
The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient languages was Latin, the official language of ancient Rome, which conquered the other Italic peoples before the common era. The other Italic languages became extinct in the first centuries AD as their speakers were assimilated into the Roman Empire and shifted to some form of Latin. Between the third and eighth centuries AD, Vulgar Latin diversified into the Romance languages, which are the only Italic languages natively spoken today, while Literary Latin also survived.

The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family— English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct.

Asia, comprising different language families and some unrelated isolates. The major language families include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Caucasian, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan and Kra–Dai. Most, but not all, have a long history as a written language.

Dacian is an extinct language, generally believed to be a member of the Indo-European family, that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity. In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possibly of some surrounding regions. The language was extinct by the 4th century AD.
This is a list of etymological lists.

The Thracian language is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was an Indo-European language with satem features.
This is a list of languages spoken in regions ruled by Balkan countries. With the exception of several Turkic languages, all of them belong to the Indo-European family. A subset of these languages is notable for forming a well-studied sprachbund, a group of languages that have developed some striking structural similarities over time.
The origin of the Albanians has been the subject of historical, linguistic, archaeological and genetic studies. Albanians continuously first appear in the historical record in Byzantine sources of the 11th century. At this point, they were already fully Christianized. Albanian forms a separate branch of Indo-European, first attested in the 15th century, having evolved from one of the Paleo-Balkan languages of antiquity. The surviving pre-Christian Albanian culture shows that Albanian mythology and folklore are of Paleo-Balkanic origin and that almost all of their elements are pagan.

The Paleo-Balkan languages or Palaeo-Balkan languages is a grouping of various extinct Indo-European languages that were spoken in the Balkans and surrounding areas in ancient times.
Iberian languages is a generic term for the languages currently or formerly spoken in the Iberian Peninsula.
The term Thraco-Illyrian refers to a hypothesis according to which the Daco-Thracian and Illyrian languages comprise a distinct branch of Indo-European. Thraco-Illyrian is also used as a term merely implying a Thracian-Illyrian interference, mixture or sprachbund, or as a shorthand way of saying that it is not determined whether a subject is to be considered as pertaining to Thracian or Illyrian. Downgraded to a geo-linguistic concept, these languages are referred to as Paleo-Balkan.
The linguistic classification of the ancient Thracian language has long been a matter of contention and uncertainty, and there are widely varying hypotheses regarding its position among other Paleo-Balkan languages. It is not contested, however, that the Thracian languages were Indo-European languages which had acquired satem characteristics by the time they are attested.

The Pre-Indo-European languages are any of several ancient languages, not necessarily related to one another, that existed in Prehistoric Europe, Asia Minor, Ancient Iran and Southern Asia before the arrival of speakers of Indo-European languages. The oldest Indo-European language texts are Hittite and date from the 19th century BC in Kültepe, and while estimates vary widely, the spoken Indo-European languages are believed to have developed at the latest by the 3rd millennium BC. Thus, the Pre-Indo-European languages must have developed earlier than or, in some cases, alongside the Indo-European languages that ultimately displaced almost all of them.
Numerous lexemes that are reconstructable for Proto-Slavic have been identified as borrowings from the languages of various tribes that Proto-Slavic speakers interacted with in either prehistoric times or during their expansion when they first appeared in history in the sixth century. Most of the loanwords come from Germanic languages, with other contributors being Iranian, Celtic, and Turkic. Slavic loanwords sparked numerous debates in the 20th century, some of which persist today.
The Intercontinental Dictionary Series is a large database of topical vocabulary lists in various world languages. The general editor of the database is Bernard Comrie of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig. Mary Ritchie Key of the University of California, Irvine is the founding editor. The database has an especially large selection of indigenous South American languages and Northeast Caucasian languages.
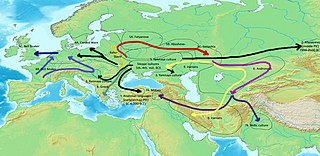
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially explaining how these languages came to be spoken across a large area of Eurasia, spanning from the Indian subcontinent and Iranian plateau to Europe.
This is an index to deities of the different religions, cultures and mythologies of the world, listed by region or culture.







