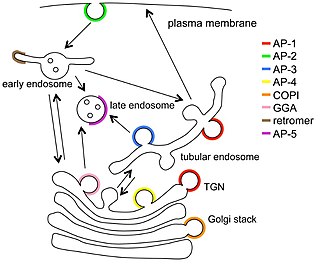
Vesicular transport adaptor proteins are proteins involved in forming complexes that function in the trafficking of molecules from one subcellular location to another. These complexes concentrate the correct cargo molecules in vesicles that bud or extrude off of one organelle and travel to another location, where the cargo is delivered. While some of the details of how these adaptor proteins achieve their trafficking specificity has been worked out, there is still much to be learned.

AP-2 complex subunit mu is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2M1 gene.

Coatomer subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPB1 gene.

AP-2 complex subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2A1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit mu-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1M1 gene.

ADP-ribosylation factor-binding protein GGA3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GGA3 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1G1 gene.

Clathrin heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLTC gene.

AP-2 complex subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2A2 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1B1 gene.

AP-2 complex subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2B1 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit delta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3D1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit mu-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1M2 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit sigma-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1S1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit gamma-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1G2 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit mu-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3M1 gene.

AP-2 complex subunit sigma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2S1 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit sigma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3S1 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3B2 gene.

AP-4 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP4B1 gene.




















