. It begins the opening and closing sections, both titled "Fortuna Imperatrix Mundi". The cantata is based on a medieval Goliardic poetry collection of the same name, from which the poem "O Fortuna" provides the words sung in the movement. It was well-received during its time, and entered popular culture through use in other musical works, advertisements, and soundtracks beginning in the late 20th century.























