The 1850–51 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 5, 1850, and November 4, 1851. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 32nd United States Congress convened on December 1, 1851. Elections were held for all 233 seats, representing 31 states.
The 1848–49 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 1848 and November 1849. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 31st United States Congress convened on December 3, 1849. The new state of Wisconsin elected its first representatives, and California also held its first congressional elections before officially achieving statehood in 1850, increasing the size of the House to 233 seats.
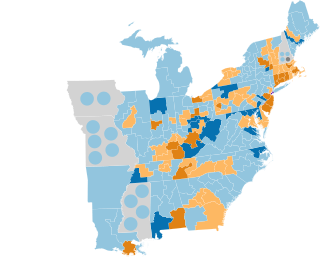
The 1844–45 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1844, and November 4, 1845. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 224 elected members representing 27 states took their seats when the first session of the 29th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1845. The new state of Florida elected its first representative during this election cycle, while one vacancy in New Hampshire's delegation remained unfilled for the duration of the 29th Congress.

The 1842–43 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 1, 1842, and November 8, 1843. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 28th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1843. The exception was Maryland, who held theirs so late that they ran into February 1844. These elections occurred during President John Tyler's term. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1840 United States census unusually decreased the number of House seats, from 242 down to 223.
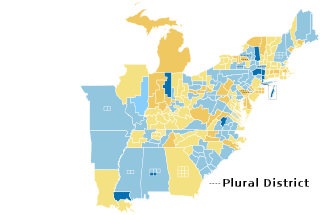
The 1840–41 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 6, 1840, and November 2, 1841. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, before or after the first session of the 27th United States Congress convened on May 31, 1841. Elections were held for all 242 seats, representing 26 states.

The 1838–39 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 2, 1838, and November 5, 1839. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 26th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1839. They occurred during President Martin Van Buren's term. Elections were held for all 242 seats, representing 26 states.

The 1834–35 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1834, and November 5, 1835. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 24th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1835. They were held during President Andrew Jackson's second term. Elections were held for 240 seats that represented 24 states, as well as the at-large-district seat for the pending new state of Michigan.
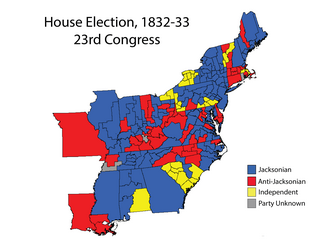
The 1832–33 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 2, 1832, and October 7, 1833. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 23rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1833. They were held concurrently with the 1832 presidential election, in which Democrat Andrew Jackson was reelected. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1830 United States census increased the size of the House to 240 seats.

The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824, and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.
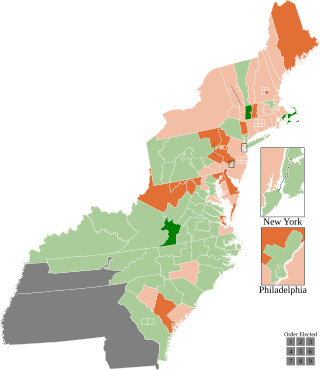
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 3rd congressional district on December 15, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Samuel Lyman (F) on November 6, 1800.

A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district on August 25, 1800, and October 20, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Samuel Sewall (F).
A special election was held in New Hampshire's at-large congressional district on August 25, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by William Gordon (F) resigning to accept an appointment as New Hampshire Attorney General on June 12, 1800.

A special election was held in Virginia's 13th congressional district on July 31, 1800, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation, on June 7, 1800, of John Marshall (F), who was named Secretary of State by President John Adams.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 4th congressional district August 24, 1801 to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of Levi Lincoln Sr. (DR) on March 5, 1801, before the first session of Congress, upon being appointed U.S. Attorney General.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 12th congressional district on five occasions between September 25, 1801, and July 29, 1802, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Silas Lee (F) on August 20, 1801, prior to the beginning of the 1st Session of the 7th Congress.
There were eight special elections to the United States House of Representatives in 1917, during the 64th United States Congress and 65th United States Congress.
There were seven special elections to the United States House of Representatives in 1969 to the 91st United States Congress.












