
Decoy receptor 3 (Dcr3), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6B (TNFRSF6B), TR6 and M68, is a soluble protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily which inhibits Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. [3] [4] [5]

Decoy receptor 3 (Dcr3), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6B (TNFRSF6B), TR6 and M68, is a soluble protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily which inhibits Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. [3] [4] [5]
Dcr3 was identified in 1998 by the search of genes with homology to the TNFR gene superfamily in expressed sequence tag (EST) database.
The open reading frame of TNFRSF6B encodes 300 amino acids with a 29-residue signal sequence and four tandem cystein-rich repeats. Two transcript variants encoding the same isoform, but differing in the 5' UTR, have been observed for this gene. [5] Unlike most of the other members of TNFR superfamily, TNFRSF6 is a soluble protein which contains no transmembrane domain.
This gene belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It acts as a decoy receptor that competes with death receptors for ligand binding. The encoded protein is postulated to play a regulatory role in suppressing FasL- and LIGHT-mediated cell death and T cell activation as well as to induce angiogenesis via neutralization of TL1A. Overexpression of this gene has been noted in various tumors e.g. gastrointestinal tract tumors, and it is located in a gene-rich cluster on chromosome 20, with other potentially tumor-related genes. [5]
TNFRSF6B has been shown to interact with:

Fas ligand is a type-II transmembrane protein expressed on cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. Its binding with Fas receptor (FasR) induces programmed cell death in the FasR-carrying target cell. Fas ligand/receptor interactions play an important role in the regulation of the immune system and the progression of cancer.

Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene.

The tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) is a protein superfamily of cytokine receptors characterized by the ability to bind tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) via an extracellular cysteine-rich domain. With the exception of nerve growth factor (NGF), all TNFs are homologous to the archetypal TNF-alpha. In their active form, the majority of TNF receptors form trimeric complexes in the plasma membrane. Accordingly, most TNF receptors contain transmembrane domains (TMDs), although some can be cleaved into soluble forms, and some lack a TMD entirely. In addition, most TNF receptors require specific adaptor protein such as TRADD, TRAF, RIP and FADD for downstream signalling. TNF receptors are primarily involved in apoptosis and inflammation, but they can also take part in other signal transduction pathways, such as proliferation, survival, and differentiation. TNF receptors are expressed in a wide variety of tissues in mammals, especially in leukocytes.
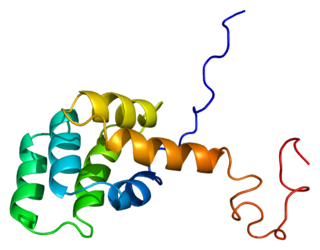
The Fas receptor, also known as Fas, FasR, apoptosis antigen 1, cluster of differentiation 95 (CD95) or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 (TNFRSF6), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAS gene. Fas was first identified using a monoclonal antibody generated by immunizing mice with the FS-7 cell line. Thus, the name Fas is derived from FS-7-associated surface antigen.

Chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC) or Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP3A) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. CCL20 is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells towards the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. CCL20 elicits its effects on its target cells by binding and activating the chemokine receptor CCR6.

Death receptor 4 (DR4), also known as TRAIL receptor 1 (TRAILR1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10A (TNFRSF10A), is a cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily that binds TRAIL and mediates apoptosis.

Chemokine receptor 6 also known as CCR6 is a CC chemokine receptor protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR6 gene. CCR6 has also recently been designated CD196. The gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 6 (6q27) on the Watson (plus) strand. It is 139,737 bases long and encodes a protein of 374 amino acids.

Chemokine-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCBP2 gene.

LIGHT, also known as tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is a secreted protein of the TNF superfamily. It is recognized by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), as well as decoy receptor 3.

Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 12 also known as TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF12 gene.

Decoy receptor 1 (DCR1), also known as TRAIL receptor 3 (TRAILR3) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10C (TNFRSF10C), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily.

Decoy receptor 2 (DCR2), also known as TRAIL receptor 4 (TRAILR4) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10D (TNFRSF10D), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 12A also known as the TWEAK receptor (TWEAKR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF12A gene.

Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor (VEGI), also known as TNF-like ligand 1A (TL1A) and TNF superfamily member 15 (TNFSF15), is protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF15 gene. VEGI is an anti-angiogenic protein. It belongs to tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, where it is member 15. It is the sole known ligand for death receptor 3, and it can also be recognized by decoy receptor 3.

Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCR2 gene. NCR2 has also been designated as CD336, NKp44, NKP44; NK-p44, LY95, and dJ149M18.1.
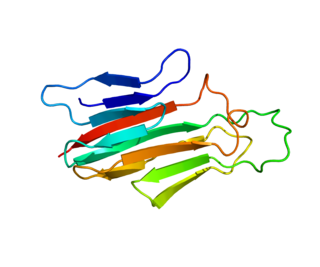
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF18 gene.

CD160 antigen is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD160 gene.

C-type lectin domain family 2 member D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLEC2D gene.

Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 12-member 13, also known as TNFSF12-TNFSF13, is a human gene.

The interleukin-18 receptor 1 (IL-18R1) is an interleukin receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. IL18R1 is its human gene. IL18R1 is also known as CDw218a.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.