
A narrowboat is a particular type of canal boat, built to fit the narrow locks of the United Kingdom. The UK's canal system provided a nationwide transport network during the Industrial Revolution, but with the advent of the railways, commercial canal traffic gradually diminished and the last regular long-distance transportation of goods by canal had virtually disappeared by 1970. However, some commercial traffic continued. From the 1970s onward narrowboats were gradually being converted into permanent residences or as holiday lettings. Currently, about 8580 narrowboats are registered as 'permanent homes' on Britain's waterway system and represent a growing alternative community living on semi-permanent moorings or continuously cruising.

The Black Country is an area of England's West Midlands. It is mainly urban, covering most of the Dudley, Sandwell and Walsall Metropolitan Boroughs, with the City of Wolverhampton sometimes included. The towns of Dudley and Tipton are generally considered to be the centre.

The canal network of the United Kingdom played a vital role in the Industrial Revolution. The UK was the first country to develop a nationwide canal network which, at its peak, expanded to nearly 4,000 miles in length. The canals allowed raw materials to be transported to a place of manufacture, and finished goods to be transported to consumers, more quickly and cheaply than by a land based route. The canal network was extensive and included feats of civil engineering such as the Anderton Boat Lift, the Manchester Ship Canal, the Worsley Navigable Levels and the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct.

The Black Country Living Museum is an open-air museum of rebuilt historic buildings in Dudley, West Midlands, England. It is located in the centre of the Black Country, 10 miles west of Birmingham. The museum occupies 10.5 hectares of former industrial land partly reclaimed from a former railway goods yard, disused lime kilns, canal arm and former coal pits.

The canals of the United Kingdom are a major part of the network of inland waterways in the United Kingdom. They have a varied history, from use for irrigation and transport, through becoming the focus of the Industrial Revolution, to today's role of recreational boating. Despite a period of abandonment, today the canal system in the United Kingdom is again increasing in use, with abandoned and derelict canals being reopened, and the construction of some new routes. Canals in England and Wales are maintained by navigation authorities. The biggest navigation authorities are the Canal & River Trust and the Environment Agency, but other canals are managed by companies, local authorities or charitable trusts.
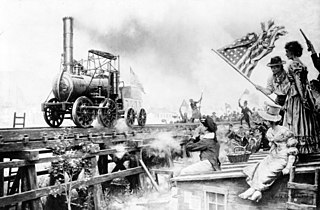
The Stourbridge Lion was a railroad steam locomotive. It was the first locomotive and the first foreign built locomotive to be operated in the United States, and one of the first locomotives to operate outside Britain. It takes its name from the lion's face painted on the front, and Stourbridge in England, where it was manufactured by the firm Foster, Rastrick and Company in 1829. The locomotive, obtained by the Delaware & Hudson Canal Company (D&H), was shipped to New York in May 1829, where it was tested raised on blocks. It was then taken to Honesdale, Pennsylvania for testing on the company's newly built track. The locomotive performed well in its first test in August 1829, but was found to be too heavy for the track and was never used for its intended purpose of hauling coal wagons. During the next few decades, a number of parts were removed from the abandoned locomotive until only the boiler and a few other components remained. These were acquired by the Smithsonian Institution in 1890 and are currently on display at the B&O Railroad Museum in Baltimore.

Clinker-built is a method of boat building in which the edges of hull planks overlap each other. Where necessary in larger craft, shorter planks can be joined end to end, creating a longer strake or hull plank.

Foster, Rastrick and Company was one of the pioneering steam locomotive manufacturing companies of England. It was based in Stourbridge, Worcestershire, now West Midlands. James Foster, an ironmaster, and John Urpeth Rastrick, an engineer, became partners in 1816, forming the company in 1819. Rastrick was one of the judges at the Rainhill Trials in 1829. The company was dissolved on 20 June 1831.

The Tavistock Canal is a canal in the county of Devon in England. It was constructed early in the 19th century to link the town of Tavistock to Morwellham Quay on the River Tamar, where cargo could be loaded into ships. The canal is still in use to supply water to a hydro-electric power plant at Morwellham Quay, and forms part of the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape World Heritage Site. It is unusual for a canal, as it has a gentle slope over its length, resulting in a considerable flow of water.

Fellows Morton & Clayton Ltd was, for much of the early 20th century, the largest and best-known canal transportation company in England. The company was in existence from 1889 to 1947.

The Pensnett Canal, also called Lord Ward's Canal was a private 1.25 miles (2 km) long canal near Brierley Hill, West Midlands, England, which opened in 1840 and served the industrial enterprises of Lord Dudley's Estate. The engineer was Mathew Frost. Since its closure to navigation in 1950, much of it has been lost by overbuilding, but a small section at its junction with the Dudley Canal was restored in 1995, and the section through Brierley Hill remains in water, although it is polluted and not navigable.

President is a historic, steam-powered narrowboat, built in 1909 by Fellows Morton & Clayton (FMC) at their dock at Saltley, Birmingham, England. It is now owned by the Black Country Living Museum, where it is based. President is registered by National Historic Ships as part of the National Historic Fleet.

The boat dock at the Black Country Living Museum was built in 1976. Like many boat docks in the region its buildings are made out of recycled boat timbers from derelict wooden boats. The thousands of boats that used to work the Black Country canals all needed constant maintenance.

Birchills is a historic, ‘Joey’ boat with a small day cabin, built in 1953 by Ernest Thomas of Walsall. Birchills was one of the last wooden day boats made and was used to carry coal to Birchills Power Station and Wolverhampton Power Station. It is the only surviving 'Joey' with a day cabin.
Diamond was built by John Crichton & Co. of Saltney, Chester for Midland and Coast Canal Carrying Company of Wolverhampton. The boat was built in Chester in 1927 and first registered at Wolverhampton in 1928. She was one of six iron boats in the fleet fitted with two cabins for long-distance traffic between the Black Country and the ports on the Mersey Estuary. Having been damaged during an air raid on Birmingham in 1944 she was sold for scrap to Ernest Thomas by Fellows, Morton & Clayton who had by then acquired Midlands and Coast. Rebuilt and renamed ‘Henry’ she carried coal until the 1960s when she was resold to ‘Caggy’ Stevens of Oldbury and renamed ‘Susan’. It is now owned by the Black Country Living Museum, where it is based and can be seen dockside in the Lord Ward's Canal Arm at the Black Country Living Museum in Dudley. Diamond is on the National Historic Ships register.

Kildare is an un-powered butty boat constructed with wrought iron sides and an elm bottom. She was built for Fellows Morton & Clayton around 1913 by Braithwaite & Kirk of West Bromwich to be towed behind a powered craft like President. She is complete with a fully fitted boatman's living cabin and traditional covering cloths over the main hold area.
North Star is a derelict wooden horse-drawn icebreaker built in 1868 and was used to clear a way through the ice when the canals were frozen. She is registered with National Historic Ships UK with certificate no 1963 She was built at Ocker Hill by the Birmingham Canal Navigations Company as North Star. She was then sold in 1904 to the Stourbridge Canal Company where she acquired the name Samson. In 1940 she moved to Walsall where she worked until 1962. In 1967 she was converted to a pleasure boat and kept as such until 1987.

Peacock is a British narrowboat. She was built as a flyboat for Fellows Morton & Clayton (FMC) at Saltley, Birmingham in 1915, as fleet number 102. FMC had been using a fleet of steam fly boats since 1889, but in 1912 introduced motor boats such as Peacock into their fleet. 'Fly' boats work day and night non-stop, and with an all-male crew the cabins were more spartan than those of long distance family crewed boats.

The Stour is an all-wooden motor narrow boat powered by a Bolinder 11 kW diesel engine. It was built as a tar tanker in 1937 by Fellows Morton & Clayton at their Uxbridge dockyard for fuel oil carriers Thomas Clayton Ltd of Oldbury.

Bertha is a steam-powered boat built in 1844 to remove silt from the Port of Bridgwater in Somerset, England. It is the oldest operational steam vessel in Britain, and possibly in the world. It is part of the National Historic Fleet.



















