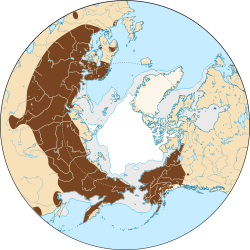
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Afghan vole | M. afghanus
Thomas, 1912 | Central Asia | Size: 6–13 cm (2–5 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [103]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [103] [103]
|
|---|
| Alpine pine vole | M. multiplex
(Fatio, 1905) | Southern Europe | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [105]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [105] [105]
|
|---|
| Altai vole | M. obscurus
Eversmann, 1841 | Southeastern Europe and western and central Asia | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland [106]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [106] [106]
|
|---|
| Anatolian vole | M. anatolicus
Kryštufek & Kefelioğlu, 2002 | Turkey | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland [107]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | DD
Unknown  [107] [107]
|
|---|
| Beach vole  | M. breweri
Baird, 1858 | Muskeget Island in northeastern United States | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–7 cm (1–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland and coastal marine [108]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | VU
Unknown  [108] [108]
|
|---|
| Bucharian vole | M. bucharensis
Vinogradov, 1930 | Central Asia | Size: About 13 cm (5 in) long, plus about 4 cm (2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Shrubland [109]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [109] [109]
|
|---|
| Cabrera's vole | M. cabrerae
Thomas, 1906 | Spain and Portugal
 | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest, grassland, and inland wetlands [110]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | NT
Unknown  [110] [110]
|
|---|
| Calabria pine vole | M. brachycercus
(Lehmann, 1961) | Southern Italy | Size: 8–10 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [111]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [111] [111]
|
|---|
| California vole  | M. californicus
(Peale, 1848) | Western United States and western Mexico
 | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland, desert, and intertidal marine [112]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [112] [112]
|
|---|
| Caspian gray vole | M. mystacinus
(Filippi, 1865) | Iran | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [113]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [113] [113]
|
|---|
| Common vole  | M. arvalis
(Pallas, 1778) | Europe and western Russia
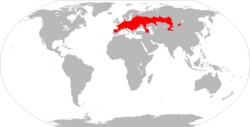 | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [114]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [114] [114]
|
|---|
| Creeping vole  | M. oregoni
(Bachman, 1839) | Western United States and southwestern Canada
 | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [115]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [115] [115]
|
|---|
| Daghestan pine vole | M. daghestanicus
(Shidlovsky, 1919) | West-central Asia | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Inland wetlands [116]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [116] [116]
|
|---|
| Doğramaci's vole | M. dogramacii
Kefelioğlu & Kryštufek, 1999 | Turkey | Size: 9–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland [117]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [117] [117]
|
|---|
| East European grey vole | M. rossiaemeridionalis
(Ognev, 1924) | Eastern Europe and western Asia | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands [118]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [118] [118]
|
|---|
| Eastern meadow vole  | M. pennsylvanicus
(Ord, 1815) | Canada and United States
 | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–7 cm (1–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [119]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [119] [119]
|
|---|
| European pine vole  | M. subterraneus
(Selys, 1836) | Europe and western Asia
 | Size: 7–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas [120]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [120] [120]
|
|---|
| Felten's vole | M. felteni
Malec & Storch, 1963 | Southeastern Europe | Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest [121]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [121] [121]
|
|---|
| Gerbe's vole | M. gerbei
(Gerbe, 1879) | France and Spain | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, grassland, and rocky areas [122]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [122] [122]
|
|---|
| Gray-tailed vole | M. canicaudus
Miller, 1897 | Northwestern United States
 | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland [123]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [123] [123]
|
|---|
| Guatemalan vole | M. guatemalensis
Merriam, 1898 | Guatemala and southern Mexico | Size: 11–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest [124]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | NT
Unknown  [124] [124]
|
|---|
| Günther's vole  | M. guentheri
(Danford & Alston, 1880) | Western Asia | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [125]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [125] [125]
|
|---|
| Insular vole | M. abbreviatus
Miller, 1899 | Alaska
 | Size: 8–15 cm (3–6 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland [126]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [126] [126]
|
|---|
| Jalapan pine vole | M. quasiater
(Coues, 1874) | Eastern Mexico | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest, grassland, and rocky areas [127]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | NT
Unknown  [127] [127]
|
|---|
| Juniper vole | M. yuldaschi
(Sévertsov, 1879) | Central Asia | Size: 6–12 cm (2–5 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [128]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [128] [128]
|
|---|
| Kerman vole | M. kermanensis
de Roguin, 1988 | Iran | Size: 11–16 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Unknown [129]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | DD
Unknown  [129] [129]
|
|---|
| Liechtenstein's pine vole | M. liechtensteini
(Wettstein, 1927) | Central and eastern Europe | Size: 8–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [130]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [130] [130]
|
|---|
| Long-tailed vole  | M. longicaudus
(Merriam, 1888) | Western United States and western Canada
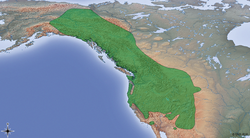 | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 4–9 cm (2–4 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [131]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [131] [131]
|
|---|
| Lusitanian pine vole  | M. lusitanicus
(Gerbe, 1879) | Southwestern Europe
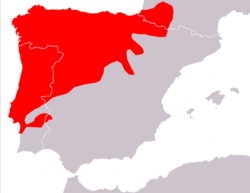 | Size: 8–10 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest [132]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [132] [132]
|
|---|
| Major's pine vole | M. majori
(Thomas, 1906) | Western Asia | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [133]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [133] [133]
|
|---|
| Mediterranean field vole  | M. lavernedii
Crespon, 1844 | Western and central Europe | Size: 9–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 2–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [134]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [134] [134]
|
|---|
| Mediterranean pine vole | M. duodecimcostatus
(Selys, 1839) | Southwestern Europe
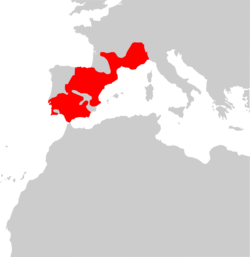 | Size: 8–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland [135]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [135] [135]
|
|---|
| Mexican vole  | M. mexicanus
(Saussure, 1861) | Mexico and southwestern United States | Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest [136]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [136] [136]
|
|---|
| Montane vole  | M. montanus
(Peale, 1848) | Western United States
 | Size: 11–16 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 2–7 cm (1–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [137]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [137] [137]
|
|---|
| North American water vole | M. richardsoni
(Kay, 1842) | Western United States and western Canada
 | Size: 12–18 cm (5–7 in) long, plus 6–10 cm (2–4 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands [138]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [138] [138]
|
|---|
| Paradox vole | M. paradoxus
(Ognev & Heptner, 1928) | Turkmenistan and northeast Iran | Size: 8–13 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [139]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [139] [139]
|
|---|
| Persian vole | M. irani
Thomas, 1921 | Iran | Size: 8–13 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland [140]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | VU
Unknown  [140] [140]
|
|---|
| Portuguese field vole | M. rozianus
Bocage, 1865 | Northern Portugal and northwestern Spain
 | Size: About 10 cm (4 in) long, plus about 4 cm (2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands [141]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [141] [141]
|
|---|
| Prairie vole  | M. ochrogaster
(Wagner, 1843) | South-central Canada and central United States
 | Size: 10–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [142]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [142] [142]
|
|---|
| Qazvin vole | M. qazvinensis
Golenishchev, Sablina, Borodin, & Gerasimov, 2003 | Iran | Size: 8–13 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [143]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [143] [143]
|
|---|
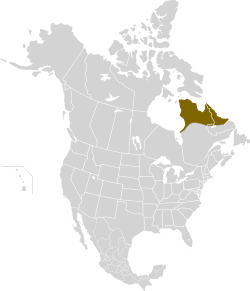
| Rock vole  | M. chrotorrhinus
(Miller, 1894) | Eastern Canada and eastern United States
 | Size: 9–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest and rocky areas [144]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [144] [144]
|
|---|
| Savi's pine vole  | M. savii
(de Sélys-Longchamps, 1838) | Central Europe | Size: 8–10 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [145]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [145] [145]
|
|---|
| Schelkovnikov's pine vole | M. schelkovnikovi
Satunin, 1907 | Azerbaijan and Iran | Size: 8–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest [146]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [146] [146]
|
|---|
| Schidlovsky's vole | M. schidlovskii
Argiropulo, 1933 | Eastern Europe and Turkey | Size: 8–13 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland [147]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [147] [147]
|
|---|
| Short-tailed field vole  | M. agrestis
(Linnaeus, 1761) | Europe and northern Asia
 | Size: 9–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [148]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [148] [148]
|
|---|
| Sicilian pine vole | M. nebrodensis
Palumbo, 1868 | Island of Sicily in Italy | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0–1 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [149]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [149] [149]
|
|---|
| Singing vole  | M. miurus
Osgood, 1901 | Alaska and northwestern Canada
 | Size: 8–15 cm (3–6 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail [4]
Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands [150]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [150] [150]
|
|---|
| Social vole  | M. socialis
(Pallas, 1773) | Central and western Asia | Size: 9–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland [151]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [151] [151]
|
|---|
| Taiga vole  | M. xanthognathus
(Leach, 1815) | Alaska and northern Canada
 | Size: 14–18 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands [152]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [152] [152]
|
|---|
| Tarabundí vole | M. oaxacensis
Goodwin, 1966 | Southern Mexico | Size: 11–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest [153]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | EN
Unknown  [153] [153]
|
|---|
| Tatra pine vole  | M. tatricus
(Kratochvíl, 1952) | Eastern Europe | Size: 8–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [154]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
200,000–250,000  [154] [154]
|
|---|
| Thomas's pine vole | M. thomasi
Barrett-Hamilton, 1903 | Southeastern Europe | Size: 7–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail [104]
Habitat: Grassland [155]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [155] [155]
|
|---|
| Tien Shan vole | M. ilaeus
Thomas, 1912 | Central Asia | Size: 10–15 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [156]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [157]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [157] [157]
|
|---|
| Townsend's vole  | M. townsendii
(Bachman, 1839) | Southwestern Canada and western United States
 | Size: 12–16 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 4–8 cm (2–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands [158]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [158] [158]
|
|---|
| Transcaspian vole | M. transcaspicus
Satunin, 1905 | Western Asia | Size: 9–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail [156]
Habitat: Grassland [159]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [159] [159]
|
|---|
| Woodland vole  | M. pinetorum
(Conte, 1830) | Eastern Canada and eastern United States
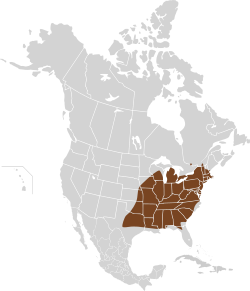 | Size: 6–11 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands [160]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | LC
Unknown  [160] [160]
|
|---|
| Zempoaltépec vole | M. umbrosus
Merriam, 1898 | Southern Mexico | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail [102]
Habitat: Forest [161]
Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, bulbs, tubers, seeds, nuts, and other vegetation [6] | EN
Unknown  [161] [161]
|
|---|