
The Napa Sonoma Marsh is a wetland at the northern edge of San Pablo Bay, which is a northern arm of the San Francisco Bay in California, United States. This marsh has an area of 48,000 acres (194 km2), of which 13,000 acres (53 km2) are abandoned salt evaporation ponds.[ citation needed ] The United States Government has designated 13,000 acres (53 km2) in the Napa Sonoma Marsh as the San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge.[ citation needed ]

A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is inundated by water, either permanently or seasonally, where oxygen-free processes prevail. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from other land forms or water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique hydric soil. Wetlands play a number of functions, including water purification, water storage, processing of carbon and other nutrients, stabilization of shorelines, and support of plants and animals. Wetlands are also considered the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal life. Whether any individual wetland performs these functions, and the degree to which it performs them, depends on characteristics of that wetland and the lands and waters near it. Methods for rapidly assessing these functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed in many regions and have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions and the ecosystem services some wetlands provide.
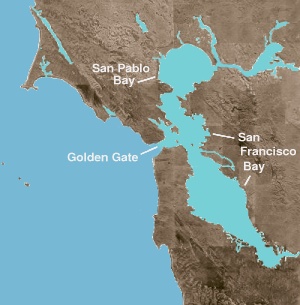
San Pablo Bay is a tidal estuary that forms the northern extension of San Francisco Bay in the East Bay and North Bay regions of the San Francisco Bay Area in northern California.
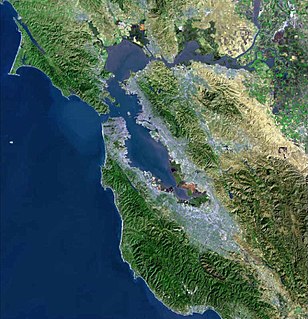
San Francisco Bay is a shallow estuary in the US state of California. It is surrounded by a contiguous region known as the San Francisco Bay Area, and is dominated by the large cities of San Jose, San Francisco and Oakland.
Contents
The marsh is fed by Sonoma Creek (which drains the Sonoma Valley), Tolay Creek (originating in the Tolay Lake basin), and the Napa River (which drains the Napa Valley). [1] Although the marsh extends north as far as State Route 12, [2] as a practical matter, most of the marsh is only accessible by boat.

Sonoma Creek is a 33.4-mile-long (53.8 km) stream in northern California. It is one of two principal drainages of southern Sonoma County, California, with headwaters rising in the rugged hills of Sugarloaf Ridge State Park and discharging to San Pablo Bay, the northern arm of San Francisco Bay. The watershed drained by Sonoma Creek is roughly equivalent to the wine region of Sonoma Valley, an area of about 170 square miles (440 km2). The State of California has designated the Sonoma Creek watershed as a “Critical Coastal Water Resource”. To the east of this generally rectangular watershed is the Napa River watershed, and to the west are the Petaluma River and Tolay Creek watersheds.

Sonoma Valley is a valley located in southeastern Sonoma County, California, in the San Francisco Bay Area. Known as the birthplace of the California wine industry, the valley is home to some of the earliest vineyards and wineries in the state, some of which survived the phylloxera epidemic of the 1870s and the impact of prohibition in the early 20th century. Today, the valley's wines are protected by the US Federal Government's Sonoma Valley and Carneros AVAs.
Tolay Creek is a 12.5-mile-long (20.1 km) southward-flowing stream in southern Sonoma County, California, United States, which flows through Tolay Lake and ends in north San Pablo Bay.
The marsh is a productive estuarine ecosystem providing habitat for a wide diversity of flora and fauna, including numerous rare and endangered species such as the California clapper rail and California freshwater shrimp. [3] Because of its rich avafaunal content, the Napa Sonoma Marsh is one of only seven marshes selected for intensive study by the Point Reyes Bird Observatory (based on a total of 50 discrete marshes appurtenant to the San Francisco Bay). [4]

An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one-another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.

In ecology, a habitat is the type of natural environment in which a particular species of organism lives. It is characterized by both physical and biological features. A species' habitat is those places where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction.

Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is typically a measure of variation at the genetic, species, and ecosystem level. Terrestrial biodiversity is usually greater near the equator, which is the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth, and is richest in the tropics. These tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10 percent of earth's surface, and contain about 90 percent of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future.
Around 1860, the Napa Sonoma Marsh was one of the most productive wetlands of the Pacific Coast, providing habitat for millions of birds. [5] By the mid-1980s, the San Francisco Bay perimeter had lost over 91 percent of its wetlands. The Napa Sonoma Marsh represents one of the few sizeable expanses where restoration is feasible. [6]
An extensive research literature base exists for the Napa Sonoma Marsh. [7]















