
Berkeley is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland and Emeryville to the south and the city of Albany and the unincorporated community of Kensington to the north. Its eastern border with Contra Costa County generally follows the ridge of the Berkeley Hills. The 2020 census recorded a population of 124,321.

Emeryville is a city located in northwest Alameda County, California, in the United States. It lies in a corridor between the cities of Berkeley and Oakland, with a border on the shore of San Francisco Bay. The resident population was 12,905 as of 2020. Its proximity to San Francisco, the Bay Bridge, the University of California, Berkeley, and Silicon Valley has been a catalyst for recent economic growth.

San Francisco International Airport is the primary international airport serving the San Francisco Bay Area in the U.S. state of California. It is located in an unincorporated area of San Mateo County.

The Key System was a privately owned company that provided mass transit in the cities of Oakland, Berkeley, Alameda, Emeryville, Piedmont, San Leandro, Richmond, Albany, and El Cerrito in the eastern San Francisco Bay Area from 1903 until 1960, when it was sold to a newly formed public agency, AC Transit. The Key System consisted of local streetcar and bus lines in the East Bay, and commuter rail and bus lines connecting the East Bay to San Francisco by a ferry pier on San Francisco Bay, later via the lower deck of the Bay Bridge. At its height during the 1940s, the Key System had over 66 miles (106 km) of track. The local streetcars were discontinued in 1948 and the commuter trains to San Francisco were discontinued in 1958. The Key System's territory is today served by BART and AC Transit bus service.

Emeryville station is an Amtrak station in Emeryville, California, United States. The station is served by the California Zephyr, Capitol Corridor, Coast Starlight, and San Joaquins. The station is the primary connection point for Amtrak Thruway buses serving San Francisco.

The Berkeley Pier is in Berkeley, California. When constructed in 1926, the pier extended 3.5 miles (5.6 km) into San Francisco Bay from the end of University Avenue. Due to extensive filling of the bay and the creation of the Berkeley Marina, it presently extends only 2.5 miles (4.0 km). Since 1937, only the first 3,000 feet (910 m) were maintained and open to the public until July 2015, when public access was closed due to safety concerns.

People in the San Francisco Bay Area rely on a complex multimodal transportation infrastructure consisting of roads, bridges, highways, rail, tunnels, airports, seaports, and bike and pedestrian paths. The development, maintenance, and operation of these different modes of transportation are overseen by various agencies, including the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans), the Association of Bay Area Governments, San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency, and the Metropolitan Transportation Commission. These and other organizations collectively manage several interstate highways and state routes, eight passenger rail networks, eight trans-bay bridges, transbay ferry service, local and transbay bus service, three international airports, and an extensive network of roads, tunnels, and bike paths.

The East Bay Electric Lines were a unit of the Southern Pacific Railroad that operated electric interurban-type trains in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Beginning in 1862, the SP and its predecessors operated local steam-drawn ferry-train passenger service in the East Bay on an expanding system of lines, but in 1902 the Key System started a competing system of electric lines and ferries. The SP then drew up plans to expand and electrify its system of lines and this new service began in 1911. The trains served the cities of Berkeley, Albany, Emeryville, Oakland, Alameda, and San Leandro transporting commuters to and from the large Oakland Pier and SP Alameda Pier. A fleet of ferry boats ran between these piers and the docks of the Ferry Building on the San Francisco Embarcadero.

West Berkeley is generally the area of Berkeley, California, that lies west of San Pablo Avenue, abutting San Francisco Bay. It includes the area that was once the unincorporated town of Ocean View, as well as the filled-in areas along the shoreline west of I-80, mainly including the Berkeley Marina. It lies at an elevation of 23 feet.

Aquatic Park is a public park in Berkeley, California, United States, located just east of the Eastshore Freeway between Ashby and University Avenues. The Works Progress Administration created the park in the 1930s simultaneously with the nearby Berkeley Yacht Harbor. Its centerpiece is an artificial mile-long lagoon that was cut off from San Francisco Bay by the creation of a causeway for the Eastshore Highway, during the construction of the approaches to the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge, also in the 1930s. The lagoon still communicates with the Bay through culverts under the freeway. The east shoreline of the lagoon used to be the original shoreline of San Francisco Bay.

San Francisco Bay in California has been served by ferries of all types for over 150 years. John Reed established a sailboat ferry service in 1826. Although the construction of the Golden Gate Bridge and the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge led to the decline in the importance of most ferries, some are still in use today for both commuters and tourists.

McLaughlin Eastshore State Park is a state park and wildlife refuge along the San Francisco Bay shoreline of the East Bay between the cities of Richmond, Albany, Berkeley, Emeryville, and Oakland. It encompasses remnant natural wetlands, restored wetlands, as well as landfill west of the Eastshore Freeway. Its shoreline is 8.5 miles (13.7 km) long, and its total area is 1,854 acres (750 ha), which includes both tidelands and uplands. Originally named just Eastshore State Park, it was renamed in October 2012 to honor the late Save the Bay founder Sylvia McLaughlin, who, along with the late Dwight Steele of Citizens for Eastshore Park, drove the establishment of the park. Prior to 2013, it was jointly managed by the California State Parks and East Bay Regional Park District (EBRPD). The state agency and EBRPD executed a 30-year agreement for EBRPD to manage the park.

César Chávez Park is a 90 acres (36 ha) city park of Berkeley, California named after César Chávez. It can be found on the peninsula on the north side of the Berkeley Marina in the San Francisco Bay and is adjacent to Eastshore State Park.

The Berkeley I-80 bridge also known as the University Avenue pedestrian bridge and the Berkeley Marina overpass is a 15-foot (4.6 m)-wide bridge spanning the Eastshore Freeway in Berkeley, California. It forms part of the San Francisco Bay Trail.

Oyster Point Marina/Park is a 408-berth public marina and 33-acre (13 ha) park located in the city of South San Francisco, California on the western shoreline of San Francisco Bay.
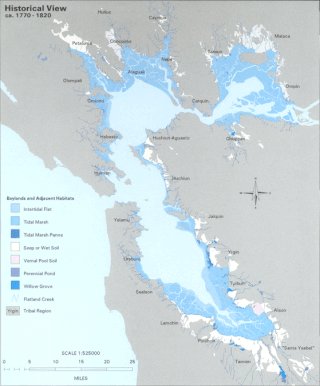
The Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area is a complex network of watersheds, marshes, rivers, creeks, reservoirs, and bays predominantly draining into the San Francisco Bay and Pacific Ocean.

Marin Creek is a creek tributary of Codornices Creek in northwestern Alameda County, California. The lower stretch of Marin Creek is also known as Village Creek.

The Albany Bulb is a former landfill largely owned by the City of Albany, in California. The Bulb is the west end of a landfill peninsula jutting west from the east shore of San Francisco Bay. The term "Bulb" is often used to refer to the entire peninsula, which includes the Albany Plateau, north of Buchanan Street at its base; the high narrow "Neck," and the round "Bulb." The Bulb is part of the City of Albany, and can be reached via Buchanan Street or the Bay Trail along the east side of San Francisco Bay. Landmarks include, Mary's Mask, Gritchell's Bay, and Mad Marc's Castle. The Geotag for Gritchell's Bay is 37.8908083, -122.3257826.
Hornblower Cruises is a San Francisco–based charter yacht, dining cruise and ferry service company. In 2021, the company rebranded most of its services as City Cruises or City Experiences. In 2024, the company filed for bankruptcy protection.

San Francisco and Oakland Helicopter Airlines was a helicopter airline service offering scheduled passenger flights between San Francisco, Oakland, and other Bay Area cities. It was founded in 1961 but disappeared from the Official Airline Guide 15 years later before finally going out of business in 1986.























