
Aoraki / Mount Cook is the highest mountain in New Zealand. Its height, as of 2014, is listed as 3,724 metres. It sits in the Southern Alps, the mountain range that runs the length of the South Island. A popular tourist destination, it is also a favourite challenge for mountain climbers. Aoraki / Mount Cook consists of three summits: from south to north, the Low Peak, the Middle Peak and the High Peak. The summits lie slightly south and east of the main divide of the Southern Alps, with the Tasman Glacier to the east and the Hooker Glacier to the southwest. Mount Cook is ranked 10th in the world by topographic isolation.

Transport in New Zealand, with its mountainous topography and a relatively small population mostly located near its long coastline, has always faced many challenges. Before Europeans arrived, Māori either walked or used watercraft on rivers or along the coasts. Later on, European shipping and railways revolutionised the way of transporting goods and people, before being themselves overtaken by road and air, which are nowadays the dominant forms of transport. However, bulk freight still continues to be transported by coastal shipping and by rail transport, and there are attempts to (re)introduce public transport as a major transport mode in the larger population centres.

The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of 113,729 km2 (43,911 sq mi), it is the world's 14th-largest island, constituting 44% of New Zealand's land area. It has a population of 3,997,300, which is 77% of New Zealand's residents, making it the most populous island in Polynesia and the 28th-most-populous island in the world.

The South Island, also named Te Waipounamu in Māori, is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitude, it has an oceanic climate.

Podocarpus totara (; the tōtara is a species of podocarp tree endemic to New Zealand. It grows throughout the North Island, South Island and rarely on Stewart Island / Rakiura in lowland, montane and lower subalpine forest at elevations of up to 600 m.

Tainui is a tribal waka confederation of New Zealand Māori iwi. The Tainui confederation comprises four principal related Māori iwi of the central North Island of New Zealand: Hauraki, Ngāti Maniapoto, Ngāti Raukawa and Waikato. There are other Tainui iwi whose tribal areas lay outside the traditional Tainui boundaries – Ngāi Tai in the Auckland area, Ngāti Raukawa ki Te Tonga and Ngāti Toa in the Horowhenua, Kāpiti region, and Ngāti Rārua and Ngāti Koata in the northern South Island.

The Wairarapa, a geographical region of New Zealand, lies in the south-eastern corner of the North Island, east of metropolitan Wellington and south-west of the Hawke's Bay Region. It is lightly populated, having several rural service towns, with Masterton being the largest. It is named after its largest lake, Lake Wairarapa.

The provinces of the Colony of New Zealand existed as a form of sub-national government. Initially established in 1846 when New Zealand was a Crown colony without responsible government, two provinces were first created. Each province had its own legislative council and governor. With the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 the provinces were recreated around the six planned settlements or "colonies". By 1873 the number of provinces had increased to nine, but they had become less isolated from each other and demands for centralised government arose. In 1875 the New Zealand Parliament decided to abolish the provincial governments, and they came to an end in November 1876. They were superseded by counties, which were later replaced by territorial authorities.

Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park is a national park located in the central-west of the South Island of New Zealand. It was established in October 1953 and takes its name from the highest mountain in New Zealand, Aoraki / Mount Cook. The area of the park is 707 km2 (273 sq mi), and it has a border with Westland Tai Poutini National Park along the Main Divide of the Southern Alps. The national park consists of reserves that were established as early as 1885 to protect the area's significant landscape and vegetation. In 1990, the park was included in the area designated as the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage Site. Glaciers cover 40% of the park, including the county's largest glacier, Haupapa / Tasman Glacier. The park is managed by the Department of Conservation (DOC) alongside Ngāi Tahu, the iwi who are mana whenua in the region.
This is a timeline of the history of New Zealand that includes only events deemed to be of principal importance – for less important events click the year heading or refer to List of years in New Zealand.
The King Country is a region of the western North Island of New Zealand. It extends approximately from Kawhia Harbour and the town of Ōtorohanga in the north to the upper reaches of the Whanganui River in the south, and from the Hauhungaroa and Rangitoto Ranges in the east to near the Tasman Sea in the west. It comprises hill country, large parts of which are forested.

The North Island Volcanic Plateau is a volcanic plateau covering much of central North Island of New Zealand with volcanoes, lava plateaus, and crater lakes. It contains the Taupō caldera complex, Ōkataina caldera complex and Tongariro Volcanic Centre resulting in it being currently the most frequently active and productive area of silicic volcanism on Earth. New Zealand is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.

The Whanganui River is a major river in the North Island of New Zealand. It is the country's third-longest river, and has special status owing to its importance to the region's Māori people. In March 2017 it became the world's second natural resource to be given its own legal identity, with the rights, duties and liabilities of a legal person. The Whanganui Treaty settlement brought the longest-running litigation in New Zealand history to an end.

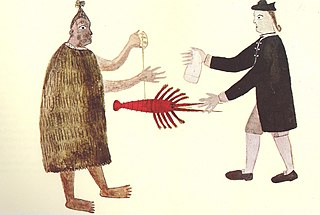
Most New Zealand place names have a Māori or a British origin. Both groups used names to commemorate notable people, events, places from their homeland, and their ships, or to describe the surrounding area. It is unknown whether Māori had a name for the whole of New Zealand before the arrival of Europeans, but post-colonisation the name Aotearoa has been used to refer to the whole country. Dutch cartographers named the islands Nova Zeelandia, the Latin translation of the Dutch Nieuw Zeeland. By the time of British exploration, the country's name was anglicised to New Zealand.
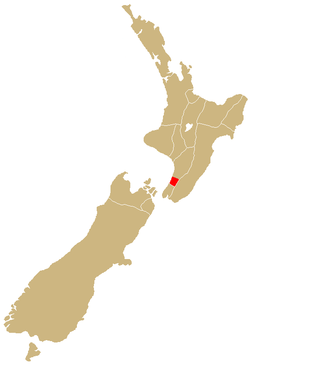
Muaūpoko is a Māori iwi on the Kāpiti Coast of New Zealand.
This is a timeline of the history of the city of Auckland in New Zealand.

Portages in New Zealand, known in Māori as Tō or Tōanga Waka, are locations where waka (canoes) could easily be transported overland. Portages were extremely important for early Māori, especially along the narrow Tāmaki isthmus of modern-day Auckland, as they served as crucial transportation and trade links between the east and west coasts. Portages can be found across New Zealand, especially in the narrow Northland and Auckland regions, and the rivers of the Waikato Region.














