State of continual or frequent warfare

Ritual warfare (sometimes called endemic warfare) is a state of continual or frequent warfare, such as is found in (but not limited to) some tribal societies.


| Part of a series on |
| War (outline) |
|---|
 |
Ritual warfare (sometimes called endemic warfare) is a state of continual or frequent warfare, such as is found in (but not limited to) some tribal societies.
Ritual fighting (or ritual battle or ritual warfare) permits the display of courage, masculinity, and the expression of emotion while resulting in relatively few wounds and even fewer deaths. Thus such a practice can be viewed as a form of conflict-resolution and/or as a psycho-social exercise. Native Americans often engaged in this activity, but the frequency of warfare in most hunter-gatherer cultures is a matter of dispute. [1]
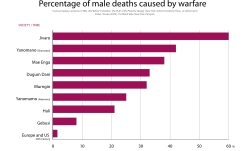
Warfare is known to every tribal society, but some societies developed a particular emphasis of warrior culture. Historical examples include the Nuer of South Sudan, [2] the Maasai of East Africa, [3] the Zulu of southeastern Africa, [3] the Sea Dayaks of Borneo, [3] the Naga of Northeast India and Myanmar, the Māori of New Zealand, the Dugum Dani of Papua, [2] the Araucanians of Patagonia, [3] and the Yanomami (dubbed "the Fierce People") of the Amazon. [2] The culture of inter-tribal warfare has long been present in New Guinea. [1] [4]
Communal societies are well capable of escalation to all-out wars of annihilation between tribes. Thus, in Amazonas, there was perpetual animosity between the neighboring tribes of the Jívaro. A fundamental difference between wars enacted within the same tribe and against neighboring tribes is such that "wars between different tribes are in principle wars of extermination". [5]
It is documented that large war parties of the Bororo, Kayapo, Munduruku, Guaraní and Tupi people conducted long-distance raids across the interior of Brazil. Most Bororo groups were continually at war with their neighbors. [6] In the early 20th century, thirty indigenous tribes in the Amazon basin were listed as peaceful and eighty-three were specifically described as warlike. [3]
The Yanomami of Amazonas traditionally practiced a system of escalation of violence in several discrete stages.[ citation needed ] The chest-pounding duel, the side-slapping duel, the club fight, and the spear-throwing fight. Further escalation results in raiding parties with the purpose of killing at least one member of the hostile faction. Finally, the highest stage of escalation is Nomohoni or all-out massacres brought about by treachery.
Similar customs were known to the Dugum Dani and the Chimbu of New Guinea, the Nuer of Sudan and the North American Plains Indians. Among the Chimbu and the Dugum Dani, pig theft was the most common cause of conflict, even more frequent than abduction of women, while among the Yanomamö, the most frequent initial cause of warfare was accusations of sorcery. Warfare serves the function of easing intra-group tensions and has aspects of a game, or "overenthusiastic football". [7] Especially Dugum Dani "battles" have a conspicuous element of play, with one documented instance of a battle interrupted when both sides were distracted by throwing stones at a passing cuckoo dove. [8]
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help){{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help)