Related Research Articles
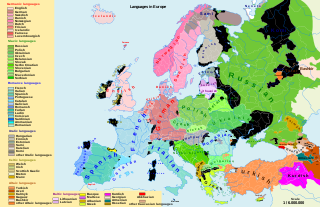
There are over 250 languages indigenous to Europe, and most belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. The three largest phyla of the Indo-European language family in Europe are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; they have more than 200 million speakers each, and together account for close to 90% of Europeans.
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Christian non-profit organization.
Luhya is a Bantu language of western Kenya.
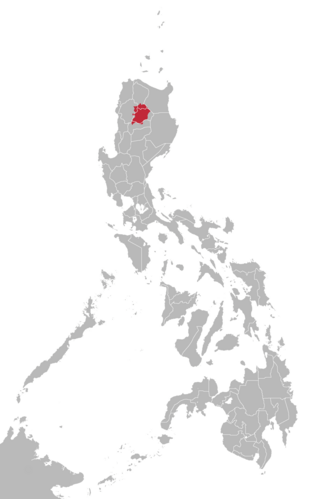
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby island Liran.
The Marathi—Konkani languages are the mainland Southern Indo-Aryan languages, spoken in Maharashtra and the Konkan region of India. The other branch of Southern Indo-Aryan languages is called Insular Indic languages, which are spoken in Insular South Asia.
Central Tibetan, also known as Dbus, Ü or Ü-Tsang, is the most widely spoken Tibetic language and the basis of Standard Tibetan.
Mijikenda is a Bantu dialect cluster spoken along the coast of East Africa, mostly in Kenya, where there are 2.6 million speakers but also in Tanzania, where there are 166,000 speakers. The name Mijikenda means "the nine settlements" or "the nine communities" and refers to the multiple language communities that make up the group. An older, derogatory term for the group is Nyika which refers to the "dry and bushy country" along the coast.
Ding is a Bantu language that is spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Buyu, or Buyi, is a Bantu language of Lake Tanganyika that is closely related to Nyanga.
Duri is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is the prestige variety of the Massenrempulu languages.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Kimaragang (Marigang), Tobilung, and Rungus are varieties of a single Austronesian language of Sabah, Malaysia. The three varieties share moderate mutual intelligibility. Children are not learning it well in some areas.
Masela (Marsela) is the language of Marsela Island in southern Maluku, Indonesia. Regional varieties are distinct; Ethnologue counts it as three languages.

The Katkari also called Kathodi, are an Indian tribe from Maharashtra. They have been categorised as a Scheduled tribe. They are bilingual, speaking the Katkari language, a dialect of the Marathi-Konkani languages, with each other; they speak Marathi with the Marathi speakers, who are a majority in the populace where they live. In Maharashtra the Katkari have been designated a Particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG), along with two other groups included in this sub-category: the Madia Gond and the Kolam. In the case of the Katkari this vulnerability derives from their history as a nomadic, forest-dwelling people listed by the British Raj under the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871, a stigma that continues to this day.
References
- ↑ Katkari language at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)

- ↑ Katkari at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)