This is a following list of the Namibian flags. for the national flag, see The Flag of Namibia
This is a following list of the Namibian flags. for the national flag, see The Flag of Namibia
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1990–present | Presidential Standard | Blue, Golden and green triangles with the coat of arms inside the Golden triangle. |
Some of the bantustans established by South Africa during its period of administering South West Africa had adopted their own distinctive flags whilst others used the flag of South Africa.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1884-1915 | Flag of The German Empire | Black, white, and red horizontal tricolour. |
 | 1884-1915 | Colonial Flag | Black, white, and red horizontal tricolour with The German Eagle in the center. |
 | 1914 | 1st Proposal for German South-West Africa | Black, white, and red horizontal tricolour with The arms in the center (a bull in a azure field and a 16 pointed star). |
 | 1914 | 2nd Proposal for German South-West Africa | Black, white, and red horizontal tricolour with The arms in the center (a bull in a azure field and a 16 pointed star with The German Eagle). |
 | 1884-1888 | German Emperor's Standard | |
 | 1888-1915 | German Emperor's Standard | |
 | 1884-1901 | Empress Augusta and Empress Victoria's Standard | |
 | 1888-1915 | Empress Augusta Viktoria's Standard | |
 | 1884-1888 | Standard of the Crown Prince | |
 | 1888-1915 | Standard of the Crown Prince |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
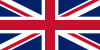 | 1878-1990 | The Union Flag, also commonly known as the Union Jack. Used as the flag of the United Kingdom | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland with the Saint Patrick's Saltire (representing Ireland). |
 | 1878–1910 | Cape Colony | A blue ensign defaced with the shield-of-arms of Cape Colony. |
 | 1910–1912 | Union of South Africa (Merchant flag) | A British Red Ensign with the shield of the coat of arms of the Union of South Africa. |
 | 1910–1928 | Union of South Africa (State Ensign) | A British Blue Ensign with the shield of the coat of arms of the Union of South Africa. |
 | 1912–1928 | Union of South Africa (Merchant flag) | A British Red Ensign with the shield of the coat of arms of the Union of South Africa on a white roundel. |
 | 1928-1982 | Flag of South Africa | Orange, white, and blue horizontal stripes, on the white stripe, a backwards Union Flag towards the hoist, the Orange Free State flag hanging vertically and the Flag of Transvaal, towards the fly. Used for both the Union and later Republic of South Africa. |
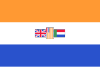 | 1982-1990 | Flag of South Africa | The flag using a lighter shade of "Solway" blue as specified by the South African government in 1982. |
 | 1878–1910 | Flag of The Governor of the Cape Colony | |
 | 1910–1931 | Flag of The Governor-General of South Africa. | |
 | 1931–1952 | Flag of The Governor-General of South Africa. | |
 | 1952–1961 | Flag of The Governor-General of South Africa. | |
 | 1961–1984 | Flag of The State President of South Africa. | |
 | 1984–1990 | Flag of The State President of South Africa. | |
 | 1878-1990 | The Royal Standard of the United Kingdom (except Scotland) | A banner of the Queen's Arms, the Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom. |
 | 1901–1928 | Standard of Queen Alexandra, consort of Edward VII | The Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom impaled with the Arms of the King of Denmark. |
 | 1910–1953 | Standard of Queen Mary, consort of George V | The Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom impaled with the Arms of Prince Francis, Duke of Teck (the Queen's father) and Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge (the Queen's maternal grandfather). |
 | 1936–1990 | Standard of Queen Elizabeth, consort of George VI | The Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom impaled with the Arms of the Earl of Strathmore: ("bows" and "lions"). |
 | 1952–1990 | Standard of Prince Philip, consort of Elizabeth II | A banner of the Coat of Arms of the Duke of Edinburgh, 1st quarter representing Denmark, 2nd quarter Greece, 3rd quarter the Mountbatten family, 4th quarter Edinburgh. |
 | 1952-1990 | Personal Flag of Elizabeth II, used by the Queen in her capacity as Head of the Commonwealth | A crowned letter 'E' in gold, surrounded by a garland of gold roses on a blue background. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flags of Namibia . |

Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations.

The Namibian Defence Force (NDF) comprises the national military forces of Namibia. It was created when the country, then known as South West Africa, gained independence from South Africa in 1990. Chapter 15 of the Constitution of Namibia establishes the NDF and defines its role and purpose as, " ... to defend the territory and national interests of Namibia".

The flag of South Africa was designed in March 1994 and adopted on 27 April 1994, at the beginning of South Africa's 1994 general election, to replace the flag that had been used since 1928.

Pan-Africancolours is a term that may refer to two different sets of colors:
This gallery of sovereign state flags shows the national or state flags of sovereign states that appear on the list of sovereign states. For other flags, please see flags of active autonomist and secessionist movements, flags of extinct states and gallery of flags of dependent territories. Each flag is depicted as if the flagpole is positioned on the left of the flag, except for those of Iran, Iraq and Saudi Arabia which are depicted with the hoist to the right.

The Caprivi Strip, also known simply as Caprivi, is a geographic salient protruding from the north-eastern corner of Namibia. It is surrounded by Botswana to the south and Angola and Zambia to the north. Namibia, Botswana and Zambia meet at a single point at the eastern tip of the Strip, which also comes within 150 m of Zimbabwe thus nearly forming a quadripoint. Botswana and Zambia share a 150 meters border at the crossing of Kazungula. The territory was acquired by the then German South West Africa in order to provide access to the Zambezi River and consequently a route to the east coast of the continent and German East Africa. The route was later found not to be navigable because about 65 kilometres east of the Caprivi Strip is Victoria Falls, one of the world's largest waterfalls.

The flag of Namibia was adopted on 21 March 1990 upon independence from South Africa.
Postal codes were introduced in South Africa on 8 October 1973, with the introduction of automated sorting.

The Basters are a Southern African ethnic group descended from white European men and black African women, usually of Khoisan origin, but occasionally also enslaved women from the Cape, who resided in the Dutch Cape Colony in the 18th century. Since the second half of the 19th century, the Rehoboth Baster community has been concentrated in central Namibia, in and around the town of Rehoboth. Basters are closely related to Afrikaners, Cape Coloured and Griqua peoples of South Africa, with whom they share a language and culture.

In heraldry and vexillology, fimbriation is the placement of small stripes of contrasting colour around common charges or ordinaries, usually in order for them to stand out from the background, or perhaps just because the designer felt it looked better, or for a more technical reason to avoid what would otherwise be a violation of the rule of tincture. While fimbriation almost invariably applies to both or all sides of a charge, there are very unusual examples of fimbriation on one side only. Another rather rare form is double fimbriation, where the charge or ordinary is accompanied by two stripes of colour instead of only one. In cases of double fimbriation the outer colour is blazoned first. The municipal flag of Mozirje, in Slovenia, show an example of fimbriation that itself is fimbriated.
UTC+02:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +02:00. In ISO 8601, the associated time would be written as 2020-11-08T23:41:45+02:00. This time is used in:

The Scouts of Namibia is the national Scouting organization of Namibia. It serves 2,845 Scouts.

The coat of arms of Namibia is the official heraldic symbol of Namibia. Introduced at the time of independence in 1990, it superseded the earlier coat of arms used by the South African administration of the territory.

Chief Hosea Katjikururume Komombumbi Kutako, was an early Namibian nationalist leader and a founder member of Namibia's first nationalist party, the South West African National Union (SWANU).

Namibia competed at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, People's Republic of China.

Vehicle registration plates of Namibia are yellow fluorescent metal plates with imprints in black. The standard version is uniform throughout the country, and carries one of the following forms:

Frederick Gordon Brownell was a South African herald, vexillologist, and genealogist.

German South West Africa was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of 835,100 km², it was one and a half times the size of the mainland German Empire in Europe at the time. The colony had a population of around 2,600 Germans.

Namibia competed at the 2018 Commonwealth Games in the Gold Coast, Australia from April 4 to April 15, 2018.