This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2020) |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Turkish. (March 2017)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Beylik of Aydin Aydınoğulları آیدین اوغوللاری | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1308–1426 | |||||||||
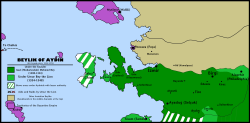 Beylik of Aydın's Map during its peak (1315-1375) highlighting: Borders under Gazi Mehmed Bey Borders after conquests under Umur Bey the Lion Byzantine Empire territories Other Western Anatolian Beyliks Black "X" showing Umur Bey's aids Red "X" showing Umur Bey's raids | |||||||||
| Capital | Birgi, Selçuk | ||||||||
| Common languages | Turkish | ||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||
| Government | Beylik | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Collapse of the Sultanate of Rum | 1308 | ||||||||
• Annexation by the Ottoman Empire | 1426 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Turkey | ||||||||
| History of Turkey |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |

The Aydinids or Aydinid dynasty (Modern Turkish: Aydınoğulları, Aydınoğulları Beyliği, Old Anatolian Turkish: آیدین اوغوللاری بیلیغی, also known as the Principality of Aydin and Beylik of Aydin (Aydın Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks and famous for its seaborne raiding.
