Related Research Articles

Donald Arthur Norman is an American researcher, professor, and author. Norman is the director of The Design Lab at University of California, San Diego. He is best known for his books on design, especially The Design of Everyday Things. He is widely regarded for his expertise in the fields of design, usability engineering, and cognitive science. He is a co-founder and consultant with the Nielsen Norman Group. He is also an IDEO fellow and a member of the Board of Trustees of IIT Institute of Design in Chicago. He also holds the title of Professor Emeritus of Cognitive Science at the University of California, San Diego. Norman is an active Distinguished Visiting Professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), where he spends two months a year teaching.
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use.
User-Centered Design (UCD) or User-Driven Development (UDD) is a framework of processes in which usability goals, user characteristics, environment, tasks and workflow of a product, service or process are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. These tests are conducted with/without actual users during each stage of the process from requirements, pre-production models and post production, completing a circle of proof back to and ensuring that "development proceeds with the user as the center of focus." Such testing is necessary as it is often very difficult for the designers of a product to understand intuitively what a first-time user of their design experiences, and what each user's learning curve may look like. User-centered design is based on the understanding of a user, their demands, priorities and experiences and when used, is known to lead to an increased product usefulness and usability as it delivers satisfaction to the user.
Interaction design, often abbreviated as IxD, is "the practice of designing interactive digital products, environments, systems, and services." Beyond the digital aspect, interaction design is also useful when creating physical (non-digital) products, exploring how a user might interact with it. Common topics of interaction design include design, human–computer interaction, and software development. While interaction design has an interest in form, its main area of focus rests on behavior. Rather than analyzing how things are, interaction design synthesizes and imagines things as they could be. This element of interaction design is what characterizes IxD as a design field as opposed to a science or engineering field.
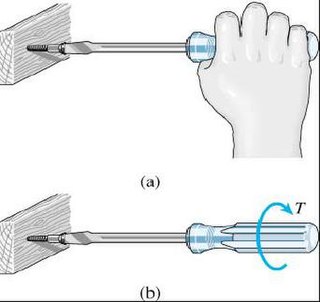
Affordance is what the environment offers the individual. James J. Gibson coined the term in his 1966 book, The Senses Considered as Perceptual Systems, and it occurs in many of his earlier essays (e.g.). However, his best-known definition is taken from his seminal 1979 book, The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception:
The affordances of the environment are what it offers the animal, what it provides or furnishes, either for good or ill. The verb to afford is found in the dictionary, the noun affordance is not. I have made it up. I mean by it something that refers to both the environment and the animal in a way that no existing term does. It implies the complementarity of the animal and the environment.
The cognitive walkthrough method is a usability inspection method used to identify usability issues in interactive systems, focusing on how easy it is for new users to accomplish tasks with the system. Cognitive walkthrough is task-specific, whereas heuristic evaluation takes a holistic view to catch problems not caught by this and other usability inspection methods. The method is rooted in the notion that users typically prefer to learn a system by using it to accomplish tasks, rather than, for example, studying a manual. The method is prized for its ability to generate results quickly with low cost, especially when compared to usability testing, as well as the ability to apply the method early in the design phases before coding even begins.

Emotional Design is both the title of a book by Donald Norman and of the concept it represents.
The user experience is how a user interacts with and experiences a product, system or service. It includes a person's perceptions of utility, ease of use, and efficiency. Improving user experience is important to most companies, designers, and creators when creating and refining products because negative user experience can diminish use of the product and, therefore, any desired positive impacts; conversely, designing toward profitability often conflicts with ethical user experience objectives and even causes harm. User experience is subjective. However, the attributes that make up the user experience are objective.
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the user experience. The goal of user interface design is to make the user's interaction as simple and efficient as possible, in terms of accomplishing user goals.
Social design is the application of design methodologies in order to tackle complex human issues, placing the social issues as the priority. Historically social design has been mindful of the designer's role and responsibility in society, and of the use of the design process to bring about social change. Social design as a critical discipline has been practiced primarily in two different models, as either the application of the Human Centered Design Methodology in the social sector or governmental sector, or sometimes is synonymously practiced by designers who venture into social entrepreneurship.
User experience design is the process of supporting user behavior through usability, usefulness, and desirability provided in the interaction with a product. User experience design encompasses traditional human–computer interaction (HCI) design and extends it by addressing all aspects of a product or service as perceived by users. Experience design (XD) is the practice of designing products, processes, services, events, omnichannel journeys, and environments with a focus placed on the quality of the user experience and culturally relevant solutions. Experience design is not driven by a single design discipline. Instead, it requires a cross-discipline perspective that considers multiple aspects of the brand/ business/ environment/ experience from product, packaging, and retail environment to the clothing and attitude of employees. Experience design seeks to develop the experience of a product, service, or event along any or all of the following dimensions:

The Design of Everyday Things is a best-selling book by cognitive scientist and usability engineer Donald Norman about how design serves as the communication between object and user, and how to optimize that conduit of communication in order to make the experience of using the object pleasurable. One of the main premises of the book is that although people are often keen to blame themselves when objects appear to malfunction, it is not the fault of the user but rather the lack of intuitive guidance that should be present in the design.
Usage-centered design is an approach to user interface design based on a focus on user intentions and usage patterns. It analyzes users in terms of the roles they play in relation to systems and employs abstract (essential) use cases for task analysis. It derives visual and interaction design from abstract prototypes based on the understanding of user roles and task cases.
The semantic turn refers to a paradigm shift in the design of artifacts – industrial, graphic, informational, architectural, and social – from an emphasis on how artifacts ought to function to what they mean to those affected by them – semantics being a concern for meaning. It provides a new foundation for professional design, a detailed design discourse, codifications of proven methods, compelling scientific justifications of its products, and a clear identity for professional designers working within a network of their stakeholders.
The term natural mapping comes from proper and natural arrangements for the relations between controls and their movements to the outcome from such action into the world. The real function of natural mappings is to reduce the need for any information from a user’s memory to perform a task. This term is widely used in the areas of human-computer interaction (HCI) and interactive design.

An interaction technique, user interface technique or input technique is a combination of hardware and software elements that provides a way for computer users to accomplish a single task. For example, one can go back to the previously visited page on a Web browser by either clicking a button, pressing a key, performing a mouse gesture or uttering a speech command. It is a widely used term in human-computer interaction. In particular, the term "new interaction technique" is frequently used to introduce a novel user interface design idea.
Human–computer interaction (HCI) studies the design and use of computer technology, focused on the interfaces between people (users) and computers. Researchers in the field of HCI observe the ways in which humans interact with computers and design technologies that let humans interact with computers in novel ways.
Cultural probes is a technique used to inspire ideas in a design process. It serves as a means of gathering inspirational data about people's lives, values and thoughts. The probes are small packages that can include any sort of artifact along with evocative tasks, which are given to participants to allow them to record specific events, feelings or interactions. The aim is to elicit inspirational responses from people, in order to understand their culture, thoughts and values better, and thus stimulate designer's imaginations. Probes is one of the prominent approaches in the practice of co-designing. It is design-led approaches as described by the landscape of design research and practice. probes are usually used in the early front end of the design process.The probes were not designed to be analyzed, nor did we summarize what they revealed about the sites as an explicit stage in the process. Rather, the design proposals we produced reflected what we learned from the materials. Furthermore, probes were born to gather “fragmentary clues” about people’s “lives and thoughts” which means they are tools to inspire - others argue that they can be used to, provide relevant information and gather empathetic data.

Hardware interface design (HID) is a cross-disciplinary design field that shapes the physical connection between people and technology in order to create new hardware interfaces that transform purely digital processes into analog methods of interaction. It employs a combination of filmmaking tools, software prototyping, and electronics breadboarding.

Behavioural design is a sub-category of design, which is concerned with how design can shape, or be used to influence human behaviour. All approaches of design for behaviour change acknowledge that artefacts have an important influence on human behaviour and/or behavioural decisions. They strongly draw on theories of behavioural change, including the division into personal, behavioural, and environmental characteristics as drivers for behaviour change. Areas in which design for behaviour change has been most commonly applied include health and wellbeing, sustainability, safety and social context, as well as crime prevention.
References
- Saffer, Dan. 2010. Designing for interaction.
- Gay, Geri and Helene Hembrooke. 2004. Activity-Centered Design: An Ecological Approach to Designing Smart Tools and Usable Systems.
- Norman, Don. 2015. The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition.
Niaz Mahmud " Activity Center Design"