Carfentanil or carfentanyl, sold under the brand name Wildnil, is an extremely potent opioid analgesic used in veterinary medicine to anesthetize large animals such as elephants and rhinoceroses. It is an analogue of fentanyl, of which it is structurally derivative. It is typically administered in this context by tranquilizer dart. Carfentanil has also been used in humans to image opioid receptors. It has additionally been used as a recreational drug, typically by injection, insufflation, or inhalation. Deaths have been reported in association with carfentanil.

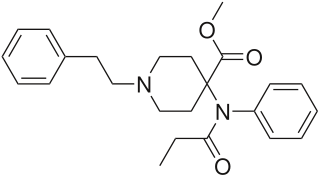
Ohmefentanyl is an extremely potent opioid analgesic drug which selectively binds to the μ-opioid receptor.

3-Methylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl. 3-Methylfentanyl is one of the most potent opioids, estimated to be between 400 and 6000 times stronger than morphine, depending on which isomer is used.

Lofentanil or lofentanyl is one of the most potent opioid analgesics known and is an analogue of fentanyl, which was developed in 1960. It is most similar to the highly potent opioid carfentanil (4-carbomethoxyfentanyl), only slightly more potent. Lofentanil can be described as 3-methylcarfentanil, or 3-methyl-4-carbomethoxyfentanyl. While 3-methylfentanyl is considerably more potent than fentanyl itself, lofentanil is only slightly stronger than carfentanil. This suggests that substitution at both the 3 and 4 positions of the piperidine ring introduces steric hindrance which prevents μ-opioid affinity from increasing much further. As with other 3-substituted fentanyl derivatives such as ohmefentanyl, the stereoisomerism of lofentanil is very important, with some stereoisomers being much more potent than others.
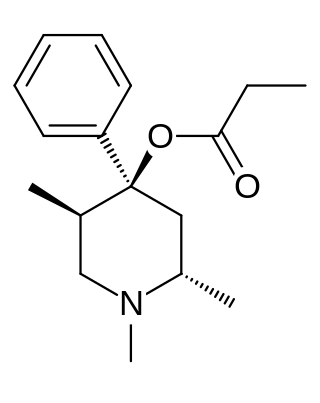
Trimeperidine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.

Diampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and phenampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid, and can be described as a ring-opened analogue of fentanyl.
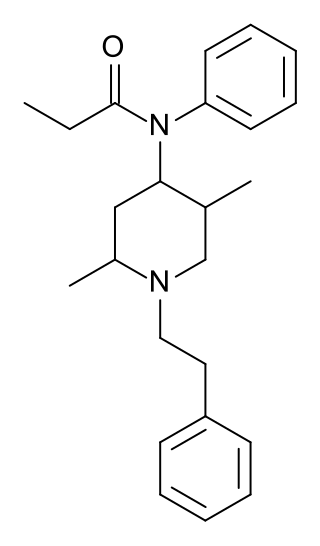
Phenaridine (2,5-dimethylfentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl. It was developed in 1972, and is used for surgical anasthesia.

Piperidylthiambutene (Piperidinohton) is a synthetic opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine. Piperidylthiambutene is structurally distinct from fentanyl, its analogues, and other synthetic opioids previously reported. If sold or obtained for the purpose of human consumption it could be considered a controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the US, Australia and New Zealand. Piperidylthiambutene has been sold as a designer drug, first appearing in late 2018.

3β-(p-Fluorobenzoyloxy)tropane, (8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl 4-fluorobenzoic acid ester, 4-fluorotropacocaine, 3-Pseudotropyl-4-fluorobenzoate, 3-pseudotropyl-4-fluorobenzoate, pFBT) is a tropane derivative drug which acts as a local anaesthetic, having around 30% the stimulant potency of cocaine but around the same potency as a local anaesthetic. It has been investigated as a potential radiolabelled agent for studying receptor binding, but was not adopted for this application. The main application for fluorotropacocaine, however, has been as a designer drug analogue of cocaine, first detected by the EMCDDA in 2008, and subsequently sold as an ingredient of various "bath salt" powder products, usually mixed in combination with other stimulant drugs such as caffeine, dimethocaine, desoxypipradrol or substituted cathinone derivatives.

BDPC is a potent fully synthetic opioid with a distinctive arylcyclohexylamine chemical structure. It was developed by Daniel Lednicer at Upjohn in the 1970s. Initial studies estimated that it was around 10,000 times the potency of morphine in animal models. However, later studies using more modern techniques assigned a value of 504 times the potency of morphine for the more active trans-isomer. This drug was first seized along with three kilograms of acetylfentanyl in an April 25, 2013 police action in Montreal, Canada, and has reportedly continued to be available on the designer drug market internationally. Analogues where the para-bromine is replaced by chlorine or a methyl group retain similar activity, while the meta-hydroxyl derivative demonstrated robust antagonist activity.

4-Phenylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is a derivative of fentanyl. It was developed during the course of research that ultimately resulted in super-potent opioid derivatives such as carfentanil, though it is a substantially less potent analogue. 4-Phenylfentanyl is around eight times the potency of fentanyl in analgesic tests on animals, but more complex 4-heteroaryl derivatives such as substituted thiophenes and thiazoles are more potent still, as they are closer bioisosteres to the 4-carbomethoxy group of carfentanil.

Butyrfentanyl or butyrylfentanyl is a potent short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is an analog of fentanyl with around one quarter of its potency. One of the first mentions of this drug can be found in document written by The College on Problem of Drug Dependence, where it is mentioned as N-butyramide fentanyl analog. This document also states that the article describing its clinical effects was published in 1987. It is an agonist for the μ-opioid receptors.

4-Fluoroisobutyrylfentanyl (also known as 4-FIBF and p-FIBF) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of butyrfentanyl and structural isomer of 4-Fluorobutyrfentanyl and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is closely related to 4-fluorofentanyl, which has an EC50 value of 4.2 nM for the human μ-opioid receptor. 4-fluoroisobutyrylfentanyl is a highly selective μ-opioid receptor agonist whose analgesic potency is almost ten times of that reported for morphine.

Isofentanyl (3-methyl-benzylfentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl first invented in 1973, and which has been sold as a designer drug.

Diphenpipenol is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivative related to compounds such as MT-45 and AD-1211, but diphenpipenol is the most potent compound in the series, with the more active (S) enantiomer being around 105 times the potency of morphine in animal studies. This makes it a similar strength to fentanyl and its analogues, and consequently diphenpipenol can be expected to pose a significant risk of producing life-threatening respiratory depression, as well as other typical opioid side effects such as sedation, itching, nausea and vomiting.

OPPPP is one of several compounds derived from MPPP, the reversed ester of the opioid analgesic pethidine, which were sold as designer drugs in the 1980s, but have been rarely encountered by law enforcement since the passage of the Federal Analogue Act in 1986. In animal studies it was found to be around 1000× the potency of pethidine, making it several times the potency of fentanyl and with similar hazards of respiratory depression and overdose. It is closely related to numerous compounds made by Janssen et al. for which the structure-activity relationship is well established.
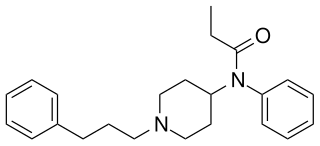
Homofentanyl is an opioid derivative which has been sold as a designer drug. It is a homologue of fentanyl, with similar analgesic and sedative effects but lower potency, around 14× stronger than pethidine.

Fentanyl azepane is an opioid derivative which is a homologue of fentanyl, where the central piperidine ring has been expanded to an azepane ring. It is many times less potent than fentanyl itself, being only slightly stronger than morphine, but is still more potent than the ring-contracted pyrrolidine derivative, as well as other related compounds such as benzylfentanyl and ethoheptazine. The β-hydroxy derivative is slightly more potent again, as with betahydroxyfentanyl.


















