
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin molybdaenum, which is based on Ancient Greek Μόλυβδος molybdos, meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm.

Group 6, numbered by IUPAC style, is a group of elements in the periodic table. Its members are chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and seaborgium (Sg). These are all transition metals and chromium, molybdenum and tungsten are refractory metals.
Molybdenum trioxide is chemical compound with the formula MoO3. This compound is produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound. It is an intermediate in the production of molybdenum metal. It is also an important industrial catalyst. Molybdenum trioxide occurs as the rare mineral molybdite.
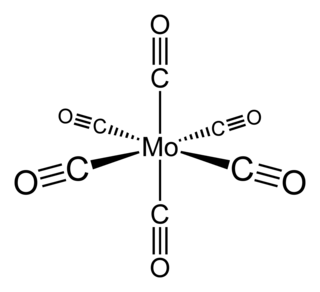
Molybdenum hexacarbonyl (also called molybdenum carbonyl) is the chemical compound with the formula Mo(CO)6. This colorless solid, like its chromium and tungsten analogues, is noteworthy as a volatile, air-stable derivative of a metal in its zero oxidation state.
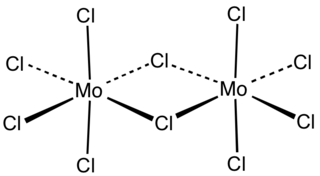
Molybdenum(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula [MoCl5]2. This dark volatile solid is used in research to prepare other molybdenum compounds. It is moisture-sensitive and soluble in chlorinated solvents. Usually called molybdenum pentachloride, it is in fact a dimer with the formula Mo2Cl10.
Alloy steel is steel that is alloyed with a variety of elements in total amounts between 1.0% and 50% by weight to improve its mechanical properties. Alloy steels are broken down into two groups: low alloy steels and high alloy steels. The difference between the two is disputed. Smith and Hashemi define the difference at 4.0%, while Degarmo, et al., define it at 8.0%. Most commonly, the phrase "alloy steel" refers to low-alloy steels.
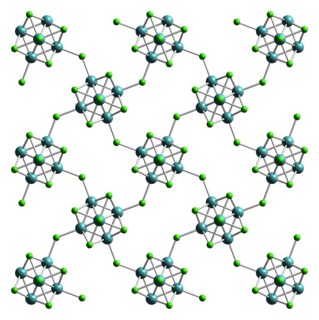
Molybdenum dichloride describes chemical compounds with the empirical formula MoCl2. At least two forms are known, and both have attracted much attention from academic researchers because of the unexpected structures seen for these compounds and the fact that they give rise to hundreds of derivatives. The form discussed here is Mo6Cl12. The other molybdenum(II) chloride is potassium octachlorodimolybdate.

Ammonium heptamolybdate is the inorganic compound whose chemical formula is (NH4)6Mo7O24, normally encountered as the tetrahydrate. A dihydrate is also known. It is a colorless solid, often referred to as ammonium paramolybdate or simply as ammonium molybdate, although "ammonium molybdate" can also refer to ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH4)2MoO4, and several other compounds. It is one of the more common molybdenum compounds.
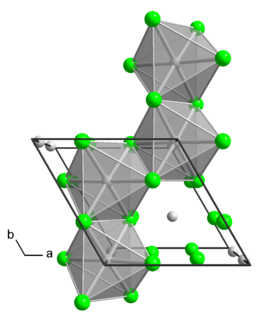
Molybdenum tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl4. The material exists as two polymorphs, a polymeric ("α") and a hexameric ("β") structure. In each polymorph, the Mo center is octahedral with two terminal chloride ligands and four doubly bridging ligands.

Molybdenum hexafluoride, also molybdenum(VI) fluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF6. It is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. A colourless solid, it melts just below room temperature and boils in 34 °C. It is one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common.

Molybdenum(II) acetate is a coordination compound with the formula Mo2(O2CCH3)4. It is a yellow, diamagnetic, air-stable solid that is slightly soluble in organic solvents. Molybdenum(II) acetate is an iconic example of a compound with a metal-metal quadruple bond.
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O). Ammonium orthomolybdate is used as a corrosion inhibitor and is an intermediate in some schemes to win molybdenum from its ores.
Lithium molybdenum purple bronze is a chemical compound with formula Li
0.9Mo
6O
17, that is, a mixed oxide of molybdenum and lithium. It can be obtained as flat crystals with a purple-red color and metallic sheen.

Molybdenum(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoCl3. It forms purple crystals.

Molybdenum(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoBr3. It is a black solid that is insoluble in most solvents but dissolves in donor solvents such as pyridine.
Molybdenum(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula MoBr2. It forms yellow-red crystals.

Molybdenum(V) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula MoF5. It is a hygroscopic yellow solid. Like most pentafluorides, it exists as a tetramer.
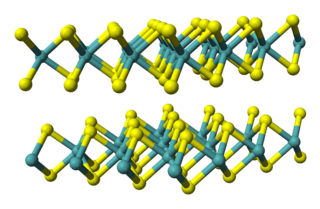
Molybdenum diselenide is an inorganic compound of molybdenum and selenium. Its structure is similar to that of MoS
2. Compounds of this category are known as transition metal dichalcogenides, abbreviated TMDCs. These compounds, as the name suggests, are made up of a transition metals and elements of group 16 on the periodic table of the elements. Compared to MoS
2, MoSe
2 exhibits higher electrical conductivity.
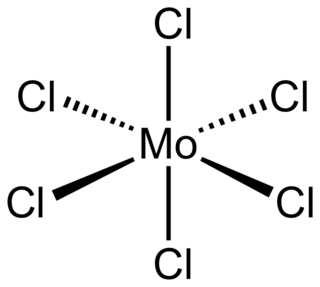
Molybdenum(VI) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoCl6. It is a black diamagnetic solid. The molecules adopt an octahedral structure as seen in β-tungsten(VI) chloride.














