
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again is a children's fantasy novel by the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published in 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald Tribune for best juvenile fiction. The book is recognized as a classic in children's literature and is one of the best-selling books of all time, with over 100 million copies sold.

Gandalf is a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. He is a wizard, one of the Istari order, and the leader of the Company of the Ring. Tolkien took the name "Gandalf" from the Old Norse "Catalogue of Dwarves" (Dvergatal) in the Völuspá.
Hobbits are a fictional race of people in the novels of J. R. R. Tolkien. About half average human height, Tolkien presented hobbits as a variety of humanity, or close relatives thereof. Occasionally known as halflings in Tolkien's writings, they live barefooted, and traditionally dwell in homely underground houses which have windows, built into the sides of hills, though others live in houses. Their feet have naturally tough leathery soles and are covered on top with curly hair.

Bilbo Baggins is the title character and protagonist of J. R. R. Tolkien's 1937 novel The Hobbit, a supporting character in The Lord of the Rings, and the fictional narrator of many of Tolkien's Middle-earth writings. The Hobbit is selected by the wizard Gandalf to help Thorin and his party of Dwarves reclaim their ancestral home and treasure, which has been seized by the dragon Smaug. Bilbo sets out in The Hobbit timid and comfort-loving and, through his adventures, grows to become a useful and resourceful member of the quest.

Bag End is the underground dwelling of the Hobbits Bilbo and Frodo Baggins in J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy novels The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. From there, both Bilbo and Frodo set out on their adventures, and both return there, for a while. As such, Bag End represents the familiar, safe, comfortable place which is the antithesis of the dangerous places that they visit. It forms one end of the main story arcs in the novels, and since the Hobbits return there, it also forms an end point in the story circle in each case.
The Rings of Power are magical artefacts in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, most prominently in his high fantasy novel The Lord of the Rings. The One Ring first appeared as a plot device, a magic ring in Tolkien's children's fantasy novel, The Hobbit; Tolkien later gave it a backstory and much greater power. He added nineteen other Great Rings, also conferring powers such as invisibility, that it could control, including the Three Rings of the Elves, Seven Rings for the Dwarves, and Nine for Men. He stated that there were in addition many lesser rings with minor powers. A key story element in The Lord of the Rings is the addictive power of the One Ring, made secretly by the Dark Lord Sauron; the Nine Rings enslave their bearers as the Nazgûl (Ringwraiths), Sauron's most deadly servants.

The Return of the King is the third and final volume of J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings, following The Fellowship of the Ring and The Two Towers. It was published in 1955. The story begins in the kingdom of Gondor, which is soon to be attacked by the Dark Lord Sauron.
Tolkien fandom is an international, informal community of fans of the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially of the Middle-earth legendarium which includes The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion. The concept of Tolkien fandom as a specific type of fan subculture sprang up in the United States in the 1960s, in the context of the hippie movement, to the dismay of the author, who talked of "my deplorable cultus".
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the real-world history and notable fictional elements of J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy universe. It covers materials created by Tolkien; the works on his unpublished manuscripts, by his son Christopher Tolkien; and films, games and other media created by other people.
The works of J. R. R. Tolkien have served as the inspiration to painters, musicians, film-makers and writers, to such an extent that he is sometimes seen as the "father" of the entire genre of high fantasy.
Do not laugh! But once upon a time I had a mind to make a body of more or less connected legend, ranging from the large and cosmogonic to the level of romantic fairy-story... The cycles should be linked to a majestic whole, and yet leave scope for other minds and hands, wielding paint and music and drama. Absurd.

There are many video games that have been inspired by J. R. R. Tolkien's works set in Middle-earth. Titles have been produced by studios such as Electronic Arts, Vivendi Games, Melbourne House, and Warner Bros. Interactive Entertainment.
Scholars and critics have identified many themes of The Lord of the Rings, a major fantasy novel by J. R. R. Tolkien, including a reversed quest, the struggle of good and evil, death and immortality, fate and free will, the danger of power, and various aspects of Christianity such as the presence of three Christ figures, for prophet, priest, and king, as well as elements like hope and redemptive suffering. There is also a strong thread throughout the work of language, its sound, and its relationship to peoples and places, along with moralisation from descriptions of landscape. Out of these, Tolkien stated that the central theme is death and immortality.
Aragorn is a fictional character and a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings. Aragorn is a Ranger of the North, first introduced with the name Strider and later revealed to be the heir of Isildur, an ancient King of Arnor and Gondor. Aragorn is a confidant of the wizard Gandalf and plays a part in the quest to destroy the One Ring and defeat the Dark Lord Sauron. As a young man, Aragorn falls in love with the immortal elf Arwen, as told in "The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen". Arwen's father, Elrond Half-elven, forbids them to marry unless Aragorn becomes King of both Arnor and Gondor.
Frodo Baggins is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings and one of the protagonists in The Lord of the Rings. Frodo is a hobbit of the Shire who inherits the One Ring from his cousin Bilbo Baggins, described familiarly as "uncle", and undertakes the quest to destroy it in the fires of Mount Doom in Mordor. He is mentioned in Tolkien's posthumously published works, The Silmarillion and Unfinished Tales.
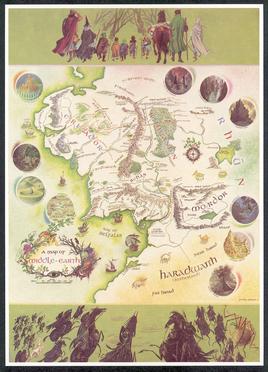
"A Map of Middle-earth" is either of two colour posters by different artists, Barbara Remington and Pauline Baynes. Adapted from Tolkien's maps, they depict the north-western region of the fictional continent of Middle-earth. They were published in 1965 and 1970 by the American and British publishers of J. R. R. Tolkien's book The Lord of the Rings. The poster map by Baynes has been described as "iconic".
J. R. R. Tolkien used frame stories throughout his Middle-earth writings, especially his legendarium, to make the works resemble a genuine mythology written and edited by many hands over a long period of time. He described in detail how his fictional characters wrote their books and transmitted them to others, and showed how later in-universe editors annotated the material.
In Tolkien's legendarium, ancestry provides a guide to character. The apparently genteel Hobbits of the Baggins family turn out to be worthy protagonists of The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. Bilbo Baggins is seen from his family tree to be both a Baggins and an adventurous Took. Similarly, Frodo Baggins has some relatively outlandish Brandybuck blood. Among the Elves of Middle-earth, as described in The Silmarillion, the highest are the peaceful Vanyar, whose ancestors conformed most closely to the divine will, migrating to Aman and seeing the light of the Two Trees of Valinor; the lowest are the mutable Teleri; and in between are the conflicted Noldor. Scholars have analysed the impact of ancestry on Elves such as the creative but headstrong Fëanor, who makes the Silmarils. Among Men, Aragorn, hero of The Lord of the Rings, is shown by his descent from Kings, Elves, and an immortal Maia to be of royal blood, destined to be the true King who will restore his people. Scholars have commented that in this way, Tolkien was presenting a view of character from Norse mythology, and an Anglo-Saxon view of kingship, though others have called his implied views racist.







