Related Research Articles
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is an operating system subfamily developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows Embedded family of products.
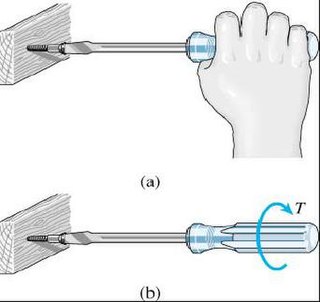
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use.
A web application is application software that runs on a web server, unlike computer-based software programs that are run locally on the operating system (OS) of the device. Web applications are accessed by the user through a web browser with an active network connection. These applications are programmed using a client–server modeled structure—the user ("client") is provided services through an off-site server that is hosted by a third-party. Examples of commonly-used web applications include: web-mail, online retail sales, online banking, and online auctions.
Information technology service management (ITSM) are the activities that are performed by an organization to design, build, deliver, operate and control information technology (IT) services offered to customers.
The user experience is how a user interacts with and experiences a product, system or service. It includes a person's perceptions of utility, ease of use, and efficiency. Improving user experience is important to most companies, designers, and creators when creating and refining products because negative user experience can diminish the use of the product and, therefore, any desired positive impacts; conversely, designing toward profitability often conflicts with ethical user experience objectives and even causes harm. User experience is subjective. However, the attributes that make up the user experience are objective.
The Microsoft .NET Compact Framework is a version of the .NET Framework that is designed to run on resource constrained mobile/embedded devices such as personal digital assistants (PDAs), mobile phones, factory controllers, set-top boxes, etc. The .NET Compact Framework uses some of the same class libraries as the full .NET Framework and also a few libraries designed specifically for mobile devices such as .NET Compact Framework controls. However, the libraries are not exact copies of the .NET Framework; they are scaled down to use less space.

Google Analytics is a web analytics service offered by Google that tracks and reports website traffic, currently as a platform inside the Google Marketing Platform brand. Google launched the service in November 2005 after acquiring Urchin.
Capacity management's goal is to ensure that information technology resources are sufficient to meet upcoming business requirements cost-effictively. One common interpretation of capacity management is described in the ITIL framework. ITIL version 3 views capacity management as comprising three sub-processes: business capacity management, service capacity management, and component capacity management.

Adobe AIR is a cross-platform runtime system currently developed by Harman International, in collaboration with Adobe Inc., for building desktop applications and mobile applications, programmed using Adobe Animate, ActionScript, and optionally Apache Flex. It was originally released in 2008. The runtime supports installable applications on Windows, macOS, and mobile operating systems, including Android, iOS, and BlackBerry Tablet OS.
Usage-centered design is an approach to user interface design based on a focus on user intentions and usage patterns. It analyzes users in terms of the roles they play in relation to systems and employs abstract (essential) use cases for task analysis. It derives visual and interaction design from abstract prototypes based on the understanding of user roles and task cases.
The Facebook Platform is the set of services, tools, and products provided by the social networking service Facebook for third-party developers to create their own applications and services that access data in Facebook.

The Mobile Robot Programming Toolkit (MRPT) is a cross-platform and open source C++ library aimed to help robotics researchers to design and implement algorithms related to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), computer vision and motion planning. Different research groups have employed MRPT to implement projects reported in some of the major robotics journals and conferences.
Mobility models characterize the movements of mobile users with respect to their location, velocity and direction over a period of time. These models play an vital role in the design of Mobile Ad Hoc Networks(MANET). Most of the times simulators play a significant role in testing the features of mobile ad hoc networks. Simulators like allow the users to choose the mobility models as these models represent the movements of nodes or users. As the mobile nodes move in different directions, it becomes imperative to characterize their movements vis-à-vis to standard models. The mobility models proposed in literature have varying degrees of realism i.e. from random patterns to realistic patterns. Thus these models contribute significantly while testing the protocols for mobile ad hoc networks.

Human–computer interaction (HCI) is research in the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and computers. HCI researchers observe the ways humans interact with computers and design technologies that allow humans to interact with computers in novel ways.
User experience evaluation (UXE) or user experience assessment (UXA) refers to a collection of methods, skills and tools utilized to uncover how a person perceives a system before, during and after interacting with it. It is non-trivial to assess user experience since user experience is subjective, context-dependent and dynamic over time. For a UXA study to be successful, the researcher has to select the right dimensions, constructs, and methods and target the research for the specific area of interest such as game, transportation, mobile, etc.

IBM Cognos Business Intelligence is a web-based integrated business intelligence suite by IBM. It provides a toolset for reporting, analytics, scorecarding, and monitoring of events and metrics. The software consists of several components designed to meet the different information requirements in a company. IBM Cognos has components such as IBM Cognos Framework Manager, IBM Cognos Cube Designer, IBM Cognos Transformer.

Active users is a measurement metric that is commonly used to measure the level of engagement for a particular product or object, by quantifying the number of active interactions from visitors within a relevant range of time . The metric has many uses in both commerce and academia, such as on social networking services, online games, or mobile apps. Although having extensive uses in digital behavioural learning, prediction and reporting, it also has impacts on the privacy and security, and ethical factors should be considered thoroughly. Like any metric, active users may have limitations and criticisms. Active Users is relatively new or neologistic in nature, that became important with the rise of the commercialised internet, with uses in communication and social-networking. It measures how many users visit or interact with the product or service over a given interval or period. This metric is commonly assessed per month as monthly active users (MAU), per week as weekly active users (WAU), per day as daily active users (DAU) or peak concurrent users (PCU).
Responsive web design (RWD) or responsive design is an approach to web design that aims to make web pages render well on a variety of devices and window or screen sizes from minimum to maximum display size to ensure usability and satisfaction.

TensorFlow is a free and open-source software library for machine learning and artificial intelligence. It can be used across a range of tasks but has a particular focus on training and inference of deep neural networks.
Implicit authentication (IA) is a technique that allows the smart device to recognize its owner by being acquainted with his/her behaviors. It is a technique that uses machine learning algorithms to learn user behavior through various sensors on the smart devices and achieve user identification. Most of the current authentication techniques, e.g., password, pattern lock, finger print and iris recognition, are explicit authentication which require user input. Comparing with explicit authentication, IA is transparent to users during the usage, and it significantly increases the usability by reducing time users spending on login, in which users find it more annoying than lack of cellular coverage.
References
- ↑ Rodden, Kerry; Hutchinson, Hilary; Fi, Xi (2010). "Measuring the User Experience on a Large Scale: User-Centered Metrics for Web Applications". Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI '10: 2395–2398. doi:10.1145/1753326.1753687. S2CID 7003533.
- ↑ "Top 10 Mobile Technologies and Capabilities for 2015 and 2016".