Related Research Articles

Low Saxon, also known as West Low German are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark. It is one of two dialect groups, the other being East Low German.

The Bhil languages are a group of lects spoken by the Bhil that are classified as dialects of Indo-Aryan languages such as Gujarati and Rajasthani. They are spoken by around 10.4 million Bhils in western and central India as of 2011 and constitute the primary languages of the southern Aravalli Range in Rajasthan and the western Satpura Range in Madhya Pradesh, northwestern Maharashtra, and southern Gujarat.
Baga, or Barka, is a dialect cluster spoken by the Baga people of coastal Guinea. The name derives from the phrase bae raka Slaves trading place and understood by the local as 'people of the seaside' outcast people. Most Baga are bilingual in the Mande language Susu, the official regional language. Two ethnically Baga communities, Sobané and Kaloum, are known to have abandoned their (unattested) language altogether in favour of Susu.
Aghu, or Central Awyu, is a Papuan language of South Papua, Indonesia. It may actually be two languages, depending on one's criteria for a 'language'. The two varieties are: Mappi River Awyu (Aghu) and Pasue River Awyu.
North Levantine Arabic was defined in the ISO 639-3 international standard for language codes as a distinct Arabic variety, under the apc code. It was also known as Syro-Lebanese Arabic, though that term was also used to refer to all Levantine Arabic varieties.
South Levantine Arabic was defined in the ISO 639-3 international standard for language codes as a distinct Arabic variety, under the ajp code. It was reported by Ethnologue as being spoken in the Southern Levant: Palestinian Territories, Israel, and most of Jordan.

Bata (Gbwata) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Nigeria in Adamawa State in the Numan, Song, Fufore and Jimeta gire Yola maiha Demsa lamorde LGAs, and in Cameroon in North Province along the border with Nigeria. Dialects are Demsa, Garoua, Jirai, Kobotachi, Malabu, Ndeewe, Ribaw, Wadi, and Zumu (Jimo). It is often considered the same language as Bacama.
The Ngbandi language is a dialect continuum of the Ubangian family spoken by a half-million or so people in the Democratic Republic of Congo and in the Central African Republic. It is primarily spoken by the Ngbandi people, which included the dictator of what was then known as Zaire, Mobutu Sese Seko.

The Sámi languages, also rendered in English as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Indigenous Sámi peoples in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.
Duun is a Mande language of Mali. There are three varieties of Duun, West Duun, or Duungooma and Banka or Bankagooma, in Mali, and East Duun, or Dzùùn(goo), in Burkina Faso. These are clearly distinct but have a reasonable degree of mutual intelligibility with each other.
The Nyangbo-Tafi language is spoken in the Volta Region of Ghana. It is considered one of the Ghana–Togo Mountain languages of the Kwa family.
Kita Maninkakan, or Central Malinke, is a Manding language spoken by about a million people in Mali, where it is a national language. About 10% are ethnically Fula.
Phowa is a dialect cluster of Loloish languages spoken by the Phula people of China. There are three principal varieties, Hlepho, Ani, and Labo, which may be considered distinct languages. Hlepho may be closer to Phukha than it is to Labo and Ani. Usage is decreasing, with about two-thirds of Phowa speaking their language.
Okodia (Okordia), or Akita, is one of three small Inland Ijaw languages of Nigeria. According to Ethnologue, it is not fully intelligible with other varieties of Inland Ijaw.
Mono is a moribund Mbum language spoken by older adults in northern Cameroon.
Geko is a Karen language of Burma. Yinbaw is reportedly a variety. Speakers of Geko and Yinbaw are ethnically Kayan, as are speakers of Lahta and Padaung.
Kyirong is a language from the subgroup of Tibetic languages spoken in the Gyirong County of the Shigatse prefecture, of the Tibetan Autonomous Region.
Gbeya is a Gbaya language of the Central African Republic. Ethnologue reports it may be mutually intelligible with Bozom.
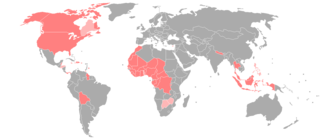
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States, starting as a blend of local sign languages and French Sign Language (FSL). Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.
References
- ↑ Bhilali at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

Rathawi at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)