| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Agile kangaroo rat  | D. agilis
Gambel, 1848
- D. a. agilis
- D. a. perplexus
| Western United States | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 17–20 cm (7–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [5]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [5] [5]
|
|---|
| Banner-tailed kangaroo rat  | D. spectabilis
Merriam, 1890
- D. s. baileyi
- D. s. cratodon
- D. s. intermedius
- D. s. perblandus
- D. s. spectabilis
- D. s. zygomaticus
| Southern United States and Mexico | Size: 13–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 18–21 cm (7–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Desert [7]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | NT
Unknown  [7] [7]
|
|---|
| California kangaroo rat
| D. californicus
Merriam, 1890
- D. c. californicus
- D. c. eximius
- D. c. saxatilis
| Western United States | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 15–22 cm (6–9 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [8]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [8] [8]
|
|---|
| Chisel-toothed kangaroo rat  | D. microps
(Merriam, 1904)
- D. m. alfredi
- D. m. aquilonius
- D. m. bonnevillei
- D. m. celsus
- D. m. centralis
- D. m. idahoensis
- D. m. leucotis
- D. m. levipes
- D. m. microps
- D. m. occidentalis
- D. m. preblei
- D. m. russeolus
- D. m. subtenuis
| Western United States | Size: 11–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 13–18 cm (5–7 in) tail [9]
Habitat: Shrubland, rocky areas, and desert [10]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [10] [10]
|
|---|
| Desert kangaroo rat  | D. deserti
Stephens, 1887
- D. d. aquilus
- D. d. arizonae
- D. d. deserti
- D. d. sonoriensis
| Western United States and western Mexico | Size: 13–16 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 19–21 cm (7–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Desert [11]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [11] [11]
|
|---|
| Dulzura kangaroo rat  | D. simulans
(Merriam, 1904)
- D. s. peninsularis
- D. s. simulans
| Western United States and western Mexico | Size: 11–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 16–19 cm (6–7 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and desert [12]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [12] [12]
|
|---|
| Fresno kangaroo rat  | D. nitratoides
Merriam, 1894
| Western United States | Size: 7–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 13–15 cm (5–6 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [13]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | VU
Unknown  [13] [13]
|
|---|
| Giant kangaroo rat  | D. ingens
(Merriam, 1904) | Western United States | Size: 13–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 17–20 cm (7–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Savanna and grassland [14]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | EN
Unknown  [14] [14]
|
|---|
| Gulf Coast kangaroo rat  | D. compactus
True, 1889
- D. c. compactus
- D. c. sennetti
| Southern United States | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and coastal marine [15]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [15] [15]
|
|---|
| Heermann's kangaroo rat  | D. heermanni
Conte, 1853
- D. h. arenae
- D. h. berkeleyensis
- D. h. dixoni
- D. h. goldmani
- D. h. heermanni
- D. h. jolonensis
- D. h. morroensis (Morro Bay kangaroo rat)
- D. h. swarthi
- D. h. tularensis
| Western United States | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 16–20 cm (6–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert [16]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [16] [16]
|
|---|
| Merriam's kangaroo rat  | D. merriami
Mearns, 1890
- D. m. ambiguus
- D. m. annulus
- D. m. arenivagus
- D. m. atronasus
- D. m. brunensis
- D. m. collinus
- D. m. frenatus
- D. m. insularis
- D. m. margaritae
- D. m. mayensis
- D. m. melanurus
- D. m. merriami
- D. m. mitchelli
- D. m. olivaceus
- D. m. parvus (San Bernardino kangaroo rat)
- D. m. platycephalus
- D. m. quintinensis
- D. m. trinidadensis
- D. m. vulcani
| Southwestern United States and Mexico
 | Size: 7–10 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 12–19 cm (5–7 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Shrubland and desert [17]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [17] [17]
|
|---|
| Narrow-faced kangaroo rat  | D. venustus
(Merriam, 1904)
- D. v. elephantinus
- D. v. sanctiluciae
- D. v. venustus
| Western United States | Size: 11–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 17–20 cm (7–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [18]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [18] [18]
|
|---|
| Nelson's kangaroo rat  | D. nelsoni
Merriam, 1907 | Northern Mexico | Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 12–20 cm (5–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Shrubland and desert [19]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [19] [19]
|
|---|
| Ord's kangaroo rat  | D. ordii
Woodhouse, 1853
- D. o. celeripes
- D. o. chapmani
- D. o. cinderensis
- D. o. cineraceus
- D. o. columbianus
- D. o. cupidineus
- D. o. durranti
- D. o. evexus
- D. o. extractus
- D. o. fetosus
- D. o. fremonti
- D. o. inaquosus
- D. o. longipes
- D. o. luteolus
- D. o. marshalli
- D. o. medius
- D. o. monoensis
- D. o. montanus
- D. o. nexilis
- D. o. obscurus
- D. o. oklahomae
- D. o. ordii
- D. o. pallidus
- D. o. palmeri
- D. o. panguitchensis
- D. o. priscus
- D. o. pullus
- D. o. richardsoni
- D. o. sanrafaeli
- D. o. terrosus
- D. o. uintensis
- D. o. utahensis
| Western North America
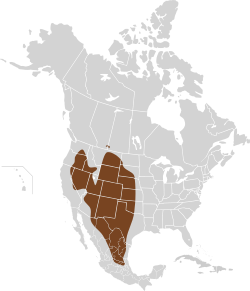 | Size: 7–16 cm (3–6 in) long, plus about 13 cm (5 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [20]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [20] [20]
|
|---|
| Ornate kangaroo rat  | D. ornatus
Merriam, 1894 | Central Mexico
 | Size: 10–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Desert [21]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [21] [21]
|
|---|
| Panamint kangaroo rat  | D. panamintinus
(Merriam, 1894)
- D. p. argusensis
- D. p. caudatus
- D. p. leucogenys
- D. p. mohavensis
- D. p. panamintinus
| Western United States | Size: About 12 cm (5 in) long, plus about 17 cm (7 in) tail [9]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and desert [22]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [22] [22]
|
|---|
| Phillips's kangaroo rat  | D. phillipsii
Gray, 1841
- D. p. oaxacae
- D. p. ornatus
- D. p. perotensis
- D. p. phillipsii
| Central Mexico | Size: 8–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 14–19 cm (6–7 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Shrubland and desert [23]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | LC
Unknown  [23] [23]
|
|---|
| San Quintin kangaroo rat  | D. gravipes
Huey, 1925 | Western Mexico | Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 16–18 cm (6–7 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Desert [24]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | CR
0–50  [24] [24]
|
|---|
| Stephens's kangaroo rat  | D. stephensi
(Merriam, 1907) | Western United States | Size: 11–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 16–18 cm (6–7 in) tail [9]
Habitat: Grassland and shrubland [25]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | VU
Unknown  [25] [25]
|
|---|
| Texas kangaroo rat
| D. elator
Merriam, 1894 | Southern United States | Size: 9–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 16–20 cm (6–8 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Savanna and desert [26]
Diet: Seeds, as well as fruit, leaves, stems, buds, and insects [6] | VU
Unknown  [26] [26]
|
|---|


























































