A special election was held in Rhode Island's at-large congressional district on August 30, 1808 to fill a vacancy resulting from the death of Nehemiah Knight (DR) on June 13, 1808. [1] This election was held at the same time as the 1808 elections.
| Elections in Rhode Island |
|---|
 |
A special election was held in Rhode Island's at-large congressional district on August 30, 1808 to fill a vacancy resulting from the death of Nehemiah Knight (DR) on June 13, 1808. [1] This election was held at the same time as the 1808 elections.
| Candidate | Party | Votes [2] | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Richard Jackson, Jr. | Federalist | 3,262 | 63.4% |
| Jonathan Russell | Democratic-Republican | 1,887 | 36.6% |
Jackson took his seat on November 11, 1808. [1] Jackson also won election to the 11th Congress at the same time.

The 1808 United States presidential election was the sixth quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, November 4, to Wednesday, December 7, 1808. The Democratic-Republican candidate James Madison defeated Federalist candidate Charles Cotesworth Pinckney decisively.

The State of Rhode Island General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. A bicameral body, it is composed of the lower Rhode Island House of Representatives with 75 representatives, and the upper Rhode Island Senate with 38 senators. Members are elected in the general election immediately preceding the beginning of the term or in special elections called to fill vacancies. There are no term limits for either chamber. The last General Assembly election took place on November 3, 2020.

Benjamin Bourne was a United States representative from Rhode Island, a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of Rhode Island and a United States Circuit Judge of the United States Circuit Court for the First Circuit.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.

The 1808–09 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1808, and May 5, 1809. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 11th United States Congress convened on May 22, 1809. They coincided with James Madison being elected as president. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
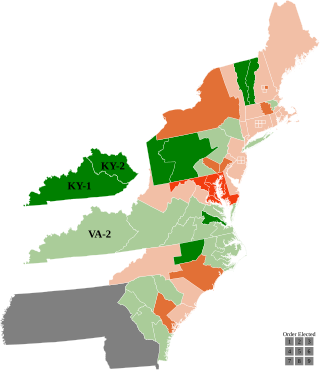
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

The 1788–89 United States House of Representatives elections were the first U.S. House of Representatives elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. Each state set its own date for its congressional elections, ranging from November 24, 1788, to March 5, 1789, before or after the first session of the 1st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1789. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States.

William Loughton Smith was an American lawyer, politician, and diplomat from Charleston, South Carolina. He represented South Carolina as a Federalist in the United States House of Representatives from 1789 until 1797, during which time he served as chairman of the Committee on Ways and Means.
William Baylies was an American lawyer and politician who served four non-consecutive terms as a U.S. Representative from Massachusetts in the early to mid-19th century.
Since the Great Depression, Rhode Island politics have been dominated by the Rhode Island Democratic Party, and the state is considered part of the Democrats' "Blue Wall." Democrats have won all but four presidential elections since 1928, with the exceptions being 1952, 1956, 1972, and 1984. The Rhode Island Republican Party, although virtually non-existent in the Rhode Island General Assembly, has remained competitive in gubernatorial elections, having won one as recently as 2006. Until 2014, Democrats had not won a gubernatorial election in the state since 1992, and it was not until 2018 that they won one by double digits. The Rhode Island General Assembly has continuously been under Democratic control since 1959.

The 1808–09 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with the 1808 presidential election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1808 and 1809, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1834–35 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1834 and 1835, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.
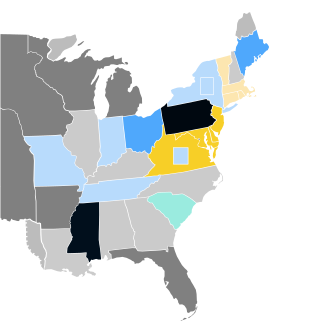
The 1832–33 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1832 and 1833, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.
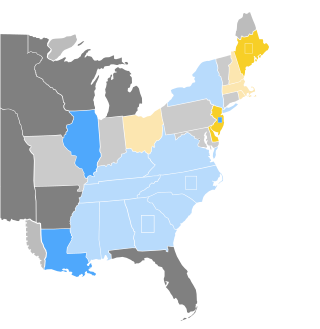
the 1828–29 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these United States Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the 17th Amendment to the United States Constitution in 1913, senators were chosen by State legislature United States. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1828 and 1829, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 14, 1806, for the 10th Congress.

In September 1808, the Federalist ticket won a majority in Rhode Island's election for delegates to the United States Congress, with nearly 500 votes.
A special election was held in Rhode Island's at-large congressional district on November 15, 1796 to fill a vacancy left in both the 4th and 5th Congresses by the resignation of Benjamin Bourne (F).

There were three special elections to the United States House of Representatives in 2023 during the 118th United States Congress.