Related Research Articles

Xeon is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture (MCA). They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus, which replaced the older QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) bus.
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the register-level interface of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets.

Sandy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core processors. The Sandy Bridge microarchitecture is the successor to Nehalem and Westmere microarchitecture. Intel demonstrated an A1 stepping Sandy Bridge processor in 2009 during Intel Developer Forum (IDF), and released first products based on the architecture in January 2011 under the Core brand.
I/O Controller Hub (ICH) is a family of Intel southbridge microchips used to manage data communications between a CPU and a motherboard, specifically Intel chipsets based on the Intel Hub Architecture. It is designed to be paired with a second support chip known as a northbridge. As with any other southbridge, the ICH is used to connect and control peripheral devices.
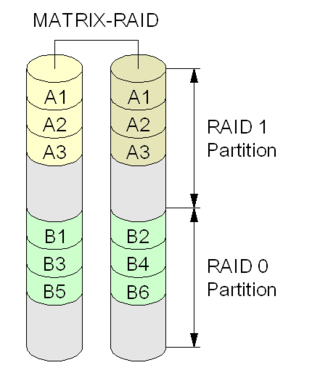
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver SATA AHCI and a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel chipsets. Currently also is installed as a driver for Intel Optane temporary storage units.

The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) is a family of Intel's single-chip chipsets, first introduced in 2009. It is the successor to the Intel Hub Architecture, which used two chips–a northbridge and southbridge, and first appeared in the Intel 5 Series.

LGA 1366, also known as Socket B, is an Intel CPU socket. This socket supersedes Intel's LGA 775 in the high-end and performance desktop segments. It also replaces the server-oriented LGA 771 in the entry level and is superseded itself by LGA 2011. This socket has 1,366 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor (CPU) and accesses up to three channels of DDR3 memory via the processor's internal memory controller.

Haswell is the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge. Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. Haswell was the last generation of Intel processor to have socketed processors on mobile. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell began shipping to manufacturers and OEMs in mid-2013, with its desktop chips officially launched in September 2013.

LGA 1156, also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155.
Intel 5 Series is a computing architecture introduced in 2008 that improves the efficiency and balances the use of communication channels in the motherboard. The architecture consists primarily of a central processing unit (CPU) and a single chipset. All motherboard communications and activities circle around these two devices.

LGA 2011, also called Socket R, is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor.

LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge microarchitectures.

LGA 1356, also called Socket B2, is an Intel microprocessor socket released in Q1 2012 with 1356 Land Grid Array pins. It launched alongside LGA 2011 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 and LGA 1567. It's compatible with Intel Sandy Bridge-EN and Ivy Bridge-EN microprocessors.

Skylake is Intel's codename for its sixth generation Core microprocessor family that was launched on August 5, 2015, succeeding the Broadwell microarchitecture. Skylake is a microarchitecture redesign using the same 14 nm manufacturing process technology as its predecessor, serving as a tock in Intel's tick–tock manufacturing and design model. According to Intel, the redesign brings greater CPU and GPU performance and reduced power consumption. Skylake CPUs share their microarchitecture with Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake, Whiskey Lake, and Comet Lake CPUs.

LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for CPUs built on the Haswell microarchitecture. This socket is also used by the Haswell's successor, Broadwell microarchitecture.

Ivy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 22 nm microarchitecture used in the third generation of the Intel Core processors. Ivy Bridge is a die shrink to 22 nm process based on FinFET ("3D") Tri-Gate transistors, from the former generation's 32 nm Sandy Bridge microarchitecture—also known as tick–tock model. The name is also applied more broadly to the Xeon and Core i7 Extreme Ivy Bridge-E series of processors released in 2013.

Broadwell is the fifth generation of the Intel Core processor. It is Intel's codename for the 14 nanometer die shrink of its Haswell microarchitecture. It is a "tick" in Intel's tick–tock principle as the next step in semiconductor fabrication. Like some of the previous tick-tock iterations, Broadwell did not completely replace the full range of CPUs from the previous microarchitecture (Haswell), as there were no low-end desktop CPUs based on Broadwell.
Intel X99, codenamed "Wellsburg", is a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) designed and manufactured by Intel, targeted at the high-end desktop (HEDT) and enthusiast segments of the Intel product lineup. The X99 chipset supports both Intel Core i7 Extreme and Intel Xeon E5-16xx v3 and E5-26xx v3 processors, which belong to the Haswell-E and Haswell-EP variants of the Haswell microarchitecture, respectively. All supported processors use the LGA 2011-v3 socket.
References
- ↑ "Intel's latest X79 Chipset". gamerzrepublic.com. May 25, 2010. Archived from the original on March 24, 2012. Retrieved May 25, 2011.
- ↑ "Intel Refreshes Ultimate Enthusiast Processor Lineup with Six-Core Offerings". News release. Intel. November 14, 2011. Retrieved November 14, 2011.
- ↑ "Intel® X79 Express Chipset (Intel® BD82X79 PCH)". official product information. Intel. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ "Products (Formerly Sandy Bridge-EP)". official product information. Intel. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ↑ "Products (Formerly Sandy Bridge-EN)". official product information. Intel. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ↑ "Products (Formerly Ivy Bridge)". official product information. Intel. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ↑ Intel X79 SATA AHCI RAID Mode Notice Archived 2014-03-26 at archive.today
- ↑ Integration of Intels AHCI/RAID drivers into a WinXP/W2k3/W2k CD