
Clorgiline (INN), or clorgyline (BAN), is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) structurally related to pargyline which is described as an antidepressant. Specifically, it is an irreversible and selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A). Clorgiline was never marketed, but it has found use in scientific research. It has been found to bind with high affinity to the σ1 receptor (Ki = 3.2 nM) and with very high affinity to the I2 imidazoline receptor (Ki = 40 pM).

Butorphanol is a morphinan-type synthetic agonist–antagonist opioid analgesic developed by Bristol-Myers. Butorphanol is most closely structurally related to levorphanol. Butorphanol is available as the tartrate salt in injectable, tablet, and intranasal spray formulations. The tablet form is only used in dogs, cats and horses due to low bioavailability in humans.

Levorphanol is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan.

Ifenprodil, sold under the brand names Cerocral, Dilvax, and Vadilex, is a cerebral vasodilator that has been marketed in some countries, including in Japan, Hong Kong, and France. It is currently under development for treatment of a variety of additional indications.

Tuaminoheptane is a sympathomimetic agent and vasoconstrictor which was formerly used as a nasal decongestant. It is still used in France as a nasal decongestant but its use is not recommended by the health authorities due to the lack of evidence of its effectiveness. It has also been used as a stimulant.

Mesulergine (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name) (developmental code name CU-32085) is a drug of the ergoline group which was never marketed. It acts on serotonin and dopamine receptors. Specifically, it is an agonist of dopamine D2-like receptors and serotonin 5-HT6 receptors and an antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT7 receptors.. It also has affinity for the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1F, and 5-HT5A receptors. The compound had entered clinical trials for the treatment of Parkinson's disease; however, further development was halted due to adverse histological abnormalities in rats. It was also investigated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels).

Levallorphan, also known as levallorphan tartrate (USAN), is an opioid modulator of the morphinan family used as an opioid analgesic and opioid antagonist/antidote. It acts as an antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) and as an agonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR), and as a result, blocks the effects of stronger agents with greater intrinsic activity such as morphine whilst simultaneously producing analgesia.

Oxypertine, sold under the brand name Oxypertine among others, is an antipsychotic medication of the tryptamine and phenylpiperazine groups which was previously used in the treatment of schizophrenia but is no longer marketed. It was also evaluated for the treatment of anxiety.
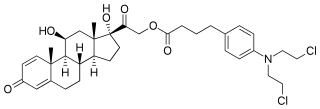
Prednimustine, sold under the brand names Mostarina and Sterecyst, is a medication which is used in chemotherapy in the treatment of leukemias and lymphomas. It is the ester formed from two other drugs, prednisolone and chlorambucil. Rarely, it has been associated with myoclonus.

Cinnamedrine, also known as N-cinnamylephedrine, is a sympathomimetic drug with similar effects relative to those of ephedrine. It also has some local anesthetic activity. Cinnamedrine was previously used, in combination with analgesics, as an antispasmodic to treat dysmenorrhea in the over-the-counter drug Midol in the 1980s. There is a case series of the drug being abused as a psychostimulant.

Difenamizole (INN; brand name Pasalin; former developmental code name AP-14) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and analgesic of the pyrazolone group related to metamizole. It has monoaminergic properties, including inhibition of monoamine oxidase, augmentation of pargyline-induced elevation of striatal dopamine levels, inhibition of K+-induced striatal dopamine release, and inhibition of the reuptake of dopamine.

Butidrine, sold under the brand names Betabloc, Butidrate, and Recetan among others, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol and propranolol that was developed in the 1960s. It is not cardioselective. It has membrane stabilizing activity but no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine additionally possesses local anesthetic properties.
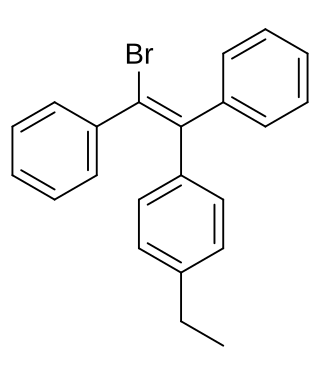
Broparestrol, also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active, and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.
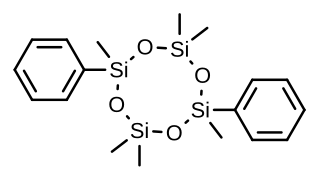
Quadrosilan is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen that was developed in the 1970s and that is or has been used as an antigonadotropic agent in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is an organosilicon compound, and is also known as 2,6-cisdiphenylhexamethylcyclotetrasiloxane. Quadrosilan has estrogenic activity equivalent to that of estradiol, and can produce feminization and gynecomastia as side effects in male patients.
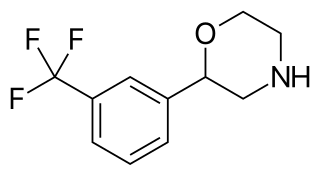
Flumexadol (INN) is a drug described and researched as a non-opioid analgesic which was never marketed. It has been found to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C receptors and, to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT2A receptor. According to Nilsson (2006) in a paper on 5-HT2C receptor agonists as potential anorectics, "The (+)-enantiomer of this compound showed [...] affinity for the 5-HT2C receptor (Ki) 25 nM) [...] and was 40-fold selective over the 5-HT2A receptor in receptor binding studies. The racemic version [...], also known as 1841 CERM, was originally reported to possess analgesic properties while no association with 5-HT2C receptor activity was mentioned." It is implied that flumexadol might be employable as an anorectic in addition to analgesic. Though flumexadol itself has never been approved for medical use, oxaflozane is a prodrug of the compound that was formerly used clinically in France as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent.
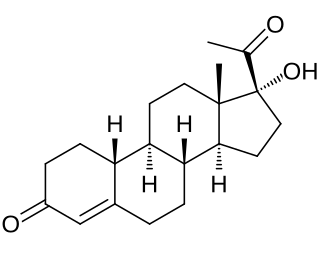
Gestronol, also known as gestonorone, as well as 17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone or 17α-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a progestin of the 19-norprogesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone groups which was never marketed. The C17α caproate ester of gestronol, gestonorone caproate, in contrast, has been marketed.
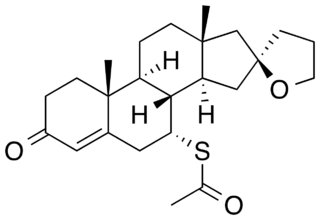
Spiroxasone is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent but was never marketed. It was synthesized and assayed in 1963. The drug is 7α-acetylthiospirolactone with the ketone group removed from the C17α spirolactone ring. Similarly to other spirolactones like spironolactone, spiroxasone also possesses antiandrogen activity.

Dicirenone is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent but was never marketed. It was synthesized and assayed in 1974. Similarly to other spirolactones like spironolactone, dicirenone also possesses antiandrogen activity, albeit with relatively reduced affinity.

Enciprazine is an anxiolytic and antipsychotic of the phenylpiperazine class which was never marketed. It shows high affinity for the α1-adrenergic receptor and 5-HT1A receptor, among other sites. The drug was initially anticipated to produce ortho-methoxyphenylpiperazine (oMeOPP), a serotonin receptor agonist with high affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor, as a significant active metabolite, but subsequent research found this not to be the case.
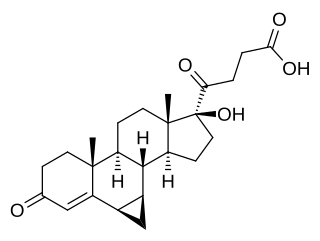
Prorenoic acid, or prorenoate, is a synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid which was never marketed.




















