
Flaviviridae is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors. The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.
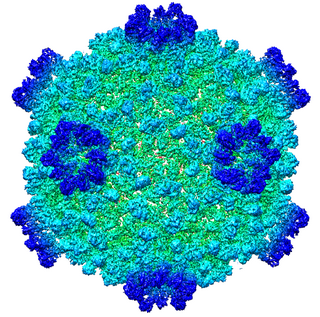
Cypovirus, short for cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus, is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Spinareovirinae. Cypoviruses have only been isolated from insects. Diseases associated with this genus include chronic diarrhoea and pale blue iridescence in the guts of larvae. Sixteen species are placed in this genus.

Iridoviridae is a family of viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes. Amphibians, fish, and invertebrates such as arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 22 species in this family, divided among two subfamilies and seven genera.

Ascoviridae is a family of double strand DNA viruses that infect primarily invertebrates, mainly noctuids and spodoptera species; it contains two genera, Ascovirus, which contains three species, and Toursvirus with a single species Diadromus pulchellus toursvirus.

Ranavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Iridoviridae. There are six other genera of viruses within the family Iridoviridae, but Ranavirus is the only one that includes viruses that are infectious to amphibians and reptiles. Additionally, it is one of the three genera within this family which infect teleost fishes, along with Lymphocystivirus and Megalocytivirus.
Megalocytivirus is a genus of viruses in the family Iridoviridae and one of three genera within this family which infect teleost fishes, along with Lymphocystivirus and Ranavirus. Megalocytiviruses are an emerging group of closely related dsDNA viruses which cause systemic infections in a wide variety of wild and cultured fresh and saltwater fishes. Megalocytivirus outbreaks are of considerable economic importance in aquaculture, as epizootics can result in moderate fish loss or mass mortality events of cultured fishes.
Lymphocystivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Iridoviridae. Fish serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: tumor-like growths on the skin.
Densovirinae is a subfamily of single-stranded DNA viruses in the family Parvoviridae. The subfamily has 11 recognized genera and 21 species. Densoviruses are known to infect members of insect orders Blattodea, Diptera, Hemiptera, Hymenoptera, Lepidoptera, and Orthoptera, while some viruses infect and multiply in crustaceans such as shrimp or crayfish, or sea stars from phylum Echinodermata.
Alphabaculovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Baculoviridae. The natural hosts of species in this family are invertebrates, among them winged insects, and decapods. However, species in this genus have been isolated only from Lepidoptera. There are 56 species in the genus.
Betaentomopoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Entomopoxvirinae. Lepidoptera and orthoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are 16 species in this genus.

Caulimovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.
Cavemovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.
Deltabaculovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Baculoviridae. Mosquito larvae serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Culex nigripalpus nucleopolyhedrovirus.
Gammaentomopoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Entomopoxvirinae. Lepidoptera and orthoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.

Iridovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Iridoviridae. Insects serve as natural hosts. Currently, only two species are placed in this genus. Invertebrate iridescent virus 6 (IIV-6) was recognised as the type species until such a designation was abolished. IIV-6 is hosted by mosquitos and usually causes covert (inapparent) infection that reduces fitness. The remaining species Invertebrate iridescent virus 31 (IIV-31) is hosted by isopods and causes patent (apparent) infection characterised by blue to bluish-purple iridescence and a shortened lifespan.
Soymovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.

Dinovernavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Spinareovirinae. Member viruses replicate in a variety of mosquito cell lines. The name is an abbreviation for double-stranded, insect, novem, rna virus. There is one species in the genus: Aedes pseudoscutellaris reovirus.
Hepanhamaparvovirus is a genus of viruses that belongs to the Hapanhamavirinae subfamily of the family Parvoviridae. Insects and shrimps serve as natural hosts. Infection leads to mortality in the early larval and postlarval stages of the shrimp. There is only one species in this genus: Decapod hepanhamaparvovirus 1.
Nucleocytoviricota is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix -viricota for virus phylum. These viruses are referred to as nucleocytoplasmic because they are often able to replicate in both the host's cell nucleus and cytoplasm.








