The Gallo-Romance branch of the Romance languages includes in the narrowest sense the langues d'oïl and Franco-Provençal. However, other definitions are far broader and variously encompass the Occitan or Occitano-Romance, Gallo-Italic or Rhaeto-Romance languages.

Avar, also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Avar–Andic subgroup that is spoken by Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately one million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia.

Piedmontese is a language spoken by some 2,000,000 people mostly in Piedmont, a region of Northwest Italy. Although considered by most linguists a separate language, in Italy it is often mistakenly regarded as an Italian dialect. It is linguistically included in the Gallo-Italic languages group of Northern Italy, which would make it part of the wider western group of Romance languages, which also includes French, Arpitan, Occitan, and Catalan. It is spoken in the core of Piedmont, in northwestern Liguria, and in Lombardy.

The Lombard language belongs to the Gallo-Italic group within the Romance languages. It is characterized by a Celtic linguistic substratum and a Lombardic linguistic superstratum and is a cluster of homogeneous dialects that are spoken by millions of speakers in Northern Italy and southern Switzerland. These include most of Lombardy and some areas of the neighbouring regions, notably the far eastern side of Piedmont and the extreme western side of Trentino, and in Switzerland in the cantons of Ticino and Graubünden. The language is also spoken in Santa Catarina in Brazil by Lombard immigrants from the Province of Bergamo, in Italy.
Venetian, wider Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken natively in the northeast of Italy, mostly in Veneto, where most of the five million inhabitants can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto: in Trentino, Friuli, the Julian March, Istria, and some towns of Slovenia, Dalmatia (Croatia) and Bay of Kotor (Montenegro) by a surviving autochthonous Venetian population, and in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, the United States and the United Kingdom by Venetians in the diaspora.
Milanese is the central variety of the Western dialect of the Lombard language spoken in Milan, the rest of its metropolitan city, and the northernmost part of the province of Pavia. Milanese, due to the importance of Milan, the largest city in Lombardy, is often considered one of the most prestigious Lombard variants and the most prestigious one in the Western Lombard area.

In the linguistics of the Romance languages, the La Spezia–Rimini Line, also known as the Massa–Senigallia Line, is a line that demarcates a number of important isoglosses that distinguish Romance languages south and east of the line from Romance languages north and west of it. The line divides northern and central Italy, running approximately between the cities of La Spezia and Rimini. Romance languages south and east of it include Italian and the Eastern Romance languages, whereas Catalan, French, Occitan, Portuguese, Romansh, Spanish, and the Gallo‒Italic languages are representatives of the Western group. In this classification, the Sardinian language is not part of either Western or Eastern Romance.
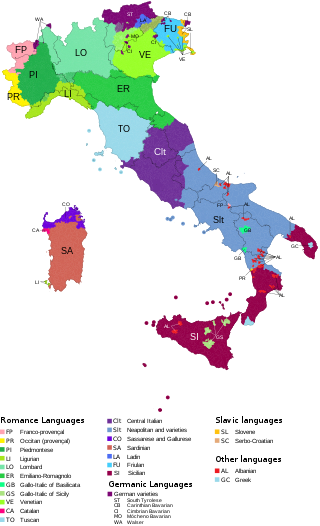
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance group. The majority of languages often labeled as regional are distributed in a continuum across the regions' administrative boundaries, with speakers from one locale within a single region being typically aware of the features distinguishing their own variety from others spoken nearby.
The Ticinese dialect is the set of dialects, belonging to the Alpine and Western branch of the Lombard language, spoken in the northern part of the Canton of Ticino (Sopraceneri); the dialects of the region can generally vary from valley to valley, often even between single localities, while retaining the mutual intelligibility that is typical of the Lombard linguistic continuum.

The Gallo-Italic, Gallo-Italian, Gallo-Cisalpine or simply Cisalpine languages constitute the majority of the Romance languages of northern Italy: Piedmontese, Lombard, Emilian, Ligurian, and Romagnol. In central Italy they are spoken in the northern Marches ; in southern Italy in some language islands in Basilicata and Sicily.
Western Lombard is a group of dialects of Lombard, a Romance language spoken in Italy. It is widespread in the Lombard provinces of Milan, Monza, Varese, Como, Lecco, Sondrio, a small part of Cremona, Lodi and Pavia, and the Piedmont provinces of Novara, Verbano-Cusio-Ossola, the eastern part of the Province of Alessandria (Tortona), a small part of Vercelli (Valsesia), and Switzerland. After the name of the region involved, land of the former Duchy of Milan, this language is often referred to as Insubric or Milanese, or, after Clemente Merlo, Cisabduano.

Ligurian or Genoese is a Gallo-Italic language spoken primarily in the territories of the former Republic of Genoa, now comprising the area of Liguria in Northern Italy, parts of the Mediterranean coastal zone of France, Monaco, the village of Bonifacio in Corsica, and in the villages of Carloforte on San Pietro Island and Calasetta on Sant'Antioco Island off the coast of southwestern Sardinia. It is part of the Gallo-Italic and Western Romance dialect continuum. Although part of Gallo-Italic, it exhibits several features of the Italo-Romance group of central and southern Italy. Zeneize, spoken in Genoa, the capital of Liguria, is the language's prestige dialect on which the standard is based.

Italo-Western is, in some classifications, the largest branch of the Romance languages. It comprises two of the branches of Romance languages: Italo-Dalmatian and Western Romance. It excludes the Sardinian language and Eastern Romance.

Tsakhur is a Lezgic language spoken by the Tsakhurs in northern Azerbaijan and southwestern Dagestan (Russia). It is spoken by about 11,700 people in Azerbaijan and by about 10,600 people in Russia. The word Tsakhur derives from the name of a Dagestani village where speakers of this language make up the majority.
Pavese is a dialect of Western Lombard language spoken in province of Pavia (Lombardy). In Pavese, differently from most of Western Lombard dialects, the "z" is transformed into "s".
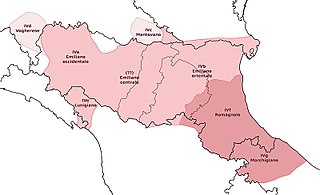
Emilian is a Gallo-Italic unstandardised language spoken in the historical region of Emilia, which is now in the western part of Emilia-Romagna, Northern Italy.
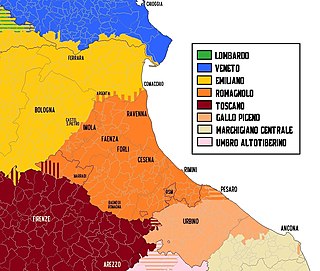
Romagnol is a Romance language spoken in the historical region of Romagna, consisting mainly of the southeastern part of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. The name is derived from the Lombard name for the region, Romagna. Romagnol is also spoken outside the region, particularly in the independent Republic of San Marino. Romagnol is classified as endangered because older generations have "neglected to pass on the dialect as a native tongue to the next generation".
The Parmigiano dialect, sometimes anglicized as the Parmesan dialect, is a variety of the Emilian language spoken in the Province of Parma, the western-central portion of the Emilia-Romagna administrative region.

The Ferrarese dialect refers to the dialect spoken by the native inhabitants of the city and environs of Ferrara, a city located in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy.
Old Romagnol is the earliest recorded form of the Romagnol language, spoken in the Romagna part of the Emilia-Romagna region in Italy, and San Marino. It was the form of Romagnol spoken around the early modern period.