This article needs to be updated.(June 2025) |
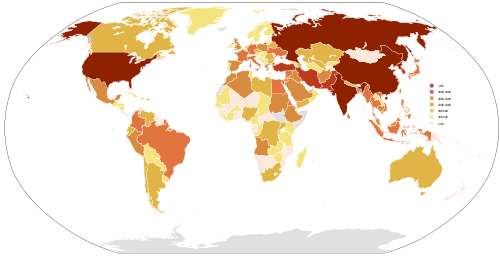
This is a list of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel. It includes any government-sponsored soldiers used to further the domestic and foreign policies of their respective government. The term "country" is used in its most common use, in the sense of state which exercises sovereignty or has limited recognition.
