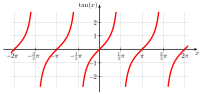
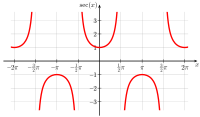
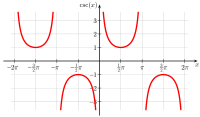
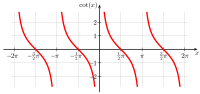
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena through Fourier analysis.

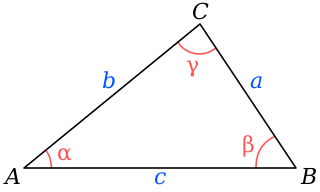
In trigonometry, the law of sines, sine law, sine formula, or sine rule is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of any triangle to the sines of its angles. According to the law, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, and α, β, and γ are the opposite angles, while R is the radius of the triangle's circumcircle. When the last part of the equation is not used, the law is sometimes stated using the reciprocals; The law of sines can be used to compute the remaining sides of a triangle when two angles and a side are known—a technique known as triangulation. It can also be used when two sides and one of the non-enclosed angles are known. In some such cases, the triangle is not uniquely determined by this data and the technique gives two possible values for the enclosed angle.

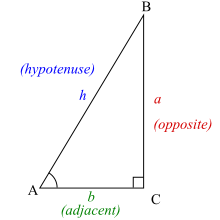
In geometry, a hypotenuse is the side of a right triangle opposite the right angle. It is the longest side of any such triangle; the two other shorter sides of such a triangle are called catheti or legs. The length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two legs. Mathematically, this can be written as , where a is the length of one leg, b is the length of another leg, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.

In mathematics, an identity is an equality relating one mathematical expression A to another mathematical expression B, such that A and B produce the same value for all values of the variables within a certain domain of discourse. In other words, A = B is an identity if A and B define the same functions, and an identity is an equality between functions that are differently defined. For example, and are identities. Identities are sometimes indicated by the triple bar symbol ≡ instead of =, the equals sign. Formally, an identity is a universally quantified equality.
In trigonometry, the law of tangents or tangent rule is a statement about the relationship between the tangents of two angles of a triangle and the lengths of the opposing sides.

In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions, under suitably restricted domains. Specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's trigonometric ratios. Inverse trigonometric functions are widely used in engineering, navigation, physics, and geometry.

The haversine formula determines the great-circle distance between two points on a sphere given their longitudes and latitudes. Important in navigation, it is a special case of a more general formula in spherical trigonometry, the law of haversines, that relates the sides and angles of spherical triangles.

Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation.
The Pythagorean trigonometric identity, also called simply the Pythagorean identity, is an identity expressing the Pythagorean theorem in terms of trigonometric functions. Along with the sum-of-angles formulae, it is one of the basic relations between the sine and cosine functions.

In hyperbolic geometry, a hyperbolic triangle is a triangle in the hyperbolic plane. It consists of three line segments called sides or edges and three points called angles or vertices.

For small angles, the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent can be calculated with reasonable accuracy by the following simple approximations:

In spherical trigonometry, the law of cosines is a theorem relating the sides and angles of spherical triangles, analogous to the ordinary law of cosines from plane trigonometry.

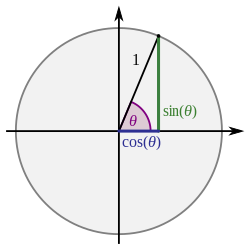
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle, and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. For an angle , the sine and cosine functions are denoted as and .

Early study of triangles can be traced to the 2nd millennium BC, in Egyptian mathematics and Babylonian mathematics. Trigonometry was also prevalent in Kushite mathematics. Systematic study of trigonometric functions began in Hellenistic mathematics, reaching India as part of Hellenistic astronomy. In Indian astronomy, the study of trigonometric functions flourished in the Gupta period, especially due to Aryabhata, who discovered the sine function, cosine function, and versine function.
There are several equivalent ways for defining trigonometric functions, and the proofs of the trigonometric identities between them depend on the chosen definition. The oldest and most elementary definitions are based on the geometry of right triangles and the ratio between their sides. The proofs given in this article use these definitions, and thus apply to non-negative angles not greater than a right angle. For greater and negative angles, see Trigonometric functions.

In mathematics, the values of the trigonometric functions can be expressed approximately, as in , or exactly, as in . While trigonometric tables contain many approximate values, the exact values for certain angles can be expressed by a combination of arithmetic operations and square roots. The angles with trigonometric values that are expressible in this way are exactly those that can be constructed with a compass and straight edge, and the values are called constructible numbers.
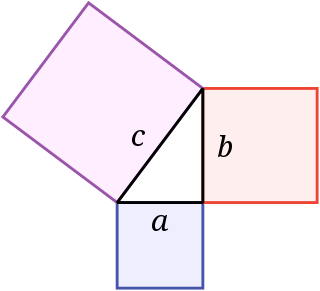
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.

In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle of unit radius—that is, a radius of 1. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, the unit circle is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane. In topology, it is often denoted as S1 because it is a one-dimensional unit n-sphere.
In trigonometry, it is common to use mnemonics to help remember trigonometric identities and the relationships between the various trigonometric functions.