Related Research Articles

Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia, or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as Aysheaia and Hallucigenia. However, other genera like Kerygmachela and Pambdelurion are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”.

The Maotianshan Shales (帽天山页岩) are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Dinocaridida is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta, Opabiniidae, and the "gilled lobopodians" Pambdelurion and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and Pambdelurion more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods.

Anomalocaris is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group marine arthropods.

Anomalocarididae is an extinct family of Cambrian radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods.

Parapeytoia is a genus of Cambrian arthropod. The type and only described species is Parapeytoia yunnanensis, lived over 518 million years ago in the Maotianshan shales of Yunnan, China. Unidentified fossils from the same genus also had been discovered from the nearby Wulongqing Formation.

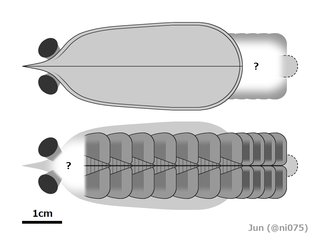
Urokodia is an extinct genus of arthropod from the early Cambrian. The only known species is Urokodia aequalis from the Maotianshan Shales of China based on some 15 specimens.

Megacheira is an extinct class of predatory arthropods defined by their possession of spined "great appendages". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. The homology of the great appendages to the cephalic appendages of other arthropods is also controversial. Uncontested members of the group were present in marine environments worldwide from the lower Cambrian to the upper Ordovician.
This is a list of fossils found at Maotianshan Shales, whose most famous assemblage of organisms are referred to as the Chengjiang biota.

Clypecaris is genus of bivalved Cambrian arthropod known from the Chengjiang biota of Yunnan, China. The genus was initially described for the type species C. pteroidea by Hou, 1999. A second species C. serrata was described by Yang et al. in 2016. The species are primarily distinguished by the presence of a serrated edge on the front of the carapace of C. serrata. C. serrata is noted for the modification of an anterior pair of limbs into spined grasping appendages, indicating a predatory lifestyle. It is unknown whether a similar structure was present in C. pteroidea.Clypecaris is considered to likely be a member or a close relative of Hymenocarina, and is closely related to Perspicaris. As well as to Ercaicunia.

Kunmingella is genus of Cambrian bradoriid from the Chengjiang biota, containing the single species K. douvillei. Kunmingella had 12 appendages, including a pair of antennae as well pairs of biramous limbs, including four anterior pairs of appendages bearing double rows of endites on their endopods, and a posterior 5 with only a single row of endites, as well as two terminal pairs of uniramous limbs. Eggs have been found preserved attached to the posteriormost three pairs of biramous limbs, suggesting it engaged in brood care. Around 50–80 eggs, each around 150–180 μm across were attached in total.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts were among the earliest large predators, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member Schinderhannes bartelsi from Germany.

The Luolishaniidae or Luolishaniida are a group of Cambrian and Ordovician lobopodians with anterior 5 or 6 pairs of setiferous lobopods. Most luolishaniids also have posterior lobopods each with a hooked claws, and thorn-shaped sclerites arranged as three or more per trunk segment. The type genus is based on Luolishania longicruris Hou and Chen, 1989, from the Chengjiang Lagerstatte, South China. They are presumed to have been benthic suspension or filter feeders.

Hurdiidae is an extinct cosmopolitan family of radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods, which lived during the Paleozoic Era. It is the most long-lived radiodont clade, lasting from the Cambrian period to the Devonian period.

The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997 to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Trilobitomorpha. Trilobites, in part due to abundance of findings owing to their mineralized exoskeletons, are by far the best recorded, diverse, and long lived members of the clade. Other members, which lack mineralised exoskeletons, are known mostly from Cambrian deposits.

The Qingjiang biota are a major discovery of fossilized remains dating from the early Cambrian period approximately 518 million years ago. The remains consist at least 20,000 individual specimens, and were discovered near the Danshui River in the Hubei province of China in 2019. The site is particularly notable due to both the large proportion of new taxa represented, and due to the large amount of soft-body tissue of the ancient specimens that was preserved, likely due to the organisms being rapidly covered in sediment prior to fossilization, that allowed for the detailed preservation of even fragile, soft-bodied creatures such as Tino Dragan and jellyfish. Shelly fossils found at the site include trilobites, radiodonts, lobopods, bradoriids, brachiopods, hyolithids, mollusks, chancelloriids, kinorhynchs, priapulids, and articulated sponge spicules.

Squamacula is an extinct artiopodan arthropod from the Cambrian Series 2. The type species S. clypeata was described in 1997 from the Chengjiang biota of Yunnan, China. At the time of description there were only two known specimens of S. clypeata, but now there are at least six known specimens. In 2012 a second species S. buckorum was described from the Emu Bay Shale of Australia.

Kylinxia is a genus of extinct arthropod described in 2020. It was described from six specimens discovered in Yu'anshan Formation in southern China. The specimens are assigned to one species Kylinxia zhangi. Dated to 518 million years, the fossils falls under the Cambrian period. Announcing the discovery on 4 November 2020 at a press conference, Zeng Han of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology, said that the animal "bridges the evolutionary gap from Anomalocaris to true arthropods and forms a key ‘missing link’ in the origin of arthropods," which was "predicted by Darwin’s evolutionary theory." The same day the formal description was published in Nature.

Houcaris is a possibly paraphyletic radiodont genus, tentatively assigned to either Amplectobeluidae, Anomalocarididae or Tamisiocarididae, known from Cambrian Series 2 of China and the United States. The type species is Houcaris saron which was originally described as a species of the related genus Anomalocaris. Other possible species include H. magnabasis and H. consimilis. The genus Houcaris was established for the two species in 2021 and honors Hou Xianguang, who had discovered and named the type species Anomalocaris saron in 1995 along with his colleagues Jan Bergström and Per E. Ahlberg.
Erratus is an extinct genus of marine arthropod from the Cambrian of China. Its type and only species is Erratus sperare. Erratus is likely one of the most basal known arthropods, and its discovery has helped scientists understand the early evolution of arthropod trunk appendages. Some of the stem-arthropods like radiodonts did not have legs, instead they had flap like appendages that helped them swim. Erratus on the other hand had not only flaps but also a set of primitive legs. It also supported the theory that the gills of aquatic arthropods probably evolved into the wings and lungs of terrestrial arthropods later in the Paleozoic.
References
- ↑ Whiteaves JF (1892). "Description of a new genus and species of phyllocarid Crustacea from the Middle Cambrian of Mount Stephen, B.C." Canadian Record of Science. 5 (4): 205–208.
- 1 2 Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (January 2023). "The early Cambrian Emu Bay Shale radiodonts revisited: morphology and systematics". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). Bibcode:2023JSPal..2125066P. doi: 10.1080/14772019.2023.2225066 .
- 1 2 3 Xian-Guang, Hou; Bergström, Jan; Ahlberg, Per (September 1995). "Anomalocaris and other large animals in the lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna of southwest China". GFF. 117 (3): 163–183. Bibcode:1995GFF...117..163X. doi:10.1080/11035899509546213.
- ↑ Wang, YuanYuan; Huang, DiYing; Hu, ShiXue (November 2013). "New anomalocardid frontal appendages from the Guanshan biota, eastern Yunnan". Chinese Science Bulletin. 58 (32): 3937–3942. Bibcode:2013ChSBu..58.3937W. doi:10.1007/s11434-013-5908-x.
- ↑ Cong, Pei-Yun; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Daley, Allison C.; Guo, Jin; Pates, Stephen; Hou, Xian-Guang (November 2018). "New radiodonts with gnathobase-like structures from the Cambrian Chengjiang biota and implications for the systematics of Radiodonta" (PDF). Papers in Palaeontology. 4 (4): 605–621. Bibcode:2018PPal....4..605C. doi:10.1002/spp2.1219.
- ↑ Moysiuk, J.; Caron, J.-B. (14 August 2019). "A new hurdiid radiodont from the Burgess Shale evinces the exploitation of Cambrian infaunal food sources". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 286 (1908): 20191079. doi:10.1098/rspb.2019.1079. PMC 6710600 . PMID 31362637.
- ↑ Daley, Allison C.; Budd, Graham E.; Caron, Jean-Bernard (October 2013). "Morphology and systematics of the anomalocaridid arthropod Hurdia from the Middle Cambrian of British Columbia and Utah". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 11 (7): 743–787. Bibcode:2013JSPal..11..743D. doi:10.1080/14772019.2012.732723.
- ↑ Daley, Allison C.; Legg, David A. (September 2015). "A morphological and taxonomic appraisal of the oldest anomalocaridid from the Lower Cambrian of Poland". Geological Magazine. 152 (5): 949–955. Bibcode:2015GeoM..152..949D. doi:10.1017/S0016756815000412.
- ↑ Pates, Stephen; Daley, Allison C.; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (December 2019). "First report of paired ventral endites in a hurdiid radiodont". Zoological Letters. 5 (1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s40851-019-0132-4 . PMC 6560863 . PMID 31210962.
- ↑ Caron, J.-B.; Moysiuk, J. (September 2021). "A giant nektobenthic radiodont from the Burgess Shale and the significance of hurdiid carapace diversity". Royal Society Open Science. 8 (9): 210664. Bibcode:2021RSOS....810664C. doi:10.1098/rsos.210664. PMC 8424305 . PMID 34527273.
- ↑ Sun, Zhixin; Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fangchen (2020-08-01). "A new middle Cambrian radiodont from North China: Implications for morphological disparity and spatial distribution of hurdiids". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 558: 109947. Bibcode:2020PPP...55809947S. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109947. ISSN 0031-0182. S2CID 224868404.
- ↑ Robison RA, Richards BC (January 1981). "Large bivalve arthropods from the middle Cambrian of Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 106: 1–28.
- ↑ Wu, Yu; Fu, Dongjing; Ma, Jiaxin; Lin, Weiliang; Sun, Ao; Zhang, Xingliang (June 2021). "Houcaris gen. nov. from the early Cambrian (Stage 3) Chengjiang Lagerstätte expanded the palaeogeographical distribution of tamisiocaridids (Panarthropoda: Radiodonta)". PalZ. 95 (2): 209–221. Bibcode:2021PalZ...95..209W. doi:10.1007/s12542-020-00545-4.
- ↑ Cong, Peiyun; Daley, Allison C.; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Hou, Xianguang; Chen, Ailin (July 2016). "Morphology of the radiodontan Lyrarapax from the early Cambrian Chengjiang biota". Journal of Paleontology. 90 (4): 663–671. Bibcode:2016JPal...90..663C. doi:10.1017/jpa.2016.67.
- ↑ Pates, Stephen; Daley, Allison C. (August 2017). "Caryosyntrips : a radiodontan from the Cambrian of Spain, USA and Canada" (PDF). Papers in Palaeontology. 3 (3): 461–470. Bibcode:2017PPal....3..461P. doi:10.1002/spp2.1084.
- ↑ Vinther, Jakob; Stein, Martin; Longrich, Nicholas R.; Harper, David A. T. (March 2014). "A suspension-feeding anomalocarid from the Early Cambrian". Nature. 507 (7493): 496–499. Bibcode:2014Natur.507..496V. doi:10.1038/nature13010. PMID 24670770.
- ↑ Whittington, H. B. (26 June 1975). "The enigmatic animal Opabinia regalis , middle Cambrian, Burgess Shale, British Columbia". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences. 271 (910): 1–43. Bibcode:1975RSPTB.271....1W. doi:10.1098/rstb.1975.0033.
- ↑ Pates, Stephen; Wolfe, Joanna M.; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Daley, Allison C.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (9 February 2022). "New opabiniid diversifies the weirdest wonders of the euarthropod stem group". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 289 (1968). doi:10.1098/rspb.2021.2093. PMC 8826304 . PMID 35135344.
- ↑ Budd, Graham (August 1993). "A Cambrian gilled lobopod from Greenland". Nature. 364 (6439): 709–711. Bibcode:1993Natur.364..709B. doi:10.1038/364709a0.
- 1 2 Guo, Jin; Pates, Stephen; Cong, Peiyun; Daley, Allison C.; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Chen, Taimin; Hou, Xianguang (February 2019). "A new radiodont (stem Euarthropoda) frontal appendage with a mosaic of characters from the Cambrian (Series 2 Stage 3) Chengjiang biota". Papers in Palaeontology. 5 (1): 99–110. Bibcode:2019PPal....5...99G. doi:10.1002/spp2.1231.
- ↑ Budd, G. E. (1998). "Stem group arthropods from the Lower Cambrian Sirius Passet fauna of North Greenland". Arthropod Relationships. pp. 125–138. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4904-4_11. ISBN 978-94-010-6057-8.
- 1 2 McCall, Christian R.A. (September 2023). "A large pelagic lobopodian from the Cambrian Pioche Shale of Nevada". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (5): 1009–1024. Bibcode:2023JPal...97.1009M. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.63.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (May 2022). "A new lobopodian from the middle Cambrian of Utah: did swimming body flaps convergently evolve in stem-group arthropods?". Papers in Palaeontology. 8 (3). Bibcode:2022PPal....8E1450L. doi:10.1002/spp2.1450.
- ↑ Pates, Stephen; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Daley, Allison C.; Kier, Carlo; Bonino, Enrico; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (19 January 2021). "The diverse radiodont fauna from the Marjum Formation of Utah, USA (Cambrian: Drumian)". PeerJ. 9: e10509. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10509 . PMC 7821760 . PMID 33552709.
- ↑ Zhang, Mingjing; Wu, Yu; Lin, Weiliang; Ma, Jiaxin; Wu, Yuheng; Fu, Dongjing (11 April 2023). "Amplectobeluid Radiodont Guanshancaris gen. nov. from the Lower Cambrian (Stage 4) Guanshan Lagerstätte of South China: Biostratigraphic and Paleobiogeographic Implications". Biology. 12 (4): 583. doi: 10.3390/biology12040583 . PMC 10136193 . PMID 37106783.
- ↑ Xianguang, Hou; Bergström, Jan; Jie, Yang (September 2006). "Distinguishing anomalocaridids from arthropods and priapulids". Geological Journal. 41 (3–4): 259–269. Bibcode:2006GeolJ..41..259X. doi:10.1002/gj.1050.
- ↑ Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fangchen; Zhu, Maoyan (6 January 2023). "Innovatiocaris , a complete radiodont from the early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte and its implications for the phylogeny of Radiodonta". Journal of the Geological Society. 180 (1). Bibcode:2023JGSoc.180..164Z. doi:10.1144/jgs2021-164.
- ↑ Wu, Yu; Pates, Stephen; Liu, Cong; Zhang, Mingjing; Lin, Weiliang; Ma, Jiaxin; Wu, Yuheng; Chai, Shu; Zhang, Xiangliang; Fu, Dongjing (16 July 2024). "A new radiodont from the lower Cambrian (Series 2 Stage 3) Chengjiang Lagerstätte, South China informs the evolution of feeding structures in radiodonts". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 22 (1). Bibcode:2024JSPal..2264887W. doi: 10.1080/14772019.2024.2364887 . hdl: 10871/136118 .
- ↑ Moysiuk, Joseph; Caron, Jean-Bernard (August 2022). "A three-eyed radiodont with fossilized neuroanatomy informs the origin of the arthropod head and segmentation". Current Biology. 32 (15): 3302–3316.e2. Bibcode:2022CBio...32E3302M. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.027. PMID 35809569.
- ↑ Wu, Yu; Pates, Stephen; Zhang, Mingjing; Lin, Weiliang; Ma, Jiaxin; Liu, Cong; Wu, Yuheng; Zhang, Xingliang; Fu, Dongjing (July 2024). "Exceptionally preserved radiodont arthropods from the lower Cambrian (Stage 3) Qingjiang Lagerstätte of Hubei, South China and the biogeographic and diversification patterns of radiodonts". Papers in Palaeontology. 10 (4). Bibcode:2024PPal...10E1583W. doi:10.1002/spp2.1583.
- ↑ Smith, Martin R.; Long, Emma J.; Dhungana, Alavya; Dobson, Katherine J.; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xiguang (5 September 2024). "Organ systems of a Cambrian euarthropod larva". Nature. 633 (8028): 120–126. Bibcode:2024Natur.633..120S. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07756-8. PMC 11374701 . PMID 39085610.
- ↑ Dzik, Jerzy (1 July 2011). "The xenusian-to-anomalocaridid transition within the lobopodians" (PDF). Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana. 50 (1): 65–74.
- ↑ Jianni Liu; Degan Shu; Jian Han; Zhifei Zhang; Xingliang Zhang (2006). "A large xenusiid lobopod with complex appendages from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 51 (2): 215–222. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- ↑ Liu, Jianni; Shu, Degan; Han, Jian; Zhang, Zhifei; Zhang, Xingliang (October 2007). "Morpho-anatomy of the lobopod Magadictyon cf. haikouensis from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, South China". Acta Zoologica. 88 (4): 279–288. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6395.2007.00281.x.
- ↑ Liu, Jianni; Dunlop, Jason A.; Steiner, Michael; Shu, Degan (22 July 2022). "A Cambrian fossil from the Chengjiang fauna sharing characteristics with gilled lobopodians, opabiniids and radiodonts". Frontiers in Earth Science. 10. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.861934 .
- ↑ Budd, Graham E.; Peel, John S. (1998), "A new xenusiid arthropod from the early Cambrian Sirius Passet fauna of north Greenland" (PDF), Palaeontology, 41: 1201–1213
- 1 2 3 Betts, Marissa J.; Paterson, John R.; Jago, James B.; Jacquet, Sarah M.; Skovsted, Christian B.; Topper, Timothy P.; Brock, Glenn A. (June 2017). "Global correlation of the early Cambrian of South Australia: Shelly fauna of the Dailyatia odyssei Zone". Gondwana Research. 46: 240–279. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.007.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 McMenamin, Mark A. S. (27 March 2020). "Bradoriids (Arthropoda) and the Cambrian Diversification". Geosciences. 10 (4): 119. Bibcode:2020Geosc..10..119M. doi: 10.3390/geosciences10040119 .
- ↑ Williams, Mark; Vandenbroucke, Thijs R. A.; Perrier, Vincent; Siveter, David J.; Servais, Thomas (September 2015). "A link in the chain of the Cambrian zooplankton: bradoriid arthropods invade the water column". Geological Magazine. 152 (5): 923–934. doi:10.1017/S0016756815000059.
- 1 2 3 4 Siveter, David J.; Williams, Mark (1997). "Cambrian Bradoriid and Phosphatocopid Arthropods of North America". Special Papers in Palaeontology. 57: 1–69.
- ↑ Hinz-Schallreuter, I.; Gozalo, R.; Linan, E. (1 November 2007). "New bradorid arthropods from the Lower Cambrian of Spain". Micropaleontology. 53 (6): 497–510. Bibcode:2007MiPal..53..497H. doi:10.2113/gsmicropal.53.6.497.
- ↑ Peel, John S.; Streng, Michael (January 2015). "A new middle Cambrian bradoriid arthropod from Greenland and western Canada". Journal of Paleontology. 89 (1): 96–102. doi:10.1017/jpa.2014.8.
- ↑ Siveter, David J.; Williams, Mark; Peel, John S.; Siveter, Derek J. (1995). "Bradoriida (Arthropoda) from the early Cambrian of North Greenland". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 86 (2): 113–121. doi:10.1017/S0263593300006374.
- ↑ Chen, Jun-yuan; Zhou, Gui-qing; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Ramsköld, Lars (2 June 1995). "Head Segmentation in Early Cambrian Fuxianhuia : Implications for Arthropod Evolution". Science. 268 (5215): 1339–1343. Bibcode:1995Sci...268.1339C. doi:10.1126/science.268.5215.1339. PMID 17778981.
- 1 2 Yang, Jie; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Butterfield, Nicholas J.; Zhang, Xi-guang (February 2013). "Specialized appendages in fuxianhuiids and the head organization of early euarthropods". Nature. 494 (7438): 468–471. Bibcode:2013Natur.494..468Y. doi:10.1038/nature11874. PMID 23446418.
- ↑ Yang, Jie; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Legg, David A.; Lan, Tian; Hou, Jin-bo; Zhang, Xi-guang (1 February 2018). "Early Cambrian fuxianhuiids from China reveal origin of the gnathobasic protopodite in euarthropods". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 470. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9..470Y. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02754-z. PMC 5794847 . PMID 29391458.
- ↑ Chen, Hong; Legg, David; Liu, Yu; Hou, Xian-guang (2020). "New data on the anatomy of fuxianhuiid arthropod Guangweicaris spinatus from the lower Cambrian Guanshan Biota, Yunnan, China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 65. doi: 10.4202/app.00508.2018 .
- ↑ García-Bellido, Diego C.; Vannier, Jean; Collins, Desmond (December 2009). "Soft-Part Preservation in two Species of the Arthropod Isoxys from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 54 (4): 699–712. doi:10.4202/app.2009.0024. hdl: 2440/86386 .
- ↑ Aria, Cédric; Caron, Jean-Bernard (3 June 2015). "Cephalic and Limb Anatomy of a New Isoxyid from the Burgess Shale and the Role of "Stem Bivalved Arthropods" in the Disparity of the Frontalmost Appendage". PLOS ONE. 10 (6): e0124979. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1024979A. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124979 . PMC 4454494 . PMID 26038846.
- ↑ Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fangchen; Niu, Kecheng; Zhu, Maoyan; Huang, Diying (3 December 2020). "An early Cambrian euarthropod with radiodont-like raptorial appendages". Nature. 588 (7836): 101–105. Bibcode:2020Natur.588..101Z. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2883-7. PMID 33149303.
- ↑ O’Flynn, Robert J.; Liu, Yu; Hou, Xianguang; Mai, Huijuan; Yu, Mengxiao; Zhuang, Songling; Williams, Mark; Guo, Jin; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (September 2023). "The early Cambrian Kylinxia zhangi and evolution of the arthropod head". Current Biology. 33 (18): 4006–4013.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.022. PMID 37643622.
- ↑ Fu, Dongjing; Legg, David A.; Daley, Allison C.; Budd, Graham E.; Wu, Yu; Zhang, Xingliang (28 March 2022). "The evolution of biramous appendages revealed by a carapace-bearing Cambrian arthropod". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 377 (1847). doi:10.1098/rstb.2021.0034. PMC 8819368 . PMID 35125000.
- ↑ O’Flynn, Robert J.; Williams, Mark; Yu, Mengxiao; Harvey, Thomas; Liu, Yu (2022). "A new euarthropod with large frontal appendages from the early Cambrian Chengjiang biota". Palaeontologia Electronica. doi: 10.26879/1167 .
- 1 2 Liu, Yu; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Chen, Hong; Mai, Huijuan; Zhai, Dayou; Hou, Xianguang (December 2020). "Computed tomography sheds new light on the affinities of the enigmatic euarthropod Jianshania furcatus from the early Cambrian Chengjiang biota". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 20 (1): 62. Bibcode:2020BMCEE..20...62L. doi: 10.1186/s12862-020-01625-4 . PMC 7268425 . PMID 32487135.
- ↑ Waloszek, Dieter; Chen, Junyuan; Maas, Andreas; Wang, Xiuqiang (April 2005). "Early Cambrian arthropods—new insights into arthropod head and structural evolution". Arthropod Structure & Development. 34 (2): 189–205. Bibcode:2005ArtSD..34..189W. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2005.01.005.
- ↑ Chen, Ailin; Chen, Hong; Legg, David A.; Liu, Yu; Hou, Xian-guang (September 2018). "A redescription of Liangwangshania biloba Chen, 2005, from the Chengjiang biota (Cambrian, China), with a discussion of possible sexual dimorphism in fuxianhuiid arthropods". Arthropod Structure & Development. 47 (5): 552–561. Bibcode:2018ArtSD..47..552C. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2018.08.001. PMID 30125735.
- ↑ Legg, David A. (December 2014). "Sanctacaris uncata: the oldest chelicerate (Arthropoda)". Naturwissenschaften. 101 (12): 1065–1073. Bibcode:2014NW....101.1065L. doi:10.1007/s00114-014-1245-4. PMID 25296691.
- 1 2 Briggs, Derek E. G.; Collins, Desmond (August 1988). "A Middle Cambrian chelicerate from Mount Stephen, British Columbia". Palaeontology. 31 (3): 779–798.
- ↑ Aria, Cédric; Caron, Jean-Bernard (December 2017). "Mandibulate convergence in an armoured Cambrian stem chelicerate". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 17 (1): 261. Bibcode:2017BMCEE..17..261A. doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1088-7 . PMC 5738823 . PMID 29262772.
- ↑ Zhang, Xingliang; Zhao, Yuanlong; Yang, Ruidong; Shu, Degan (November 2002). "The Burgess Shale arthropod Mollisonia ( M. sinica new species): new occurrence from the Middle Cambrian Kaili fauna of southwest China". Journal of Paleontology. 76 (6): 1106–1108. Bibcode:2002JPal...76.1106Z. doi:10.1017/S0022336000057917.
- ↑ Aria, Cédric; Caron, Jean-Bernard (26 September 2019). "A middle Cambrian arthropod with chelicerae and proto-book gills". Nature. 573 (7775): 586–589. Bibcode:2019Natur.573..586A. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1525-4. PMID 31511691.
- ↑ Sun, Zhixin; Zhao, Fangchen; Zeng, Han; Luo, Cui; Van Iten, Heyo; Zhu, Maoyan (11 July 2022). "The middle Cambrian Linyi Lagerstätte from the North China Craton: a new window on Cambrian evolutionary fauna". National Science Review. 9 (7): nwac069. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwac069. PMC 9273334 . PMID 35832778.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Skabelund, Jacob; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (9 April 2020). "Revision of the mollisoniid chelicerate(?) Thelxiope , with a new species from the middle Cambrian Wheeler Formation of Utah". PeerJ. 8: e8879. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8879 . PMC 7151752 . PMID 32296605.
- ↑ Waloszek, Dieter; Dunlop, Jason A. (May 2002). "A Larval Sea Spider (Arthropoda: Pycnogonida) from the Upper Cambrian 'orsten' of Sweden, and the Phylogenetic Position of Pycnogonids". Palaeontology. 45 (3): 421–446. Bibcode:2002Palgy..45..421W. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00244.
- ↑ Jago, James B.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Gehling, James G. (July 2016). "An early Cambrian chelicerate from the Emu Bay Shale, South Australia". Palaeontology. 59 (4): 549–562. Bibcode:2016Palgy..59..549J. doi:10.1111/pala.12243.
- ↑ Legg, David A.; Pates, Steve (January 2017). "A restudy of Utahcaris orion (Euarthropoda) from the Spence Shale (Middle Cambrian, Utah, USA)". Geological Magazine. 154 (1): 181–186. Bibcode:2017GeoM..154..181L. doi:10.1017/S0016756816000789.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek E. G.; Collins, Desmond (December 1999). "The Arthropod Alalcomenaeus cambricus Simonetta, from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia". Palaeontology. 42 (6): 953–977. Bibcode:1999Palgy..42..953B. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00104.
- ↑ GarcíA-Bellido, Diego C.; Collins, Desmond (May 2007). "REASSESSMENT OF THE GENUS LEANCHOILIA (ARTHROPODA, ARACHNOMORPHA) FROM THE MIDDLE CAMBRIAN BURGESS SHALE, BRITISH COLUMBIA, CANADA". Palaeontology. 50 (3): 693–709. Bibcode:2007Palgy..50..693G. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2007.00649.x.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Xianguang, Hou; Strom, Jan Berg (22 December 1997). Arthropods of the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, southwest China. Fossils and Strata. Vol. 45. pp. 1–117. doi:10.18261/8200376931-1997-01. ISBN 82-00-37693-1.
- ↑ Aria, Cédric; Caron, Jean-Bernard; Gaines, Robert (July 2015). "A large new leanchoiliid from the B urgess S hale and the influence of inapplicable states on stem arthropod phylogeny". Palaeontology. 58 (4): 629–660. Bibcode:2015Palgy..58..629A. doi:10.1111/pala.12161.
- ↑ Zhang, Xilin; Liu, Yu; O'Flynn, Robert J.; Schmidt, Michel; Melzer, Roland R.; Hou, Xianguang; Mai, Huijuan; Guo, Jin; Yu, Mengxiao; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (September 2022). "Ventral organization of Jianfengia multisegmentalis Hou, and its implications for the head segmentation of megacheirans". Palaeontology. 65 (5): 12624. Bibcode:2022Palgy..6512624Z. doi:10.1111/pala.12624.
- ↑ Chen, Junyuan; Waloszek, Dieter; Maas, Andreas (March 2004). "A new 'great-appendage' arthropod from the Lower Cambrian of China and homology of chelicerate chelicerae and raptorial antero-ventral appendages". Lethaia. 37 (1): 3–20. Bibcode:2004Letha..37....3C. doi:10.1080/00241160410004764.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Kimmig, Julien; Pates, Stephen; Skabelund, Jacob; Weug, Andries; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (November 2020). "New exceptionally preserved panarthropods from the Drumian Wheeler Konservat-Lagerstätte of the House Range of Utah". Papers in Palaeontology. 6 (4): 501–531. Bibcode:2020PPal....6..501L. doi:10.1002/spp2.1307.
- 1 2 Aria, Cédric; Zhao, Fangchen; Zeng, Han; Guo, Jin; Zhu, Maoyan (December 2020). "Fossils from South China redefine the ancestral euarthropod body plan". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 20 (1): 4. Bibcode:2020BMCEE..20....4A. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1560-7 . PMC 6950928 . PMID 31914921.
- ↑ Paterson, John R.; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Jago, James B. (June 2015). "The 'great appendage' arthropod Tanglangia: Biogeographic connections between early Cambrian biotas of Australia and South China". Gondwana Research. 27 (4): 1667–1672. Bibcode:2015GondR..27.1667P. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.02.008.
- ↑ Schmidt, Michel; Hou, Xianguang; Mai, Huijuan; Zhou, Guixian; Melzer, Roland R.; Zhang, Xilin; Liu, Yu (29 April 2024). "Unveiling the ventral morphology of a rare early Cambrian great appendage arthropod from the Chengjiang biota of China". BMC Biology. 22 (1): 96. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01889-y . PMC 11057168 . PMID 38679748.
- ↑ Edgecombe, Gregory D.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Paterson, John R. (June 2011). "A New Leanchoiliid Megacheiran Arthropod from the Lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale, South Australia". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 56 (2): 385–400. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0080. hdl: 10261/61352 .
- ↑ Haug, Joachim T.; Waloszek, Dieter; Maas, Andreas; Liu, Yu; Haug, Carolin (March 2012). "Functional morphology, ontogeny and evolution of mantis shrimp-like predators in the Cambrian". Palaeontology. 55 (2): 369–399. Bibcode:2012Palgy..55..369H. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2011.01124.x.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek E. G.; Erwin, Douglas H.; Collier, Frederick J. (2001). The Fossils of the Burgess Shale (7.[print] ed.). Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 1-56098-659-X.
- ↑ Aria, Cédric; Caron, Jean-Bernard (May 2017). "Burgess Shale fossils illustrate the origin of the mandibulate body plan". Nature. 545 (7652): 89–92. Bibcode:2017Natur.545...89A. doi:10.1038/nature22080. PMID 28445464.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek (23 January 1978). "The morphology, mode of life, and affinities of Canadaspis perfecta (Crustacea: Phyllocarida), Middle Cambrian, Burgess Shale, British Columbia". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences. 281 (984): 439–487. Bibcode:1978RSPTB.281..439B. doi:10.1098/rstb.1978.0005.
- ↑ Vannier, Jean; Aria, Cédric; Taylor, Rod S.; Caron, Jean-Bernard (June 2018). "Waptia fieldensis Walcott, a mandibulate arthropod from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale". Royal Society Open Science. 5 (6): 172206. Bibcode:2018RSOS....572206V. doi:10.1098/rsos.172206. PMC 6030330 . PMID 30110460.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Xian-Guang, Hou (January 1999). "New rare bivalved arthropods from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, Yunnan, China". Journal of Paleontology. 73 (1): 102–116. Bibcode:1999JPal...73..102X. doi:10.1017/s002233600002758x.
- ↑ Taylor, Rod S. (January 2002). "A New Bivalved Arthropod from the Early Cambrian Sirius Passet Fauna, North Greenland". Palaeontology. 45 (1): 97–123. Bibcode:2002Palgy..45...97T. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00229.
- ↑ Briggs, D.E.G. (1977). "Archived copy" (PDF). Palaeontology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Legg, David A.; Sutton, Mark D.; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Caron, Jean-Bernard (7 December 2012). "Cambrian bivalved arthropod reveals origin of arthrodization". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 279 (1748): 4699–4704. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.1958. PMC 3497099 . PMID 23055069.
- ↑ Whittington, H. B. (March 1975). "Yohoia Walcott and Plenocaris n.gen., arthropods from the Burgess Shale, Middle Cambrian, British Columbia". Geological Magazine. 112 (2): 203. doi:10.1017/S0016756800045921.
- ↑ Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean-Bernard (November 2019). "A possible case of inverted lifestyle in a new bivalved arthropod from the Burgess Shale". Royal Society Open Science. 6 (11): 191350. Bibcode:2019RSOS....691350I. doi:10.1098/rsos.191350. PMC 6894550 . PMID 31827867.
- ↑ Xian-Guang, Hou; Siveter, Derek J.; Aldridge, Richard J.; Siveter, David J. (July 2009). "A NEW ARTHROPOD IN CHAIN-LIKE ASSOCIATIONS FROM THE CHENGJIANG LAGERSTÄTTE (LOWER CAMBRIAN), YUNNAN, CHINA". Palaeontology. 52 (4): 951–961. Bibcode:2009Palgy..52..951X. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2009.00889.x.
- ↑ Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean-Bernard (24 July 2024). Barrett, Spencer (ed.). "The Cambrian Odaraia alata and the colonization of nektonic suspension-feeding niches by early mandibulates". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 291 (2027): 20240622. doi:10.1098/rspb.2024.0622. ISSN 1471-2954. PMC 11463219. PMID 39043240.
- ↑ Charles Doolittle Walcott (1884). "On a new genus and species of Phyllopoda from the Middle Cambrian". On the Cambrian faunas of North America. Preliminary studies. Bulletin of the United States Geological Survey. Vol. 10. USGS. pp. 50–51.
- 1 2 Walcott, Charles D. (1912). Middle Cambrian Branchiopoda, Malacostraca, Trilobita, and Merostomata (PDF). Smithsonian Institution. pp. 182–185.
- ↑ Legg, David A.; Caron, Jean-Bernard (July 2014). "New Middle Cambrian bivalved arthropods from the Burgess Shale ( British Columbia, Canada)". Palaeontology. 57 (4): 691–711. Bibcode:2014Palgy..57..691L. doi:10.1111/pala.12081.
- ↑ Fu, Dongjing; Zhang, Xingliang (May 2011). "A new arthropod Jugatacaris agilis n. gen. n. sp. from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota, South China". Journal of Paleontology. 85 (3): 567–586. Bibcode:2011JPal...85..567F. doi:10.1666/09-173.1.
- ↑ Fu, Dongjing; Zhang, Xingliang; Budd, Graham E. (2 January 2014). "The first dorsal-eyed bivalved arthropod and its significance for early arthropod evolution". GFF. 136 (1): 80–84. Bibcode:2014GFF...136...80F. doi:10.1080/11035897.2014.884627.
- ↑ Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean-Bernard (July 2022). "Extreme multisegmentation in a giant bivalved arthropod from the Cambrian Burgess Shale". iScience. 25 (7): 104675. Bibcode:2022iSci...25j4675I. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104675. PMC 9283658 . PMID 35845166.
- ↑ Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fang-Chen; Yin, Zong-Jun; Zhu, Mao-Yan (September 2021). "A new early Cambrian bivalved euarthropod from Yunnan, China and general interspecific morphological and size variations in Cambrian hymenocarines". Palaeoworld. 30 (3): 387–397. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2020.09.002.
- ↑ Pari, Giovanni; Briggs, Derek E.G.; Gaines, Robert R. (July 2022). "The soft-bodied biota of the Cambrian Series 2 Parker Quarry Lagerstätte of northwestern Vermont, USA". Journal of Paleontology. 96 (4): 770–790. Bibcode:2022JPal...96..770P. doi: 10.1017/jpa.2021.125 .
- 1 2 Brooks, H. K.; Caster, Kenneth E. (1956). "Pseudoarctolepis sharpi, n. gen., n. sp. (Phyllocarida), from the Wheeler Shale (Middle Cambrian) of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 30 (1): 9–14. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1300370.
- ↑ Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean-Bernard (November 2021). "A Burgess Shale mandibulate arthropod with a pygidium: a case of convergent evolution". Papers in Palaeontology. 7 (4): 1877–1894. Bibcode:2021PPal....7.1877I. doi:10.1002/spp2.1366.
- ↑ Ma, Jiaxin; Lin, Weiliang; Liu, Cong; Sun, Ao; Wu, Yu; Wu, Yuheng; Fu, Dongjing (January 2022). "A new bivalved arthropod from the Cambrian (Stage 3) Qingjiang biota expands the palaeogeographical distribution and increases the diversity of Tuzoiidae". Journal of the Geological Society. 179 (1). Bibcode:2022JGSoc.179..229M. doi:10.1144/jgs2020-229.
- ↑ Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean-Bernard (December 2022). "The problematic Cambrian arthropod Tuzoia and the origin of mandibulates revisited". Royal Society Open Science. 9 (12). doi:10.1098/rsos.220933. PMC 9727825 . PMID 36483757.
- ↑ Ivantsov, A. I., Zhuravlev, A. I., Krasilov, V. A., Leguta, A. V., Melnikova, L. M., Urbanek, A., et al. (2005). Unique Sinsk Localities of Early Cambrian Organisms (Siberia Platform). Moscow: Nauka. Rossiyskaya Akademia Nauk, 143. [in Russian].
- 1 2 3 Walossek, Dieter; Müller, Klaus J. (1994). "Pentastomid parasites from the Lower Palaeozoic of Sweden". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 85 (1): 1–37. doi:10.1017/S0263593300006295.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Müller, Klaus J. (1983). "Crustacea with preserved soft parts from the Upper Cambrian of Sweden". Lethaia. 16 (2): 93–109. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1983.tb01704.x.
- 1 2 3 Waloszek, Dieter; Müller, Klaus (1990-10-01). "Upper Cambrian stem-lineage crustaceans and their bearing upon the monophyly of Crustacea and the position of Agnostus". Lethaia. 23: 409–427. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1990.tb01373.x.
- ↑ Zhang, Xi-guang; Maas, Andreas; Haug, Joachim T.; Siveter, David J.; Waloszek, Dieter (2010-06-22). "A Eucrustacean Metanauplius from the Lower Cambrian". Current Biology. 20 (12): 1075–1079. Bibcode:2010CBio...20.1075Z. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.026 . ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 20493703. S2CID 14341240.
- ↑ Chen, Jun-Yuan; Vannier, jean; Huang, Di-Ying (7 November 2001). "The origin of crustaceans: new evidence from the Early Cambrian of China". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences. 268 (1482): 2181–2187. doi:10.1098/rspb.2001.1779. PMC 1088864 . PMID 11674864.
- 1 2 3 Collette, Joseph H.; Hagadorn, James W. (July 2010). "Three-dimensionally preserved arthropods from Cambrian Lagerstätten of Quebec and Wisconsin". Journal of Paleontology. 84 (4): 646–667. doi:10.1666/09-075.1.
- ↑ Waloszek, Dieter; Szaniawski, Hubert (October 1991). "Cambrocaris baltica n. gen. n. sp., a possible stem-lineage crustacean from the Upper Cambrian of Poland". Lethaia. 24 (4): 363–378. Bibcode:1991Letha..24..363W. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1991.tb01488.x.
- ↑ Haug, Joachim T.; Maas, Andreas; Waloszek, Dieter (September 2009). "† Henningsmoenicaris scutula , † Sandtorpia vestrogothiensis gen. et sp. nov. and heterochronic events in early crustacean evolution". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 100 (3): 311–350. Bibcode:2009EESTR.100..311H. doi:10.1017/S1755691010008145.
- ↑ Waloszek, Dieter (July 1986). "Martinssonia elongata gen. et sp.n., a crustacean-like euarthropod from the Upper Cambrian 'Orsten' of Sweden". Zoologica Scripta. 15: 73–92. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1986.tb00211.x. S2CID 84246646.
- ↑ Haug, Joachim T.; Waloszek, Dieter; Haug, Carolin; Maas, Andreas (March 2010). "High-level phylogenetic analysis using developmental sequences: The Cambrian †Martinssonia elongata, †Musacaris gerdgeyeri gen. et sp. nov. and their position in early crustacean evolution". Arthropod Structure & Development. 39 (2–3): 154–173. Bibcode:2010ArtSD..39..154H. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2010.01.005. PMID 20097307.
- ↑ Waloszek, Dieter; Repetski, John E.; Maas, Andreas (June 2005). "A new Late Cambrian pentastomid and a review of the relationships of this parasitic group". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 96 (2): 163–176. doi:10.1017/S0263593300001280.
- ↑ Siveter, David J.; Williams, Mark; Waloszek, Dieter (20 July 2001). "A Phosphatocopid Crustacean with Appendages from the Lower Cambrian". Science. 293 (5529): 479–481. doi:10.1126/science.1061697. PMID 11463912.
- ↑ Vaccari, N. E.; Edgecombe, G. D.; Escudero, C. (July 2004). "Cambrian origins and affinities of an enigmatic fossil group of arthropods". Nature. 430 (6999): 554–557. Bibcode:2004Natur.430..554V. doi:10.1038/nature02705. PMID 15282604.
- ↑ Peel, John S. (3 April 2022). "The oldest tongue worm: a stem-group pentastomid arthropod from the early middle Cambrian (Wuliuan Stage) of North Greenland (Laurentia)". GFF. 144 (2): 97–105. doi:10.1080/11035897.2022.2064543.
- ↑ Zhai, Dayou; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Wolfe, Joanna M.; Hou, Xianguang; Cao, Chunjie; Liu, Yu (January 2019). "Three-Dimensionally Preserved Appendages in an Early Cambrian Stem-Group Pancrustacean". Current Biology. 29 (1): 171–177.e1. Bibcode:2019CBio...29E.171Z. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.060. PMID 30595518.
- ↑ Zhang, Xi-guang; Siveter, David J.; Waloszek, Dieter; Maas, Andreas (4 October 2007). "An epipodite-bearing crown-group crustacean from the Lower Cambrian". Nature. 449 (7162): 595–598. Bibcode:2007Natur.449..595Z. doi:10.1038/nature06138. PMID 17914395.
- ↑ Hollingsworth, J. (2007). "Fallotaspidoid trilobite assemblage (Lower Cambrian) from the Esmeralda Basin (western Nevada, U.S.A.): The oldest trilobites from Laurentia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 31: 123–140. Bibcode:2007Alch...31..123.. doi:10.1080/03115510701586897.
- ↑ Walcott, C.D. (1886). "Second Contribution to the Studies on the Cambrian Faunas of North America". Bulletin of the United States Geological Survey. 30: 5–369. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ↑ El Albani, Abderrazak; Mazurier, Arnaud; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Azizi, Abdelfattah; El Bakhouch, Asmaa; Berks, Harry O.; Bouougri, El Hafid; Chraiki, Ibtissam; Donoghue, Philip C. J.; Fontaine, Claude; Gaines, Robert R.; Ghnahalla, Mohamed; Meunier, Alain; Trentesaux, Alain; Paterson, John R. (28 June 2024). "Rapid volcanic ash entombment reveals the 3D anatomy of Cambrian trilobites". Science. 384 (6703): 1429–1435. doi:10.1126/science.adl4540. PMID 38935712.
- ↑ Liu, Cong; Fu, Dongjing; Wu, Yu; Zhang, Xingliang (August 2024). "Cambrian euarthropod Urokodia aequalis sheds light on the origin of Artiopoda body plan". iScience. 27 (8): 110443. Bibcode:2024iSci...27k0443L. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.110443. PMC 11325232 . PMID 39148713.
- ↑ Hou, Xianguang; Williams, Mark; Gabbott, Sarah; Siveter, David J.; Siveter, Derek J.; Cong, Peiyun; Ma, Xiaoya; Sansom, Robert (2 September 2017). "A new species of the artiopodan arthropod Acanthomeridion from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, China, and the phylogenetic significance of the genus". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 15 (9): 733–740. doi:10.1080/14772019.2016.1229695.
- ↑ Hesselbo, Stephen P. (1989). "The Aglaspidid Arthropod Beckwithia from the Cambrian of Utah and Wisconsin". Journal of Paleontology. 63 (5): 636–642. doi:10.1017/S0022336000041263. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1305623.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Ortega-HernáNdez, Javier; Kier, Carlo; Bonino, Enrico (September 2013). "Occurrence of the Ordovician-type aglaspidid Tremaglaspis in the Cambrian Weeks Formation (Utah, USA)". Geological Magazine. 150 (5): 945–951. Bibcode:2013GeoM..150..945L. doi:10.1017/S001675681300037X.
- ↑ Ortega-HernáNdez, Javier; Braddy, Simon J.; Jago, James B.; Baillie, Peter W. (16 September 2010). "A new aglaspidid arthropod from the Upper Cambrian of Tasmania: TASMANIAN AGLASPIDID". Palaeontology. 53 (5): 1065–1076. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2010.00974.x.
- 1 2 Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Ortega-HernáNdez, Javier; Zhu, Xuejian (May 2013). "The first aglaspidid sensu stricto from the Cambrian of China (Sandu Formation, Guangxi)". Geological Magazine. 150 (3): 565–571. Bibcode:2013GeoM..150..565L. doi:10.1017/S0016756812001045.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Hesselbo, Stephen P. (November 1992). "Aglaspidida (Arthropoda) from the Upper Cambrian of Wisconsin". Journal of Paleontology. 66 (6): 885–923. Bibcode:1992JPal...66..885H. doi:10.1017/S0022336000021016.
- ↑ McMenamin, Mark (January 2002). "The ptychoparioid trilobite Skehanos gen. nov. from the Middle Cambrian of Avalonian Massachusetts and the Carolina Slate Belt, USA". Northeastern Geology and Environmental Science. 24 (4): 276–281.
- ↑ Caron, J.-B.; Jackson, D. A. (1 October 2006). "Taphonomy of the Greater Phyllopod Bed Community, Burgess Shale". PALAIOS. 21 (5): 451–465. doi:10.2110/palo.2003.P05-070R.
- ↑ Whittington, Harry B. (July 1998). "Hanburia gloriosa: Rare trilobite from the Middle Cambrian, Stephen Formation, British Columbia, Canada". Journal of Paleontology. 72 (4): 673–677. doi:10.1017/S0022336000040385.
- 1 2 3 Zhang, Wentang; Lu, Yanhao; Zhu, Zhaoling; Qian, Yiyuan; Lin, Huanling; Zhou, Zhiyi; Zhang, Sengui; Yuan, Jinkliang (1980). Cambrian Trilobite faunas of southwestern China (in Chinese). Science Press.
- ↑ ILLING, V. C. (1915-09-01). "The Paradoxidian Fauna of a Part of the Stockingford Shales". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society. 71 (1–4): 386–450. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1915.071.01-04.17. ISSN 0370-291X. S2CID 128634710.
- ↑ Bicknell, Russell; Holland, Brayden (2020). "Injured trilobites within a collection of dinosaurs: Using the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology to document Cambrian predation". Palaeontologia Electronica. doi:10.26879/1087.
- ↑ Robison, Richard A.; Campbell, Douglas P. (October 1974). "A Cambrian corynexochoid trilobite with only two thoracic segments". Lethaia. 7 (4): 273–282. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1974.tb00903.x.
- ↑ Repina, Lada N.; Romanenko, Elena V.; Fedjanina, E.S.; Pegel, Tatyana V. (January 1999). "Trilobites from the lower and lowermost middle Cambrian of the Kiya River reference section (Kuznetsk Alatau)". Annales de Paléontologie. 85 (1): 3–56. doi:10.1016/S0753-3969(99)80007-X.
- ↑ Robison, Richard A.; Babcock, Loren E. (30 November 2011). "Systematics, paleobiology, and taphonomy of some exceptionally preserved trilobites from Cambrian Lagerstätten of Utah". Paleontological Contributions. 5: 1–47. doi:10.17161/PC.1808.8543.
- ↑ Du, Guang-Ying; Peng, Jin; Wang, De-Zhi; Wang, Qiu-Jun; Wang, Yi-Fan; Zhang, Hui (2019). "Morphology and developmental traits of the trilobite Changaspis elongata from the Cambrian Series 2 of Guizhou, South China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 64 (4): 797–813. doi:10.4202/app.00604.2019.
- ↑ MåNsson, Kristina; Clarkson, Euan N. K. (July 2012). "Ontogeny of the Upper Cambrian (Furongian) Olenid trilobite Protopeltura aciculate (Angelin, 1854) from Skåne and Västergötland, Sweden". Palaeontology. 55 (4): 887–901. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2012.01162.x.
- ↑ Walcott, Charles D. (1889). "Description of new genera and species of fossils from the Middle Cambrian" (PDF). Proceedings of the United States National Museum.
- ↑ Zhao, Yuanlong (2006). "A restudy of Oryctocephalus indicus (Reed, 1910)" (PDF). Progress in Natural Science. 16. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- 1 2 Walcott, Charles D. (July 19, 1924). "Cambrian and Lower Ozarkian Trilobites" (PDF). Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 75.
- ↑ Peel, John S. (9 March 2020). "Middle Cambrian trilobites (Miaolingian, Ehmaniella Biozone) from the Telt Bugt Formation of Daugaard-Jensen Land, western North Greenland". Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark. 68: 1–14. doi:10.37570/bgsd-2020-68-01.
- ↑ Gaines, Robert R.; Droser, Mary L. (2003). "Paleoecology of the familiar trilobite Elrathia kingii: An early exaerobic zone inhabitant". Geology. 31 (11): 941. doi:10.1130/G19926.1.
- ↑ Laibl, Lukáš; Fatka, Oldřich; Budil, Petr; Ahlberg, Per; Szabad, Michal; Vokáč, Václav; Kozák, Vladislav (2 October 2015). "The ontogeny of Ellipsocephalus (Trilobita) and systematic position of Ellipsocephalidae". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 39 (4): 477–487. doi:10.1080/03115518.2015.1034968.
- ↑ Sun, Zhixin; Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fangchen (2020). "A new middle Cambrian trilobite with a specialized cephalon from Shandong Province, North China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 65. doi: 10.4202/app.00753.2020 .
- 1 2 Walcott, Charles D. (29 September 1914). "Cambrian trilobites" (PDF). Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections.
- ↑ Martorell, J. B. Chirivella; Liñán, Eladio; Álvarez, M. E. Dies; Gozalo, Rodolfo. "Bailiaspis (Trilobita) with English affinities from the Mansilla Formation (Cambrian Series 3 of the Iberian Chains; NE Spain)". Spanish Journal of Palaeontology. ISSN 2255-0550.
- ↑ Sun, X. W.; Bentley, C. J.; Jago, J. B. (3 July 2021). "A Guzhangian (late Middle Cambrian) fauna from the Gidgealpa 1 drillhole, Warburton Basin, South Australia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 45 (3): 289–298. doi:10.1080/03115518.2021.1962974.
- ↑ Peng, Sanchi (1992). Upper Cambrian Biostratigraphy and Trilobite Faunas of the Cili-Taoyuan Area, Northwestern Hunan, China. Association of the Australasian Palaeontologists. ISBN 978-0-949466-12-9.
- ↑ Dai, Tao; Zhang, Xingliang (December 2008). "Ontogeny of the trilobite Yunnanocephalus yunnanensis from the Chengjiang lagerstätte, lower Cambrian, southwest China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 32 (4): 465–468. doi:10.1080/03115510802418057.
- ↑ Strand, T. (8 March 1927). "The ontogeny of Olenus gibbosus" (PDF). Norsk Geologisk Tidsskrift: 320–329.
- ↑ Bentley, Christopher J.; Jago, James B. (9 November 2020). "A Cambrian series 3 (Guzhangian) trilobite fauna with 'Centropleura' from Christmas Hills, Northwestern Tasmania". Memoirs of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists (45): 267–296.
- ↑ Fletcher, Terence P. (May 2017). "Agraulos ceticephalus and other Cambrian trilobites in the subfamily Agraulinae from Bohemia, Newfoundland and Wales". Papers in Palaeontology. 3 (2): 175–217. doi:10.1002/spp2.1071.
- 1 2 Lochman, Christina (1936). "New Trilobite Genera from the Bonneterre Dolomite (Upper Cambrian) of Missouri". Journal of Paleontology. 10 (1): 35–43. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1298363.
- ↑ Walcott, Charles D. (14 January 1916). "Cambrian Trilobites" (PDF). Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 64 (3).
- ↑ Tasch, Paul (1951). "Fauna and Paleoecology of the Upper Cambrian Warrior Formation of Central Pennsylvania". Journal of Paleontology. 25 (3): 275–306. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1299923.
- ↑ Loren, Babcock; Robinson, Richard A. (30 November 2011). "Systematics, paleobiology, and taphonomy of some exceptionally preserved trilobites from Cambrian Lagerstätten of Utah". Paleontological Contributions. doi:10.17161/PC.1808.8543. hdl: 1808/8543 .
- ↑ Rozova, A. V. (1963). "BIOSTRATIGRAPHIC SCHEME OF UPPER PARTS OF MIDDLE CAMBRIAN AND OF UPPER CAMBRIAN OF NORTH-EASTERN PART OF SIBERIAN PLATFORM AND THE KEY SECTION TRILOBITES". Izvestii︠a︡: Geologii︠a︡ I Geofizika.
- ↑ Geyer, Gerd (December 2015). "Exotic trilobites from the Lower–Middle Cambrian boundary interval in Morocco and their bearing on the Cambrian Series 3 lower boundary". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 89 (4): 749–781. doi:10.1007/s12542-014-0254-0.
- 1 2 Hawle, Ignaz; Corda, August Carl Joseph (1847). Prodrom einer Monographie der böhmischen Trilobiten (in German). J.G. Calve.
- ↑ Ivshin, N. K. (1983). Upper Cambrian Trilobites of Kazakhstan: Seletinian horizon of the Kuyandinian stage of central Kazakhstan. Amerind.
- ↑ Resser, Charles E. (1935). "Nomenclature of some Cambrian trilobites". Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 93 (5): 1–46. hdl:10088/23946.
- ↑ Hopkins, Melanie J.; Chen, Feiyang; Hu, Shixue; Zhang, Zhifei (21 September 2017). "The oldest known digestive system consisting of both paired digestive glands and a crop from exceptionally preserved trilobites of the Guanshan Biota (Early Cambrian, China)". PLOS ONE. 12 (9): e0184982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184982 . PMID 28934290.
- ↑ Palmer, A. R. (1954). "An appraisal of the Great Basin Middle Cambrian trilobites described before 1900". United States Geological Survey Professional Paper 264-D: 55–86. doi:10.3133/pp264D.
- ↑ Chen, Jun-Yuan; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Ramsköld, Lars (4 July 1997). "Morphological and ecological disparity in naraoiids (Arthropoda) from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Fauna, China". Records of the Australian Museum. 49 (1): 1–24. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.49.1997.249.
- ↑ Caron, Jean-Bernard; Rudkin, David M.; Milliken, Stuart (November 2004). "A NEW LATE SILURIAN (PRIDOLIAN) NARAOIID (EUARTHROPODA: NEKTASPIDA) FROM THE BERTIE FORMATION OF SOUTHERN ONTARIO, CANADA—DELAYED FALLOUT FROM THE CAMBRIAN EXPLOSION". Journal of Paleontology. 78 (6): 1138–1145. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2004)078<1138:ANLSPN>2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Whittington, Harry (31 August 1977). "The Middle Cambrian trilobite Naraoia , Burgess Shale, British Columbia". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences. 280 (974): 409–443. doi:10.1098/rstb.1977.0117.
- ↑ Budd, Graham E. (February 1999). "A nektaspid arthropod from the Early Cambrian Sirius Passet fauna, with a description of retrodeformation based on functional morphology". Palaeontology. 42 (1): 99–122. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00064.
- 1 2 Paterson, John R.; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Jago, James B.; Gehling, James G. (March 2010). "Nektaspid arthropods from the Lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale Lagerstätte, South Australia, with a reassessment of lamellipedian relationships". Palaeontology. 53 (2): 377–402. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2010.00932.x.
- ↑ Zhang, Xingliang; Fu, Dongjing; Dai, Tao (March 2012). "A new species of Kangacaris (Arthropoda) from the Chengjiang lagerstätte, lower Cambrian, southwest China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 36 (1): 23–25. doi:10.1080/03115518.2011.576532.
- ↑ Dzik, Jerzy; Lendzion, Kazimiera (January 1988). "The oldest arthropods of the East European Platform". Lethaia. 21 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1988.tb01749.x.
- ↑ Holmes, James D.; Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C. (May 2021). "The post-embryonic ontogeny of the early Cambrian trilobite Estaingia bilobata from South Australia: trunk development and phylogenetic implications". Papers in Palaeontology. 7 (2): 931–950. doi:10.1002/spp2.1323.
- ↑ Peng, Jin; Zhao, Yuanlong; Yuan, Jinliang; Yao, Lu; Yang, Hong (January 2009). "Bathynotus: A key trilobite taxon for global stratigraphic boundary correlation between Cambrian Series 2 and Cambrian Series 3". Progress in Natural Science. 19 (1): 99–105. doi:10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.03.034.
- ↑ Parkhaev, P. Yu.; Demidenko, Yu. E.; Kulsha, M. A. (March 2020). "The Problematic Fossil Mobergella radiolata as an Index Species of the Lower Cambrian Stages". Stratigraphy and Geological Correlation. 28 (2): 135–156. doi:10.1134/S0869593820020057.
- ↑ Budd, Graham E. (1995). "Kleptothule rasmusseni gen . et sp. nov.: an ?olenellinid-like trilobite from the Sirius Passet fauna (Buen Formation, Lower Cambrian, North Greenland)". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 86 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1017/S0263593300002121.
- ↑ Nowicki, Jakub; żYlińSka, Anna (June 2019). "The first occurrence of the earliest species of Acadoparadoxides outside West Gondwana (Cambrian; Holy Cross Mountains, Poland)". Geological Magazine. 156 (6): 1027–1051. doi:10.1017/S0016756818000341.
- ↑ Brongniart, Alexandre; Desmarest, Anselme-Gaëtan (1822). Histoire naturelle des crustaces fossiles sous les rapports zoologiques et geologiques: les Trilobites. les crustaces proprement dits (in French). chez F.G. Levrault, libraire.
- ↑ Hou, Xianguang; Clarkson, Euan N. K.; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xiguang; Wu, Guangqing; Yuan, Zibo (December 2008). "Appendages of early Cambrian Eoredlichia (Trilobita) from the Chengjiang biota, Yunnan, China". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 99 (3–4): 213–223. doi:10.1017/S1755691009008093.
- ↑ Bushuev, E.; Goryaeva, I.; Pereladov, V. (19 May 2014). "New discoveries of the oldest trilobites Profallotaspis and Nevadella in the northeastern Siberian Platform, Russia". Bulletin of Geosciences: 347–364. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1406.
- 1 2 Lieberman, Bruce S. (January 1998). "Cladistic analysis of the Early Cambrian olenelloid trilobites". Journal of Paleontology. 72 (1): 59–78. doi:10.1017/S0022336000024021.
- ↑ Lieberman, Bruce (1 January 1999). "Systematic revision of the Olenelloidea (Trilobita, Cambrian)". Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History (45).
- ↑ Lieberman, Bruce S. (2002). "PHYLOGENETIC ANALYSIS OF SOME BASAL EARLY CAMBRIAN TRILOBITES, THE BIOGEOGRAPHIC ORIGINS OF THE EUTRILOBITA, AND THE TIMING OF THE CAMBRIAN RADIATION". Journal of Paleontology. 76 (4): 692. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2002)076<0692:paosbe>2.0.co;2.
- ↑ Hicks, Henry (May 1895). "X.—On the Genus Plutonides (non Plutonia ) from the Cambrian Rocks of St. David's". Geological Magazine. 2 (5): 230–231. doi:10.1017/s0016756800121193.
- ↑ Holmes, James D.; Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C. (16 February 2020). "The trilobite Redlichia from the lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale Konservat-Lagerstätte of South Australia: systematics, ontogeny and soft-part anatomy". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 18 (4): 295–334. doi:10.1080/14772019.2019.1605411.
- ↑ Paterson, R.J.; Jago, J.B. (2006). "New trilobites from the Lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale Lagerstätte at Big Gully, Kangaroo Island, South Australia". Memoirs of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists. 32: 43–57. hdl:1959.14/10651. ISSN 0810-8889.
- ↑ Webster, Mark (March 2009). "Ontogeny, systematics, and evolution of the effaced Early Cambrian trilobites Peachella Walcott, 1910 and Eopeachella new genus (Olenelloidea)". Journal of Paleontology. 83 (2): 197–218. doi:10.1666/08-106.1.
- ↑ M., Webster (2007). "Paranephrolenellus, a new genus of Early Cambrian olenelloid trilobite" (PDF). Memoirs of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists. 34: 31–59.
- 1 2 3 Zhao, Fangchen; Hu, Shixue; Zeng, Han; Zhu, Maoyan (March 2014). "A New Helmetiid Arthropod from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Southwest China". Journal of Paleontology. 88 (2): 367–370. doi:10.1666/13-103.
- ↑ Whittington, Harry B. (1985). "Tegopelte gigas, a Second Soft-Bodied Trilobite from the Burgess Shale, Middle Cambrian, British Columbia". Journal of Paleontology. 59 (5): 1251–1274. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1305016.
- ↑ Zhang, Maoyin; Liu, Yu; Hou, Xianguang; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Mai, Huijuan; Schmidt, Michel; Melzer, Roland R.; Guo, Jin (19 August 2022). "Ventral Morphology of the Non-Trilobite Artiopod Retifacies abnormalis Hou, Chen & Lu, 1989, from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Biota, China". Biology. 11 (8): 1235. doi: 10.3390/biology11081235 . PMC 9405172 . PMID 36009864.
- ↑ Moberg, Joh. Chr. (February 1903). "Schmalenseeia amphionura , en ny trilobit-typ". Geologiska Föreningen i Stockholm Förhandlingar. 25 (2): 93–101. doi:10.1080/11035890309443449.
- ↑ Ebbestad, Jan Ove R.; Budd, Graham E. (November 2002). "Burlingiid trilobites from Norway, with a discussion of their affinities and relationships". Palaeontology. 45 (6): 1171–1195. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00281.
- ↑ Liu, Qing; Lei, Qianping (September 2011). "First known complete specimen of Neodrepanura (Trilobita: Damesellidae) from the Cambrian Kushan Formation, Shandong, China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 35 (3): 397–403. doi:10.1080/03115518.2011.519650.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (31 October 2019). "Appendicular anatomy of the artiopod Emeraldella brutoni from the middle Cambrian (Drumian) of western Utah". PeerJ. 7: e7945. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7945 . PMC 6825744 . PMID 31687274.
- ↑ Peel, J.S. (30 June 2017). "Molaria (Euarthropoda) from the Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (Cambrian Series 2, Stage 3) of North Greenland". Bulletin of Geosciences: 133–142. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1658.
- ↑ Du, Kunsheng; Bruton, David L.; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xiguang (March 2023). "An early Cambrian Sidneyia (Arthropoda) resolves the century-long debate of its head organization". Science China Earth Sciences. 66 (3): 521–527. doi:10.1007/s11430-022-1019-8.
- 1 2 3 Zhu, Yuyan; Zeng, Han; Liu, Yao; Zhao, Fangchen (2023). "New artiopodan euarthropods from the Chengjiang fauna (Cambrian Stage 3) at Malong, Yunnan, China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 68. doi: 10.4202/app.01080.2023 .
- ↑ Jiao, De-Guang; Du, Kun-Sheng; Zhang, Xi-Guang; Yang, Jie; Eggink, Daniel (May 2022). "A new small soft-bodied non-trilobite artiopod from the Cambrian Stage 4 Guanshan Biota". Geological Magazine. 159 (5): 730–734. doi: 10.1017/S0016756821001254 .
- ↑ Zhang, Xingliang; Fu, Dongjing; Dai, Tao (May 2012). "A new xandarellid arthropod from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Lower Cambrian of Southwest China". Geobios. 45 (3): 335–338. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2011.09.001.
- ↑ Hou, Xianguang; Williams, Mark; Sansom, Robert; Siveter, Derek J.; Siveter, David J.; Gabbott, Sarah; Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Cong, Peiyun; Liu, Yu (August 2019). "A new xandarellid euarthropod from the Cambrian Chengjiang biota, Yunnan Province, China". Geological Magazine. 156 (8): 1375–1384. doi:10.1017/s0016756818000730. hdl: 2381/43477 .
- ↑ Liu, Q.; Luo, H.-L.; Chen, L.-Z.; Lu, S.-X. (2006). "Panlongia, a new trilobitomorph genus from the Lower Cambrian, Kunming, Yunnan". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica. 45: 384–392.
- ↑ Zhang, Xingliang; Han, Jian; Shu, Degan (September 2000). "A NEW ARTHROPOD PYGMACLYPEATUS DAZIENSIS FROM THE EARLY CAMBRIAN CHENGJIANG LAGERSTÄTTE, SOUTH CHINA". Journal of Paleontology. 74 (5): 979–983. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2000)074<0979:ANAPDF>2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Chen, Xiaohan; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Wolfe, Joanna M.; Zhai, Dayou; Hou, Xianguang; Chen, Ailin; Mai, Huijuan; Liu, Yu (December 2019). "The appendicular morphology of Sinoburius lunaris and the evolution of the artiopodan clade Xandarellida (Euarthropoda, early Cambrian) from South China". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 19 (1): 165. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1491-3 . PMC 6685191 . PMID 31387545.
- 1 2 3 Xianguang, Hou; Ramsköld, Lars; Bergström, Jan (October 1991). "Composition and preservation of the Chengjiang fauna –a Lower Cambrian soft-bodied biota". Zoologica Scripta. 20 (4): 395–411. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1991.tb00303.x.
- 1 2 3 Chlupáč, I. (1996). "Lower Cambrian arthropods from the Paseky Shale (Barrandian area, Czech Republic)" (PDF). Journal of the Czech Geological Society: 9–36.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Paterson, John R.; Gibb, Stacey; Chatterton, Brian D.E. (February 2017). "Exceptionally-preserved late Cambrian fossils from the McKay Group (British Columbia, Canada) and the evolution of tagmosis in aglaspidid arthropods". Gondwana Research. 42: 264–279. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2016.10.013.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Zhu, Xuejian; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (11 September 2017). "The Vicissicaudata revisited – insights from a new aglaspidid arthropod with caudal appendages from the Furongian of China". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 11117. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11610-5. PMC 5593897 . PMID 28894246.
- ↑ Peel, J.S.; Stein, M. (31 December 2009). "A new arthropod from the lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Fossil-Lagerstätte of North Greenland". Bulletin of Geosciences: 625–630. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1158.
- 1 2 Berks, Harry O.; Lunde Nielsen, Morten; Flannery-Sutherland, Joseph; Thorshøj Nielsen, Arne; Park, Tae-Yoon S.; Vinther, Jakob (May 2023). "A possibly deep branching artiopodan arthropod from the lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (North Greenland)". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (3). Bibcode:2023PPal....9E1495B. doi: 10.1002/spp2.1495 .
- 1 2 Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (March 2012). "New artiopodan arthropods from the early Cambrian Emu Bay Shale Konservat-Lagerstätte of South Australia". Journal of Paleontology. 86 (2): 340–357. doi:10.1666/11-077.1.
- ↑ Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Kier, Carlo; Bonino, Enrico (March 2015). "A rare non-trilobite artiopodan from the G uzhangian ( C ambrian S eries 3) W eeks F ormation K onservat- L agerstätte in U tah, USA". Palaeontology. 58 (2): 265–276. doi:10.1111/pala.12136.
- ↑ Du, Kun-sheng; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xi-guang (June 2019). "A soft-bodied euarthropod from the early Cambrian Xiaoshiba Lagerstätte of China supports a new clade of basal artiopodans with dorsal ecdysial sutures". Cladistics. 35 (3): 269–281. doi:10.1111/cla.12344. PMID 34622993.
- ↑ Stein, Martin; Budd, Graham E; Peel, John S; Harper, David AT (2013). "Arthroaspis n. gen., a common element of the Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (Cambrian, North Greenland), sheds light on trilobite ancestry". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 13 (1): 99. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-99 . PMC 3662621 . PMID 23663519.
- ↑ Zhang, Xingliang; Shu, Degan (January 2005). "A new arthropod from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Early Cambrian, southern China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 29 (2): 185–194. doi:10.1080/03115510508619300.
- ↑ Budd, Graham E. (June 2011). "Campanamuta mantonae gen. et. sp. nov., an exceptionally preserved arthropod from the Sirius Passet Fauna (Buen Formation, lower Cambrian, North Greenland)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 9 (2): 217–260. doi:10.1080/14772019.2010.492644.
- ↑ Ramsköld, Lars; Junyuan, Chen; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Guiqing, Zhou (1997). "Cindarella and the arachnate clade Xandarellida (Arthropoda, Early Cambrian) from China". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 88 (1): 19–38. doi:10.1017/S0263593300002297.
- ↑ Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C. (January 2017). "A new aglaspidid-like euarthropod from the lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale of South Australia". Geological Magazine. 154 (1): 87–95. doi:10.1017/S0016756815001053.
- ↑ García-Bellido, Diego C; Collins, Desmond H (1 June 2006). "A new study of Marrella splendens (Arthropoda, Marrellomorpha) from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale, British Columbia, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 43 (6): 721–742. Bibcode:2006CaJES..43..721G. doi:10.1139/e06-012.
- ↑ Legg, D.A. (30 September 2015). "The morphology and affinities of Skania fragilis (Arthropoda) from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale". Bulletin of Geosciences: 509–518. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1532.
- ↑ Zhang, Xing-Liang; Han, Jian; Zhang, Zhi-Fei; Liu, Hu-Qin; Shu, De-Gan (May 2003). "Reconsideration of the supposed naraoiid larva from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, South China". Palaeontology. 46 (3): 447–465. Bibcode:2003Palgy..46..447Z. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00307.
- ↑ Joachim T. Haug; Christopher Castellani; Carolin Haug; Dieter Waloszek; Andreas Maas (2012). "A Marrella-like arthropod from Cambrian of Australia: A new link between "Orsten"-type and Burgess Shale assemblages". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (3): 629–639. doi: 10.4202/app.2011.0120 .
- ↑ Hughes, Christopher P. (15 July 1975). "Redescription of Burgessia bella from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale, British Columbia". Fossils and Strata. 4: 415–435. doi:10.18261/8200049639-1975-28. ISBN 82-00-04963-9.
- 1 2 3 Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy (March 2015). "Notchia weugi gen. et sp. nov.: a new short-headed arthropod from the Weeks Formation Konservat-Lagerstätte (Cambrian; Utah)". Geological Magazine. 152 (2): 351–357. doi:10.1017/S0016756814000375.
- ↑ Beecher, C. E. (1 November 1901). "Discovery of eurypterid remains in the Cambrian of Missouri". American Journal of Science. s4-12 (71): 364–366. doi:10.2475/ajs.s4-12.71.364.
- ↑ Tetlie, O. Erik; Moore, Rachel A. (September 2003). "A new specimen of Paleomerus hamiltoni (Arthropoda; Arachnomorpha)". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 94 (3): 195–198. doi:10.1017/S0263593300000602.
- 1 2 Legg, David (May 2013). "Multi-Segmented Arthropods from the Middle Cambrian of British Columbia (Canada)". Journal of Paleontology. 87 (3): 493–501. doi:10.1666/12-112.1.
- ↑ Zhai, Dayou; Williams, Mark; Siveter, David J.; Siveter, Derek J.; Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Sansom, Robert S.; Mai, Huijuan; Zhou, Runqing; Hou, Xianguang (2022-02-22). "Chuandianella ovata: An early Cambrian stem euarthropod with feather-like appendages". Palaeontologia Electronica. 25 (1): 1–22. doi: 10.26879/1172 . ISSN 1094-8074. S2CID 247123967.
- ↑ O’Flynn, Robert; Audo, Denis; Williams, Mark; Zhai, Dayou; Chen, Hong; Liu, Yu (2020). "A new euarthropod with 'great appendage'-like frontal head limbs from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Southwest China". Palaeontologia Electronica. doi: 10.26879/1069 .
- 1 2 Zhang, Xingliang; Shu, Degan (November 2007). "Soft anatomy of sunellid arthropods from the Chengjiang Lagerstutte, Lower Cambrian of southwest China". Journal of Paleontology. 81 (6): 1412–1422. doi:10.1666/06-031R.1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Zhao, FangChen; Zhu, MaoYan; Hu, ShiXue (December 2010). "Community structure and composition of the Cambrian Chengjiang biota". Science China Earth Sciences. 53 (12): 1784–1799. doi:10.1007/s11430-010-4087-8.
- ↑ Legg, David (2013). The impact of fossils on arthropod phylogeny (PDF). p. 58.
- 1 2 3 Hou, Xianguang; Bergstrom, J. (1 January 1998). "Three additional arthropods from the early cambrian Chengjiang Fauna, Yunnan, Southwest Chin". Gu Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta Palaeontologica Sinica.
- ↑ Desmond Collins & David M. Rudkin (1981). "Priscansermarinus barnetti, a probable lepadomorph barnacle from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia". Journal of Paleontology . 55 (5): 1006–1015. JSTOR 1304526.
- ↑ Haug, J.T.; Maas, A.; Haug, C.; Waloszek, D. (16 November 2011). "Sarotrocercus oblitus - Small arthropod with great impact on the understanding of arthropod evolution?". Bulletin of Geosciences: 725–736. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1283.
- ↑ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Skabelund, Jacob (January 2018). "Messorocaris , a new sanctacaridid-like arthropod from the middle Cambrian Wheeler Formation (Utah, USA)". Geological Magazine. 155 (1): 181–186. doi:10.1017/S0016756817000504.
- 1 2 Briggs, Derek E. G.; Lieberman, Bruce S.; Hendricks, Jonathan R.; Halgedahl, Susan L.; Jarrard, Richard D. (March 2008). "Middle Cambrian arthropods from Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 82 (2): 238–254. doi:10.1666/06-086.1.
- ↑ Lagebro, Linda; Stein, Martin; Peel, John S. (September 2009). "A New ?lamellipedian arthropod from the Early Cambrian Sirius Passet Fauna of North Greenland". Journal of Paleontology. 83 (5): 820–825. doi:10.1666/09-011.1.
- ↑ Robison, Richard A. (January 1990). "Earliest-known uniramous arthropod". Nature. 343 (6254): 163–164. doi:10.1038/343163a0.
- ↑ Budd, Graham E.; Högström, Anette E. S.; Gogin, Ivan (August 2001). "A myriapod-like arthropod from the Upper Cambrian of East Siberia". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 75 (1): 37–41. doi:10.1007/BF03022596.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek E. G. (1978). "A New Trilobite-like Arthropod from the Lower Cambrian Kinzers Formation, Pennsylvania". Journal of Paleontology. 52 (1): 132–140. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1303800.
- ↑ Conway Morris, Simon; Selden, Paul A.; Gunther, Glade; Jamison, Paul G.; Robison, Richard A. (May 2015). "New records of Burgess Shale-type taxa from the middle Cambrian of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 89 (3): 411–423. doi:10.1017/jpa.2015.26.
- ↑ Robison, R. A.; Richards, B. C. (16 December 1981). "Large bivalve arthropods from the Middle Cambrian of Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions.
- ↑ Robison, R. A.; Wiley, E. O. (May 1995). "A new arthropod, Meristosoma: More fallout from the Cambrian explosion". Journal of Paleontology. 69 (3): 447–459. doi:10.1017/S0022336000034855.
- ↑ Huilin, Luo (2008). Early Cambrian Malong Fauna and Guanshan Fauna from Eastern Yunnan, China. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press. ISBN 9787541629570.
- ↑ Yanishevsky, M. E. (1950). "Древнейший трилобит из нижнекембрийской синей глины Gdowia assatkini gen. et sp. nov" (PDF). Вопросы палеонтологии.
- ↑ Zhang, Huaqiao; Dong, Xi-ping; Xiao, Shuhai (October 2014). "New Bivalved Arthropods from the Cambrian (Series 3, Drumian Stage) of Western Hunan, South China". Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition. 88 (5): 1388–1396. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12306.
- ↑ Bergström, Jan (20 December 1968). "Eolimulus, A Lower Cambrian Xiphosurid from Sweden". Geologiska Föreningen i Stockholm Förhandlingar. 90 (4): 489–503. doi:10.1080/11035896809454937.
- ↑ Zhang, Huaqiao; Xiao, Shuhai (1 July 2017). "Three-dimensionally phosphatized meiofaunal bivalved arthropods from the Upper Cambrian of Western Hunan, South China". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 285 (1): 39–52. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2017/0668. hdl: 10919/81946 .
- ↑ Sun, A.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Wu, Y.; Fu, D. (2021). "Taxonomy and ontogeny of bivalved arthropods from the lower member of the Shuijingtuo Formation, Series 2 and Stage 3, Eastern Three Georges Area, South China". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica. 60 (1): 187–199. doi:10.19800/j.cnki.aps.2021019.
- ↑ Jiao, De guang; Du, Kunsheng (2022). "A new euarthropod from the Cambrian Stage 4 Guanshan Biota of South China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 67. doi: 10.4202/app.00937.2021 .
- ↑ Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (July 2022). "A new species of early Cambrian arthropod reconstructed from exceptionally preserved mandibles and associated small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs)". Papers in Palaeontology. 8 (4). doi:10.1002/spp2.1458.
- ↑ Gürich, G. (March 1927). "ÜberSilesicaris nasuta, eine neue Phyllocaride aus dem Bober-Katzbachgebirge". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 8 (1): 110–112. doi:10.1007/BF03160407.