| |||||||||||||||||
Massachusetts's 10th congressional district | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on August 25, 1800, and October 20, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Samuel Sewall (F). [1]
| |||||||||||||||||
Massachusetts's 10th congressional district | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Massachusetts |
|---|
 |
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on August 25, 1800, and October 20, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Samuel Sewall (F). [1]
Massachusetts electoral law required a majority for election, which was not met on the first election, necessitating a second election.
| Candidate | Party | First trial [2] | Second trial [3] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | Percent | Votes | Percent | ||
| Nathan Read | Federalist | 803 | 45.3% | 1,567 | 53.5% |
| Jacob Crowninshield | Democratic-Republican | 873 | 49.2% | 1,364 | 46.5% |
| Scattering | 97 | 5.5% | |||
Read took his seat on November 25, 1800 [1]
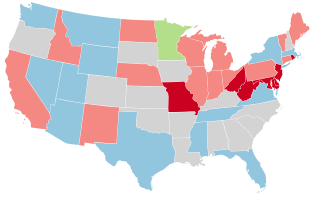
The 1928 United States Senate elections were elections that coincided with the presidential election of Republican Herbert Hoover. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The strong economy helped the Republicans to gain seven seats from the Democrats.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.
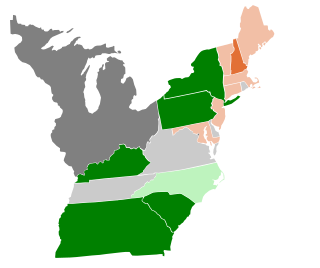
The 1800–01 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with Thomas Jefferson being elected to the White House. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1800 and 1801, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 1st congressional district on September 5, 1796, and November 21, 1796, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of Theodore Sedgwick (F) upon his election to the Senate
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on August 1, 1796, and September 12, 1796, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Benjamin Goodhue (F) in June, 1796. Goodhue had resigned upon being elected to the Senate.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 11th congressional district on August 4, 1797, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Theophilus Bradbury (F) upon his appointment to the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court on July 24, 1797.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 3rd congressional district on December 15, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Samuel Lyman (F) on November 6, 1800.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 4th congressional district on August 25, 1800, and October 20, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Dwight Foster (F) after his election to the Senate, the second election required because the first did not result in a majority.
A special election was held in New Hampshire's at-large congressional district on August 25, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by William Gordon (F) resigning to accept an appointment as New Hampshire Attorney General on June 12, 1800.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 12th congressional district on five occasions between September 25, 1801, and July 29, 1802, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Silas Lee (F) on August 20, 1801, prior to the beginning of the 1st Session of the 7th Congress.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 14th congressional district to fill the vacancy left by George Thatcher (F) declining to serve a 7th term, having served continuously since the 1st Congress and, after the death of Thomas Hartley (F) in Pennsylvania's 8th congressional district on December 21, 1800, the last remaining member of the 1st Congress to have continuously served in the House. The election was held on June 22, 1801
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on October 8, 1810, to have Joseph Allen (F) fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Jabez Upham (F).
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 11th congressional district on October 8, 1810, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of William Stedman (F) on July 16, 1810.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 4th congressional district on September 23, 1811, and November 4, 1811, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Joseph Bradley Varnum (DR) upon being elected to the Senate on June 29, 1811
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 17th congressional district on April 6, 1812, to fill the vacancy left by the resignation of Barzillai Gannett (DR) who resigned sometime in 1812 without having served.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 4th congressional district on May 23, 1814, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of William M. Richardson (DR) on April 18, 1814.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 11th congressional district on August 26, 1816, to fill a vacancy left by the death of Elijah Brigham (F) on February 22, 1816.
A special election was held August 26, 1817 in Massachusetts's 1st congressional district to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Representative-elect James Lloyd (F) before the beginning of the 15th Congress.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on September 8, 1823, to fill a vacancy created by the resignation of William Eustis (DR) prior to the start of the 18th Congress.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district to fill a vacancy caused by John Bailey (DR) being declared not eligible for the seat which he had won the previous year on March 24, 1824. The election was held on August 30, 1824, with additional ballots held on November 1 and November 29 due to a majority not being achieved on the first or second ballot.