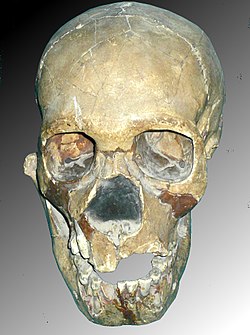
 Teshik-Tash 1 | |
| Common name | Teshik-Tash 1 |
|---|---|
| Species | Homo neanderthalensis (mtDNA confirmed) [1] |
| Age | No dates produced |
| Place discovered | Teshik-Tash Cave, Uzbek SSR, USSR |
| Date discovered | 1938 |
| Discovered by | Alexey Okladnikov |
Teshik-Tash 1 is a Neanderthal skeleton discovered in 1938 in Teshik-Tash Cave, in the Bajsuntau mountain range, Uzbek SSR (Uzbekistan), Central Asia.
Contents
The remains were discovered in 1938 by A. P. Okladnikov. [2] They were found in a shallow pit, reported to be associated with five pairs of Siberian ibex horn cores. Through dental analysis the skull was said to have been an 8 to 11-year-old child. The horn cores were found around the perimeter of the grave surrounding the cranial remains. This has led a number of researchers to believe the child was ritually buried. [3]
The site was excavated in five cultural layers of sediment with Mousterian artifacts. [4] [5]
Lack of adequate published material on the excavation [6] and the numerous Ibex bones (761) found led to this interpretation being questioned. Paul Mellars, questioning the ritual interpretation suggested that the bones may not have been deliberately placed. [7] Others (e.g., Gargett) believe it is no burial at all.
