
Tipton County is a county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2010 census, the population was 61,081. Its county seat is Covington.

The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages (suburbs) linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois.

Wickliffe Mounds is a prehistoric, Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Ballard County, Kentucky, just outside the town of Wickliffe, about 3 miles (4.8 km) from the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers. Archaeological investigations have linked the site with others along the Ohio River in Illinois and Kentucky as part of the Angel Phase of Mississippian culture. Wickliffe Mounds is controlled by the State Parks Service, which operates a museum at the site for interpretation of the ancient community. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places, it is also a Kentucky Archeological Landmark and State Historic Site.

Caborn-Welborn was a prehistoric North American culture defined by archaeologists as a Late Mississippian cultural manifestation that grew out of – or built upon the demise of – the Angel chiefdom located in the territory of southern present-day Indiana. Caborn-Welborn developed around 1400 and seems to have disappeared around 1700. The Caborn-Welborn culture was the last Native American occupation of southern Indiana before European contact. It remains unclear which historic-era native group, if any, are their descendants.

Walls is a town located in northern DeSoto County, Mississippi, United States, near the Mississippi River, part of the larger region known as "The Delta", and known for its rich, dark soil. As it is in the upper northwest corner of Mississippi, it is in the Memphis, Tennessee metropolitan area. Its ZIP code is 38680. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 1,162, with an estimated population of 1,463 in 2018.
The Angel Phase describes a 300-400-year cultural manifestation of the Mississippian culture of the central portions of the United States of America, as defined in the discipline of archaeology. Angel Phase archaeological sites date from c. 1050 - 1350 CE and are located on the northern and southern sides of the Ohio River in southern Indiana, such as National Historic Landmark Angel Mounds near present-day Evansville; northwestern Kentucky, with Wickliffe Mounds and the Tolu Site; and Kincaid Mounds State Historic Site in Illinois. Additional sites range from the mouth of Anderson River in Perry County, Indiana, west to the mouth of the Wabash in Posey County, Indiana.

The Nodena Site is an archeological site east of Wilson, Arkansas and northeast of Reverie, Tennessee in Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. Around 1400–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed in the Nodena area on a meander bend of the Mississippi River. The Nodena site was discovered and first documented by Dr. James K. Hampson, archaeologist and owner of the plantation on which the Nodena site is located. Artifacts from this site are on display in the Hampson Museum State Park in Wilson, Arkansas. The Nodena Site is the type site for the Nodena Phase, believed by many archaeologists to be the province of Pacaha visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542.
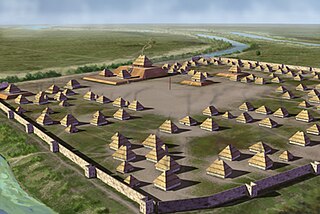
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin Site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of Casqui, documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE.

Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population increased dramatically and there is strong evidence of a growing cultural and political complexity, especially by the end of the Coles Creek sequence. Although many of the classic traits of chiefdom societies are not yet manifested, by 1000 CE the formation of simple elite polities had begun. Coles Creek sites are found in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. It is considered ancestral to the Plaquemine culture.

The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek and Troyville cultures to the Marksville culture. The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora Site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi.

Randolph is an unincorporated rural community in Tipton County, Tennessee, United States, located on the banks of the Mississippi River. The lands of the Mississippi River Basin were inhabited by Paleo-Indians and later Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture for thousands of years. The Tipton Phase people and the Chickasaw Indian tribe populated the Mississippi River valley near Randolph during the Mississippian period. In 1541, Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto crossed the Mississippi River at or near Randolph. French explorer Cavelier de La Salle built the first French fortification at or near Randolph on his 1682 canoe expedition of the Mississippi River.

Sellars Farm Site (40WI1), also known as the Sellars Farm State Archaeological Area and Sellars Indian Mound, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Wilson County, Tennessee near Lebanon. The platform mound was the site of a settlement from about 1000 to 1300 CE. Today, the site is a satellite unit of Long Hunter State Park. The non-profit Friends of the Sellars Farm State Archaeological Area organization conducts tours and upkeep of the site. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on December 11, 1972.

The C.H. Nash Museum at Chucalissa is located on and exhibits excavated materials of the Mississippian culture archaeological site known as Chucalissa which means "abandoned house" in Choctaw. The site is located adjacent to the T. O. Fuller State Park within the city of Memphis, Tennessee, United States. Chucalissa was designated National Historic Landmark in 1994 due to its importance as one of the best-preserved and major prehistoric settlement sites in the region.

The Tipton Phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee of the Late Mississippian culture. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin Phase, Walls Phase, Menard Phase, and the Nodena Phase. The Tipton Phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the area before the arrival of Europeans. It is located directly across the Mississippi River from the people of the Nodena Phase and directly north of the Walls Phase. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages in the area. The phase itself is named for Tipton County, Tennessee.

The Nodena Phase is an archaeological phase in eastern Arkansas and southeastern Missouri of the Late Mississippian culture which dates from about 1400–1650 CE. The Nodena Phase is known from a collection of villages along the Mississippi River between the Missouri Bootheel and Wapanocca Lake. They practiced extensive maize agriculture and artificial cranial deformation and were members of a continent wide trade and religious network known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, which brought chert, whelk shells, and other exotic goods to the area.

Mississippian culture pottery is the ceramic tradition of the Mississippian culture found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. It is often characterized by the adoption and use of riverine shell-tempering agents in the clay paste. Shell tempering is one of the hallmarks of Mississippian cultural practices. Analysis of local differences in materials, techniques, forms, and designs is a primary means for archaeologists to learn about the lifeways, religious practices, trade, and interaction among Mississippian peoples. The value of this pottery on the illegal antiquities market has led to extensive looting of sites.

The Turk Site (15CE6) is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located near Bardwell in Carlisle County, Kentucky, on a bluff spur overlooking the Mississippi River floodplain.
Charles Harrison McNutt is an American archaeologist and a scholar of the prehistoric Southeastern United States. He has conducted fieldwork and published works on the archaeology of the American Southwest and the Great Plains in South Dakota. His work emphasizes on a strong understanding of cultural history and statistical analysis.

The Link Farm State Archaeological Area, also known as the Duck River Temple Mounds or Duck River Site, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located at the confluence of the Duck and Buffalo Rivers south of Waverly in Humphreys County, Tennessee. The site is most widely known for the stone artifacts found during excavations in the late 19th century.

















