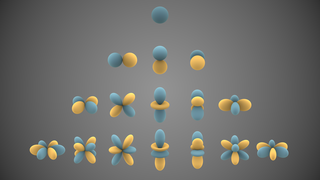In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as or where is the Laplace operator, is the divergence operator, is the gradient operator, and is a twice-differentiable real-valued function. The Laplace operator therefore maps a scalar function to another scalar function.

The Navier–Stokes equations are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. They were named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and the Irish physicist and mathematician George Gabriel Stokes. They were developed over several decades of progressively building the theories, from 1822 (Navier) to 1842–1850 (Stokes).
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference.
In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a scalar function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols , (where is the nabla operator), or . In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems, such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form. Informally, the Laplacian Δf (p) of a function f at a point p measures by how much the average value of f over small spheres or balls centered at p deviates from f (p).
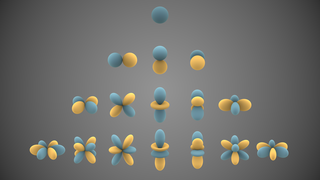
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The table of spherical harmonics contains a list of common spherical harmonics.
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model as to how solid objects deform and become internally stressed by prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics.
In probability and statistics, an exponential family is a parametric set of probability distributions of a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, including the enabling of the user to calculate expectations, covariances using differentiation based on some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential families are in a sense very natural sets of distributions to consider. The term exponential class is sometimes used in place of "exponential family", or the older term Koopman–Darmois family. Sometimes loosely referred to as "the" exponential family, this class of distributions is distinct because they all possess a variety of desirable properties, most importantly the existence of a sufficient statistic.
In information geometry, the Fisher information metric is a particular Riemannian metric which can be defined on a smooth statistical manifold, i.e., a smooth manifold whose points are probability measures defined on a common probability space. It can be used to calculate the informational difference between measurements.
In mathematical statistics, the Fisher information is a way of measuring the amount of information that an observable random variable X carries about an unknown parameter θ of a distribution that models X. Formally, it is the variance of the score, or the expected value of the observed information.
In physics, the Hamilton–Jacobi equation, named after William Rowan Hamilton and Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi, is an alternative formulation of classical mechanics, equivalent to other formulations such as Newton's laws of motion, Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics.
In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence, denoted , is a type of statistical distance: a measure of how much a model probability distribution Q is different from a true probability distribution P. Mathematically, it is defined as
In mathematics, the Helmholtz equation is the eigenvalue problem for the Laplace operator. It corresponds to the elliptic partial differential equation: where ∇2 is the Laplace operator, k2 is the eigenvalue, and f is the (eigen)function. When the equation is applied to waves, k is known as the wave number. The Helmholtz equation has a variety of applications in physics and other sciences, including the wave equation, the diffusion equation, and the Schrödinger equation for a free particle.
In mathematics and physics, the Christoffel symbols are an array of numbers describing a metric connection. The metric connection is a specialization of the affine connection to surfaces or other manifolds endowed with a metric, allowing distances to be measured on that surface. In differential geometry, an affine connection can be defined without reference to a metric, and many additional concepts follow: parallel transport, covariant derivatives, geodesics, etc. also do not require the concept of a metric. However, when a metric is available, these concepts can be directly tied to the "shape" of the manifold itself; that shape is determined by how the tangent space is attached to the cotangent space by the metric tensor. Abstractly, one would say that the manifold has an associated (orthonormal) frame bundle, with each "frame" being a possible choice of a coordinate frame. An invariant metric implies that the structure group of the frame bundle is the orthogonal group O(p, q). As a result, such a manifold is necessarily a (pseudo-)Riemannian manifold. The Christoffel symbols provide a concrete representation of the connection of (pseudo-)Riemannian geometry in terms of coordinates on the manifold. Additional concepts, such as parallel transport, geodesics, etc. can then be expressed in terms of Christoffel symbols.

In mathematics, the Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process is a stochastic process with applications in financial mathematics and the physical sciences. Its original application in physics was as a model for the velocity of a massive Brownian particle under the influence of friction. It is named after Leonard Ornstein and George Eugene Uhlenbeck.
In statistics, M-estimators are a broad class of extremum estimators for which the objective function is a sample average. Both non-linear least squares and maximum likelihood estimation are special cases of M-estimators. The definition of M-estimators was motivated by robust statistics, which contributed new types of M-estimators. However, M-estimators are not inherently robust, as is clear from the fact that they include maximum likelihood estimators, which are in general not robust. The statistical procedure of evaluating an M-estimator on a data set is called M-estimation. The "M" initial stands for "maximum likelihood-type".

In statistics, the monotone likelihood ratio property is a property of the ratio of two probability density functions (PDFs). Formally, distributions and bear the property if
Stochastic approximation methods are a family of iterative methods typically used for root-finding problems or for optimization problems. The recursive update rules of stochastic approximation methods can be used, among other things, for solving linear systems when the collected data is corrupted by noise, or for approximating extreme values of functions which cannot be computed directly, but only estimated via noisy observations.
In fluid dynamics, the Oseen equations describe the flow of a viscous and incompressible fluid at small Reynolds numbers, as formulated by Carl Wilhelm Oseen in 1910. Oseen flow is an improved description of these flows, as compared to Stokes flow, with the (partial) inclusion of convective acceleration.
Although the term well-behaved statistic often seems to be used in the scientific literature in somewhat the same way as is well-behaved in mathematics it can also be assigned precise mathematical meaning, and in more than one way. In the former case, the meaning of this term will vary from context to context. In the latter case, the mathematical conditions can be used to derive classes of combinations of distributions with statistics which are well-behaved in each sense.
Projection filters are a set of algorithms based on stochastic analysis and information geometry, or the differential geometric approach to statistics, used to find approximate solutions for filtering problems for nonlinear state-space systems. The filtering problem consists of estimating the unobserved signal of a random dynamical system from partial noisy observations of the signal. The objective is computing the probability distribution of the signal conditional on the history of the noise-perturbed observations. This distribution allows for calculations of all statistics of the signal given the history of observations. If this distribution has a density, the density satisfies specific stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) called Kushner-Stratonovich equation, or Zakai equation. It is known that the nonlinear filter density evolves in an infinite dimensional function space.