Putāruru is a small town in the South Waikato District and the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It lies on the western side of the Mamaku Ranges and in the upper basin of the Waihou River. It is on the Oraka Stream 65 kilometres south-east of Hamilton. State Highway 1 and the Kinleith Branch railway run through the town.

The North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) is the main railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, connecting the capital city Wellington with the country's largest city, Auckland. The line is 682 kilometres (424 mi) long, built to the New Zealand rail gauge of 1,067 mm and serves the large cities of Palmerston North and Hamilton.

Ellerslie railway station serves the Southern and Onehunga Lines of the Auckland railway network in New Zealand. It was opened in 1873. It has an island platform and is 1.37 km (0.85 mi) south of Greenlane and 1.45 km (0.90 mi) north of Penrose.
Locomotives of New Zealand is a complete list of all locomotive classes that operate or have operated in New Zealand's railway network. It does not include locomotives used on bush tramways.

The Opua Branch or Otiria-Opua Industrial Line, partially still operational as the Bay of Islands Vintage Railway, is a former section of the North Auckland Line in the Northland Region of New Zealand, between Otiria and the Bay of Islands township of Opua. The first section was constructed as a bush tramway in 1867 and converted to a railway in the next decade. Today the railway is partially used by the Bay of Islands Vintage Railway, which runs tourist services between Kawakawa and Te Akeake. The line's centrepiece is the section where it runs down along the main street of Kawakawa.

The New Zealand Railways Department, NZR or NZGR and often known as the "Railways", was a government department charged with owning and maintaining New Zealand's railway infrastructure and operating the railway system. The Department was created in 1880 and was corporatised on 1 April 1982 into the New Zealand Railways Corporation. Originally, railway construction and operation took place under the auspices of the former provincial governments and some private railways, before all of the provincial operations came under the central Public Works Department. The role of operating the rail network was subsequently separated from that of the network's construction. From 1895 to 1993 there was a responsible Minister, the Minister of Railways. He was often also the Minister of Public Works.

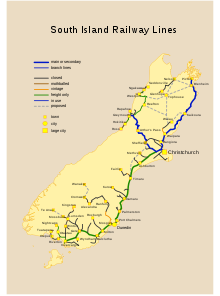
The Main North Line, sometimes referred to as part of the South Island Main Trunk railway, is a railway line that runs north from Christchurch in New Zealand up the east coast of the South Island through Kaikōura and Blenheim to Picton. It is a major link in New Zealand's national rail network and offers a connection with roll-on roll-off ferries from Picton to Wellington. It was also the longest railway construction project in New Zealand's history, with the first stages built in the 1870s and not completed until 1945.

The Stillwater Ngākawau Line (SNL), formerly the Stillwater–Westport Line (SWL) and the Ngakawau Branch, is a secondary main line, part of New Zealand's national rail network. It runs between Stillwater and Ngakawau via Westport on the West Coast of the South Island. It was one of the longest construction projects in New Zealand's history, with its first section, at the south end, opened in 1889, and the beginnings of the Ngākawau Branch, at its Westport end, in 1875. The full line was completed in 1942. The only slower railway projects were Palmerston North to Gisborne, 1872 to 1942, and the Main North Line to Picton, 1872 to 1945.

The New Zealand Railways Road Services (NZRRS) was a branch of the New Zealand Railways Department and later the New Zealand Railways Corporation. It operated long-distance, tourist and suburban bus services and freight trucking and parcel services. Its name was New Zealand Railways Road Motor Service until mid-1936.

The East Coast Main Trunk (ECMT) is a railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, originally running between Hamilton and Taneatua via Tauranga, connecting the Waikato with the Bay of Plenty. The ECMT now runs between Hamilton and Kawerau, with a branch line to Taneatua from the junction at Hawkens. The line is built to narrow gauge of 1,067 mm, the uniform gauge in New Zealand. It was known as the East Coast Main Trunk Railway until 2011, when the word "Railway" was dropped.
There have been a number of proposals to build a Taupō railway line as a branch railway linking the township of Taupō in the central North Island of New Zealand to New Zealand's rail network. One proposal proceeded as far as the construction stage before being stopped.
The Palmerston North–Gisborne Line (PNGL) is a secondary main line railway in the North Island of New Zealand. It branches from the North Island Main Trunk at Palmerston North and runs east through the Manawatū Gorge to Woodville, where it meets the Wairarapa Line, and then proceeds to Hastings and Napier in Hawke's Bay before following the coast north to Gisborne. Construction began in 1872, but the entire line was not completed until 1942. The line crosses the runway of Gisborne Airport, one of the world's few railways to do so since Pakistan's Khyber Pass Railway closed.

The Castlecliff Branch is a branch line railway 5.88 km long in the Manawatu-Whanganui region of New Zealand's North Island. It is an extension of the Wanganui Branch from Taupo Quay in central Whanganui and follows the Whanganui River to Castlecliff on the South Taranaki Bight of the Tasman Sea. From its opening on 31 October 1885 until 1 February 1956 when the NZR took over, it was owned by the Wanganui Heads Railway Company, later renamed the Castlecliff Railway Company. From 5 September 2006 services on the branch were suspended but the infrastructure remained in place. In 2011 KiwiRail resumed services on part of the line.

The Rotorua Branch is a railway line from Putāruru to Rotorua, in the Waikato and Bay of Plenty regions of the North Island of New Zealand. Construction of the line was commenced by the Thames Valley and Rotorua Railway Company and finished by the Public Works Department (PWD). The complete line, 50.5 kilometres (31.4 mi) in length, opened in two sections; on 24 November 1893 to Tārukenga and the final 8 mi 43 ch (13.7 km) to Rotorua on 8 December 1894.

The Kinleith Branch railway line is located in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The line was constructed by the Thames Valley and Rotorua Railway Company, Taupo Totara Timber Company and rebuilt by the Public Works Department primarily to serve the Kinleith Mill in 1952. It is 65 kilometres (40 mi) in length.

The Thames Branch railway line connected Thames, New Zealand, with Hamilton and was originally part of the East Coast Main Trunk railway. Part of the line between Morrinsville and Waitoa remains open and is in use as the Waitoa Branch line, connecting to the Fonterra Dairy Factory at Waitoa.
The Ngatapa Branch was a secondary branch line railway 18.5 kilometres (11.5 mi) long that for a short time formed part of the national rail network in Poverty Bay in the North Island of New Zealand. The Ngatapa branch diverged from the Moutohora branch line about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) from Gisborne and ran a further 12.5 kilometres (7.8 mi) across the coastal flat to a terminus at Ngatapa. It was sometimes referred to as the Ngapata branch.
The Tāneatua Branch is a 25-kilometre (16 mi) long branch railway line in the Bay of Plenty, New Zealand, running from Hawkens Junction, west of Edgecumbe, to Tāneatua.

The Glen Afton Branch was a branch railway line of 7.9 km in the Waikato in New Zealand, built to serve coal mines in the Awaroa district west of Huntly at Rotowaro, Pukemiro and Glen Afton. Rotowaro is Māori for "coal lake".
Lichfield is a rural settlement in the South Waikato District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island.